14 I Operating Instructions
I – 1 Fundamentals of Positioning
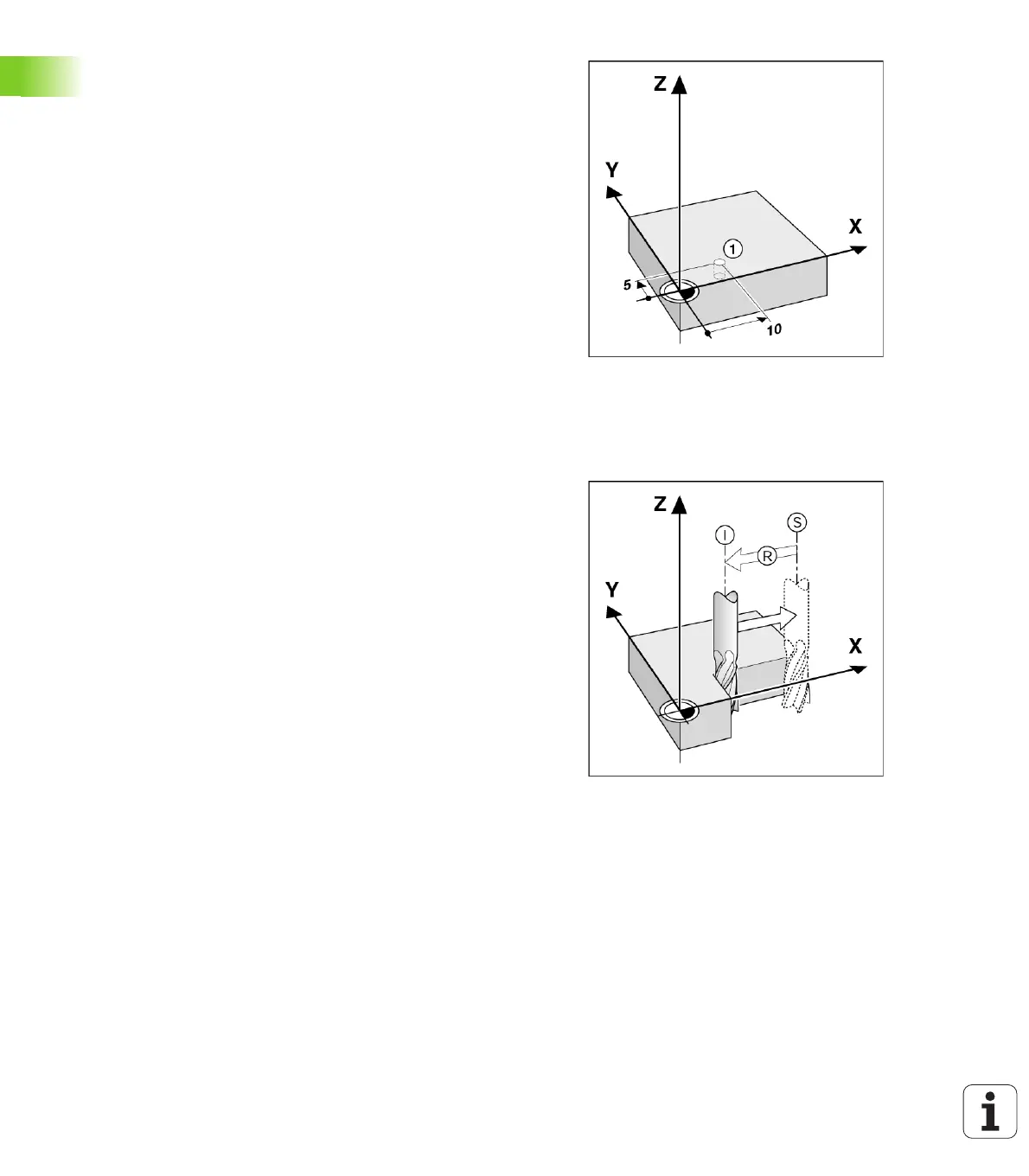
Example: Coordinates of hole 1:
X =10 mm
Y = 5 mm
Z = 0 mm (hole depth: Z = – 5 mm)
The datum of the Cartesian coordinate system is located 10 mm from
hole 1 in the X axis and 5 mm from it in the Y axis. See Fig. I.4.
The KT Edge Finder from HEIDENHAIN, together with the
POSITIP 880's edge finding functions, facilitates finding and setting
datums.
Nominal Position, Actual Position and Distance-
To-Go
The position that the tool is to move to is called the nominal position
while the position of the tool at any given moment is called the actual
position. The distance from the nominal position to the actual position
is called the distance-to-go. See Fig. I.5.
Sign for distance-to-go
The distance-to go has a positive sign if the axis direction from the
actual towards the nominal position is negative.
The distance-to-go has a negative sign if the axis direction from the
actual towards the nominal position is positive.
Fig. I.4 Hole 1
defines the coordinatesystem
Fig. I.5 Nominal position S, actual position I and
distance-to-go R

 Loading...
Loading...