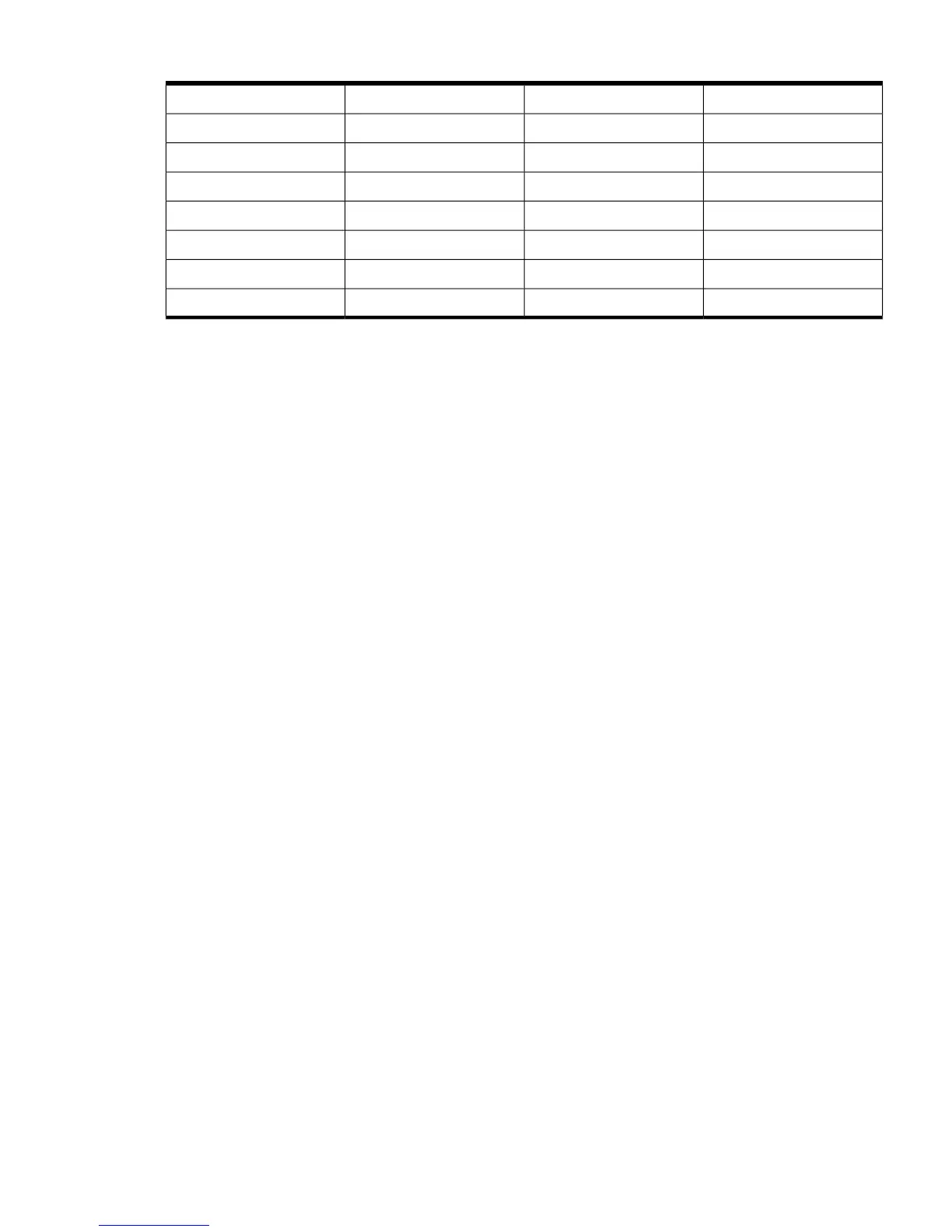
Table 4-10 Load Balancing based on Destination IP Address (four- and five-port teams) (continued)
network port 1000network port 1000
network port 2001network port 2001
network port 3010network port 3010
network port 4011network port 4011
network port 5100network port 1100
network port 1101network port 2101
network port 2110network port 3110
network port 3111network port 4111
If the Destination IP Address algorithm is chosen, and the frame doesn’t have an IP header, the
frame is load balanced by destination MAC address (refer to “TLB Destination MAC Address
Method” below).
Scenario 4-C: A TLB Team Using IP Address-Based Load Balancing
Using the concepts reviewed in “Scenario A-2: One Device Pings Another on a Different Layer
2 Network” in Appendix A and Figure A-2, this section describes how TLB IP addressed- based
load-balancing functions.
Beginning at the point in Scenario A-2 where Blue/2.2.2.1 transmits the ping reply to Red/1.1.1.1,
Blue must decide whether to use network port B or E. Blue’s teaming driver calculates using the
IP address of Red (1.1.1.1) because Red is the frame’s destination. Because a dotted decimal 1.1.1.1
is equal to 0000 0001 . 0000 0001 . 0000 0001 . 0000 0001 in binary, and the last three bits (001) are
used to determine the transmitting network port (refer to Table 4-9 – Two-port team), 001 is
assigned to network port 2 (or the Non-Primary port). Therefore, when communicating with
Red, Blue will always use the Non-Primary port to transmit frames.
If Blue transmits a frame to Yellow, the same calculation must be made. Yellow’s IP address in
dotted decimal is 1.1.1.4 and equal to 0000 0001 . 0000 0001 . 0000 0001 . 0000 0100 in binary.
Blue’s teaming driver will again use the last three bits to determine which network port will
transmit the frame. Referring to Table 4-9 – Two-port team, 100 is assigned to network port 1 (or
the Primary port). Therefore, when communicating with Yellow, Blue will always use the Primary
port to transmit frames.
It is important to note that if an implementer uses the MAC address load balancing algorithm
for the network in Figure 4-15, load balancing will not function as expected, and traffic will not
be load balanced using all teamed ports. Because Blue transmits all frames destined for Red and
Yellow via Green (Blue’s gateway), Blue uses Green’s Layer 2 address (MAC) as the frame’s
Destination MAC Address but uses Red’s and Yellow’s Layer 3 addresses (IP) as the frame’s
Destination IP Address. Blue never transmits frames directly to Red’s or Yellow’s MAC address
because Blue is on a different Layer 2 network. Because Blue always transmits to Red and Yellow
using Green’s MAC address, the teaming driver will assign all conversations with clients on
Network 1.0.0.0 to the same network port. When an HP Integrity Network adapter team needs
to load balance traffic that traverses a Layer 3 device (router), at a minimum IP address-based
load balancing should be used. Ideally, Automatic should be used.
Types of HP Integrity Network Adapter Teams 63
 Loading...
Loading...