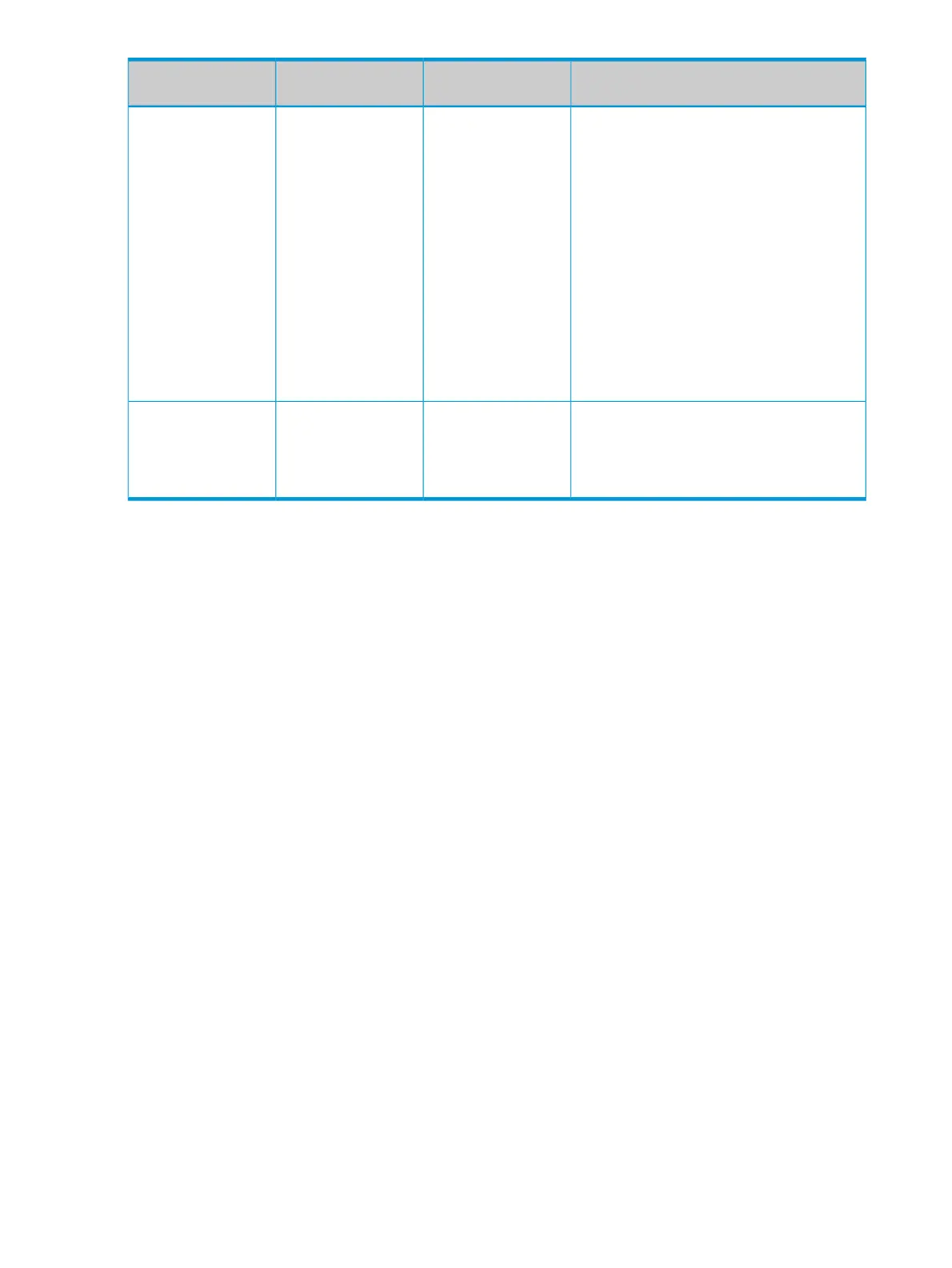
Default IGMP behaviorIGMP fast-leave
setting
Data-driven IGMP
included?
Switch model or series
traffic, except on IGMP-forward ports, which
forward all multicast traffic.
Switch 6200yl
Switch 5400zl
Switch 5300xl
Switch 4200vl
Switch 3500
Switch 3500yl
Switch 3400cl
Switch 2910
Switch 2900
Switch 2610
Switch 2510
Switch 2500
IGMP fast-leave disabled in the default
configuration. Floods unjoined multicast traffic
Disabled in the default
configuration
NoSwitch 2600
Switch 2600-PWR
to all ports. Selectively forwards joined
Switch 4100gl
multicast traffic, except on IGMP-forward ports,
which forward all multicast traffic.
Switch 6108
On switches that do not support data-driven IGMP, unregistered multicast groups are flooded to
the VLAN rather than pruned. In this scenario, fast-leave IGMP can actually increase the problem
of multicast flooding by removing the IGMP group filter before the Querier has recognized the
IGMP leave. The Querier will continue to transmit the multicast group during this short time, and
because the group is no longer registered, the switch will then flood the multicast group to all ports.
On HP switches that do support data-driven IGMP ("Smart" IGMP), when unregistered multicasts
are received the switch automatically filters (drops) them. Thus, the sooner the IGMP leave is
processed, the sooner this multicast traffic stops flowing.
Because of the multicast flooding problem mentioned above, the IGMP fast-leave feature is disabled
by default on all HP switches that do not support data-driven IGMP (see the table above.) The
feature can be enabled on these switches via an SNMP set of this object:
hpSwitchIgmpPortForceLeaveState.<vid>.<port number>
However, HP does not recommend this because it will increase the amount of multicast flooding
during the period between the client's IGMP leave and the Querier's processing of that leave. For
more information on this topic, see “Forced fast-leave IGMP” (page 17).
If a switch port has the following characteristics, the fast-leave operation will apply:
• Connected to only one end node.
• The end node currently belongs to a multicast group, that is, is an IGMP client.
• The end node subsequently leaves the multicast group.
Then the switch does not need to wait for the Querier status update interval, but instead immediately
removes the IGMP client from its IGMP table and ceases transmitting IGMP traffic to the client. (If
the switch detects multiple end nodes on the port, automatic fast-leave does not activate—regardless
of whether one or more of these end nodes are IGMP clients.)
In Figure 1, automatic fast-leave operates on the switch ports for IGMP clients "3A" and "5A," but
not on the switch port for IGMP clients "7A" and "7B," server "7C," and printer "7D."
16 Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
 Loading...
Loading...











