FortiGate-3000 and FortiGate-3600 FortiOS 3.0MR4 Install Guide
32 01-30004-0270-20070215
Planning the FortiGate configuration Configuring the FortiGate unit
You typically use NAT/Route mode when the FortiGate unit is operating as a
gateway between private and public networks. In this configuration, you would
create NAT mode firewall policies to control traffic flowing between the internal,
private network and the external, public network (usually the Internet).
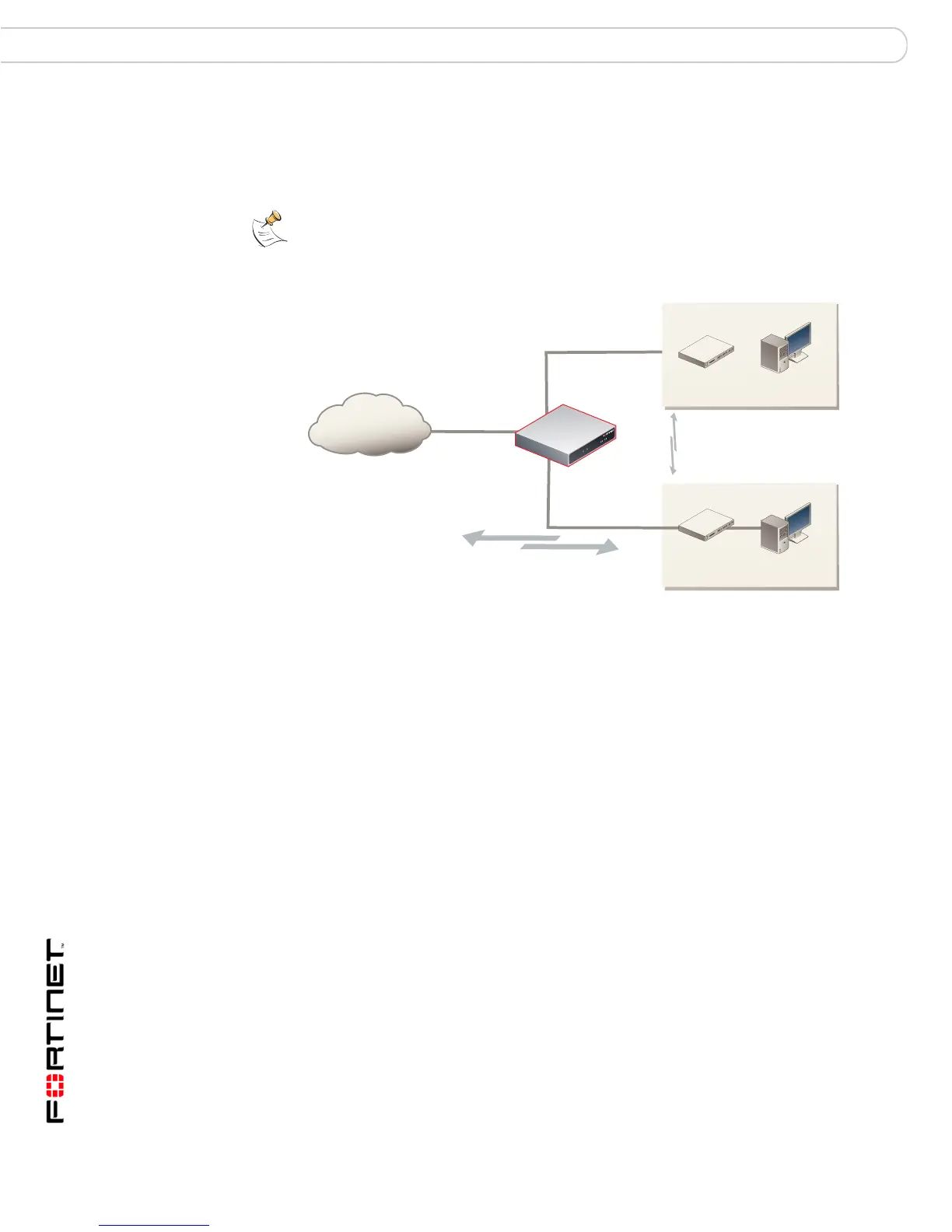
Figure 6: Example NAT/Route mode configuration.
NAT/Route mode with multiple external network connections
In NAT/Route mode, you can configure the FortiGate unit with multiple redundant
connections to the external network (usually the Internet).
For example, you could create the following configuration:
• External is the default interface to the external network (usually the Internet)
• Internal is the interface to the internal network
• Port 1 is the redundant interface to the external network
• Port 2 is the interface to the DMZ network
You must configure routing to support redundant Internet connections. Routing
can automatically redirect connections from an interface if its connection to the
external network fails.
Otherwise, security policy configurations is similar to a NAT/Route mode
configuration with a single Internet connection. You would create NAT mode
firewall policies to control traffic following between the internal, private network
and the external, public network (usually the Internet).
Note: If you have multiple internal networks, such as a DMZ network in addition to the
internal, private network, you could create route mode firewall policies for traffic flowing
between them.
Internet
Port 3
10.10.10.2
Internal
192.168.1.99
Route mode policies
controlling traffic between
Internal networks.
NAT policies controlling
traffic between internal
and external networks.
External
204.23.1.5
Internal network
192.168.1.3
DMZ network
10.10.10.23
 Loading...
Loading...











