to forward or drop the response. For more information, see “Validation of
server response packets” (page 71).
Specifies the remote ID suboption that the switch uses in Option 82 fields
added or appended to DHCP client packets. The type of remote ID defines
[ ip | mac |
mgmt-vlan ]
DHCP policy areas in the client requests sent to the DHCP server. If a remote
ID suboption is not configured, the routing switch defaults to the mac option.
See “Option 82 field content” (page 68).
• ip: Specifies the IP address of the VLAN on which the client DHCP packet
enters the switch.
• mac: Specifies the routing switch's MAC address. (The MAC address used
is the same MAC address that is assigned to all VLANs configured on the
routing switch.) This is the default setting.
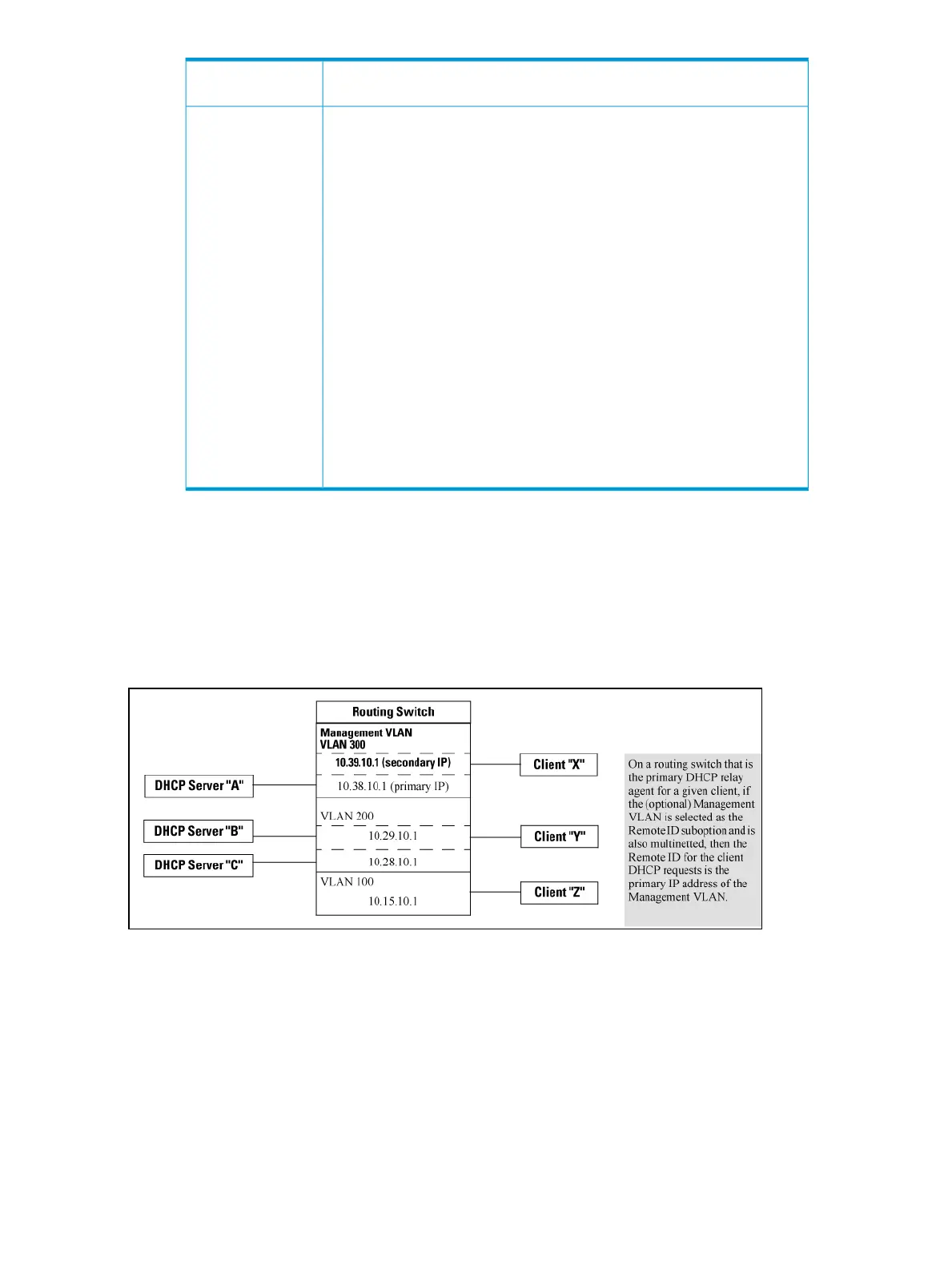
• mgmt-vlan:Specifies the IP address of the (optional) management VLAN
configured on the routing switch. Requires that a management VLAN is
already configured on the switch. If the management VLAN is multinetted,
the primary IP address configured for the management VLAN is used for
the remote ID.
If you enter the dhcp-relay option 82 command without specifying either
ip or mac, the MAC address of the switch on which the packet was received
from the client is configured as the remote ID. For information about the remote
ID values used in the Option 82 field appended to client requests, see “Option
82 field content” (page 68).
Example of Option 82 configuration
In the routing switch shown below, option 82 has been configured with mgmt-vlan for the remote
ID.
HP Switch(config)# dhcp-relay option 82 append mgmt-vlan
The resulting effect on DHCP operation for clients X, Y, and Z is shown in Table 8.
Figure 10 DHCP Option 82 when using the management VLAN as the remote ID sub-option
74 IP Routing Features
 Loading...
Loading...











