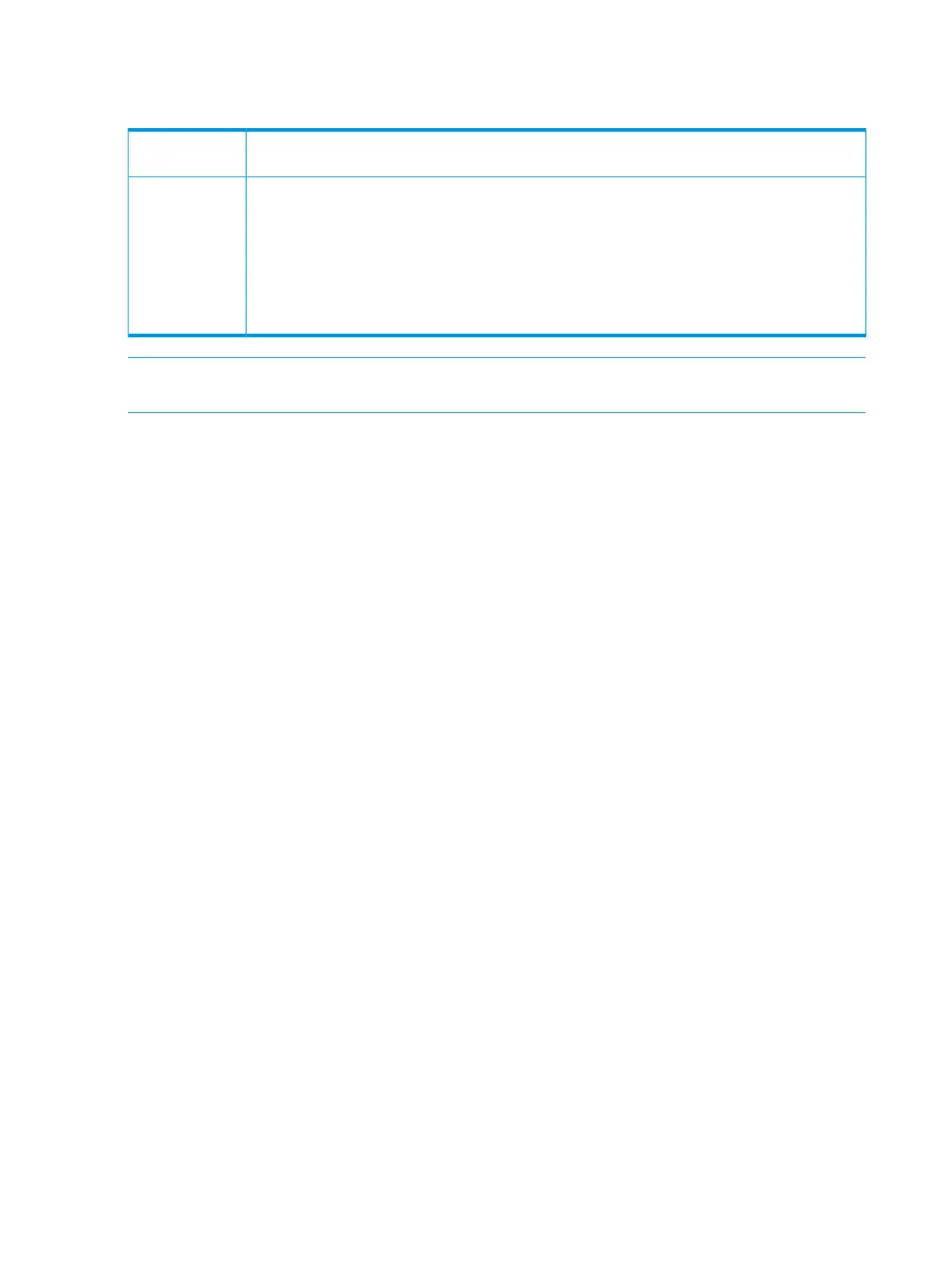
Static route types
You can configure the following types of static IP routes:
The static route consists of a destination network address or host, a corresponding network mask,
and the IP address of the next-hop IP address.
Standard
The null route consists of the destination network address or host, a corresponding network mask,
and either the reject or blackhole keyword. Typically, the null route is configured as a backup
Null (discard)
route for discarding traffic if the primary route is unavailable. By default, when IP routing is enabled,
a route for the 127.0.0.0/8 network is created to the null interface. Traffic to this interface is rejected
(dropped).
This route is for all traffic to the "loopback" network, with the single exception of traffic to the host
address of the switch's loopback interface (127.0.0.1/32.) “Displaying the currently configured
static routes” (page 48) shows the default null route entry in the switch's routing table.
NOTE: On a single routing switch you can create one null route to a given destination. Multiple
null routes to the same destination are not supported.
Other sources of routes in the routing table
The IP route table can also receive routes from the following sources:
• Directly connected networks: One route is created per IP interface. When you add an IP
interface, the routing switch automatically creates a route for the network the interface is in.
• RIP: If RIP is enabled, the routing switch can learn about routes from the advertisements other
RIP routers send to the routing switch. If the RIP route has a lower administrative distance than
any other routes from different sources to the same destination, the routing switch places the
route in the IP route table. See “Administrative distance” (page 37).
• Default route: This is a specific static route that the routing switch uses if other routes to the
destination are not available. See “Configuring the default route” (page 48).
Static IP route parameters
When you configure a static IP route, you must specify the following parameters:
• The IP address and network mask for the route's destination network or host.
• The route's path, which can be one of the following:
IP address of a next-hop router.•
• "Null" interface; the routing switch drops traffic forwarded to the null interface.
The routing switch also applies default values for the route's administrative distance (“Administrative
distance” (page 37)). In the case of static routes, this is the value the routing switch uses to compare
a static route to routes from other route sources to the same destination before placing a route in
the IP route table.
The default administrative distance for static IP routes is 1, but can be configured to any value from
1 to 255.
The fixed administrative distance values ensure that the routing switch always prefers static IP routes
over routes from other sources to the same destination.
Static route states follow VLAN states
IP static routes remain in the IP route table only so long as the IP interface to the next-hop router is
up. If the next-hop interface goes down, the software removes the static route from the IP route
table. If the next-hop interface comes up again, the software adds the route back to the route table.
This feature allows the routing switch to adjust to changes in network topology.
46 IP Routing Features
 Loading...
Loading...











