Similarly, if you want to define specific ranges of addresses for clients on different ports in the
same VLAN, you can configure the server with the range of IP addresses allowed for each circuit
ID (port) associated with the remote ID (IP address) for the selected VLAN.
Forwarding policies
DHCP Option 82 on HP switches offers four forwarding policies, with an optional validation of
server responses for three of the policy types (append, replace, or drop.)
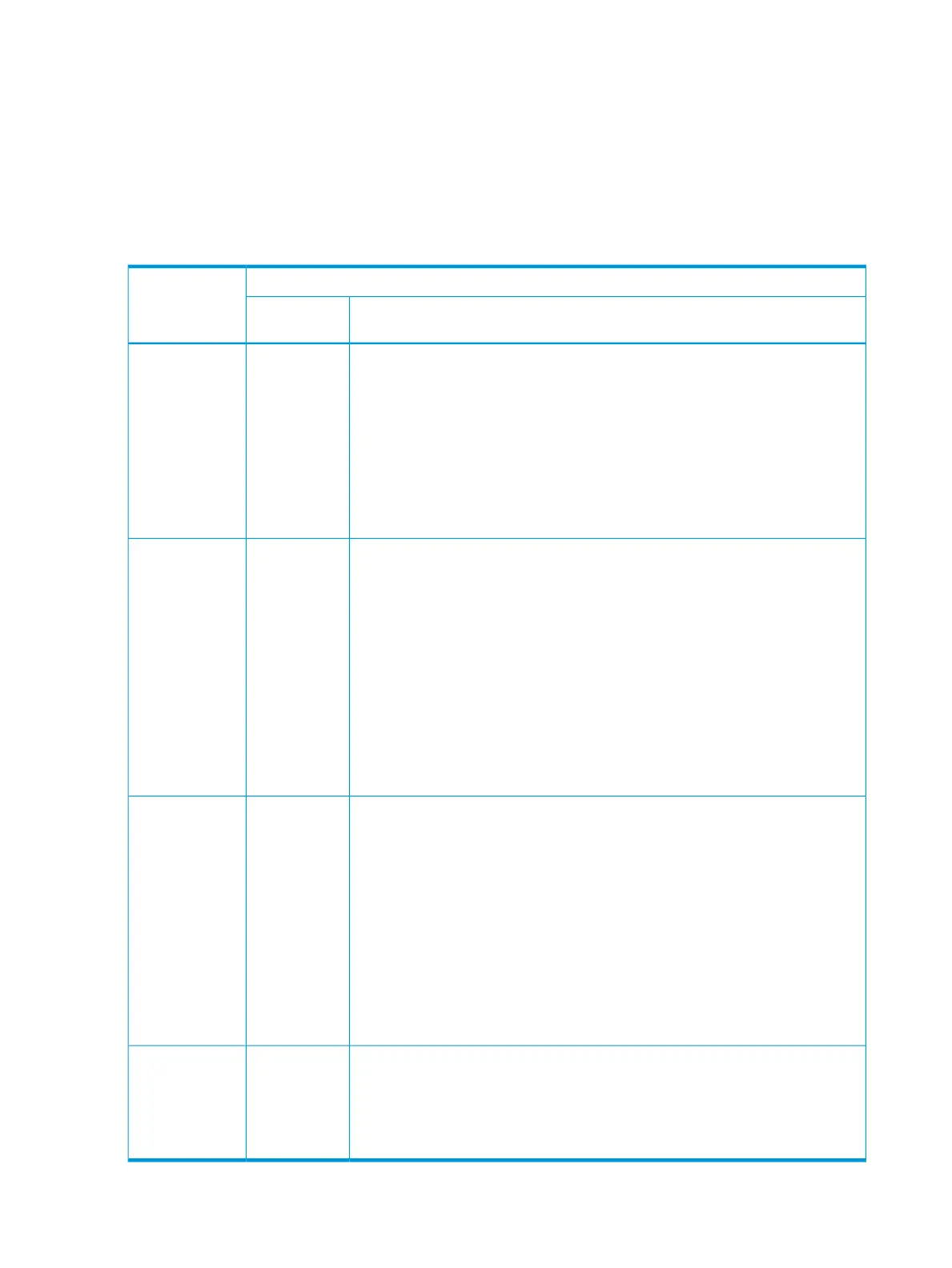
Configuration options for managing DHCP client request packets
DHCP client request packet inbound to the routing switchOption 82
configuration
Packet includes an Option 82 fieldPacket has no
Option 82 field
Append allows the most detail in defining DHCP policy boundaries. For example,
where the path from a client to the DHCP Option 82 server includes multiple relay
Append an
Option 82
field
Append
agents with Option 82 capability, each relay agent can define a DHCP policy
boundary and append its own Option 82 field to the client request packet. The
server can then determine in detail the agent hops the packet took, and can be
configured with a policy appropriate for any policy boundary on the path. Note:
NOTE: In networks with multiple relay agents between a client and an Option
82 server, append can be used only if the server supports multiple Option 82
fields in a client request. If the server supports only one Option 82 field in a request,
consider using the keep option.
If the relay agent receives a client request that already has one or more Option
82 fields, keep causes the relay agent to retain such fields and forward the request
Append an
Option 82
field
Keep
without adding another Option 82 field. But if the incoming client request does
not already have any Option 82 fields, the relay agent appends an Option 82
field before forwarding the request. Some applications for keep include:
• The DHCP server does not support multiple Option 82 packets in a client request,
and there are multiple Option 82 relay agents in the path to the server.
• The unusual case where DHCP clients in the network add their own Option 82
fields to their request packets, and you do not want any additional fields added
by relay agents.
This policy does not include the validate option (described in the next section)
and allows forwarding of all server response packets arriving inbound on the
routing switch (except those without a primary relay agent identifier.)
Replace replaces any existing Option 82 fields from downstream relay agents
(and/or the originating client) with an Option 82 field for the current relay agent.
Some applications for replace include:
Append an
Option 82
field
Replace
• The relay agent is located at a point in the network that is a DHCP policy
boundary, and you want to replace any Option 82 fields appended by
down-stream devices with an Option 82 field from the relay agent at the
boundary. (This eliminates downstream Option 82 fields you do not want the
server to use when determining which IP addressing policy to apply to a client
request.)
• In applications where the routing switch is the primary relay agent for clients
that may append their own Option 82 field, you can use replace to delete
these fields if you do not want them included in client requests reaching the
server.
Drop causes the routing switch to drop an inbound client request with an Option
82 field already appended. If no Option 82 fields are present, drop causes the
Append an
Option 82
field
Drop
routing switch to add an Option 82 field and forward the request. As a general
guideline, configure drop on relay agents at the edge of a network, where an
inbound client request with an appended Option 82 field may be unauthorized,
a security risk, or for some other reason, should not be allowed.
70 IP Routing Features

 Loading...
Loading...











