Page 44
KG/KC 024, 030, 036, 048, 060, 072, 074, 090
TABLE 12
KGA 060S -5 & HIGHER; KCA 060S -4 & HIGHER
NORMAL OPERATING PRESSURES
Outdoor Coil
Entering Air Temp
Discharge
+
10 psig
Suction + 5
psig
65 279 130
75 317 135
85 359 139
95 404 143
105 454 143
115 508 143
D-Charge Verification-Approach Method--Fin/Tube Coils
KGA/KCA 036-060 Units
1- Using the same thermometer, compare liquid
temperature to outdoor ambient temperature.
Approach Temperature = Liquid temperature minus
ambient temperature.
2- Approach temperature should match values in table
13. An approach temperature greater than value
shown indicates an undercharge. An approach
temperature less than value shown indicates an
overcharge.
3- Do not use the approach method if system pressures
do not match pressures in tables 7 through 12. The
approach method is not valid for grossly over or
undercharged systems.
TABLE 13
APPROACH TEMPERATURE
Unit Liquid Temp. Minus Ambient Temp.
036S 7°F + 1 (3.9°C + 0.5)
048S 11°F + 1 (6.1°C + 0.5)
060S 6°F + 1 (3.3°C + 0.5)
E-Refrigerant Charge and Check - All-Aluminum Coil
KGA/KCA 072, 090 & KGB/KCB024-074
WARNING-Do not exceed nameplate charge under
any condition.
This unit is factory charged and should require no further
adjustment. If the system requires additional refrigerant,
reclaim the charge,
evacuate the system, and add
required nameplate charge.
NOTE - System charging is not recommended below
60F (15C). In temperatures below 60F (15C), the
charge must be weighed into the system.
If weighing facilities are not available, or to check the
charge, use the following procedure:
IMPORTANT - Charge unit in standard cooling mode.
1- Make sure outdoor coil is clean. Attach gauge
manifolds and operate unit at full CFM in cooling mode
with economizer disabled until system stabilizes
(approximately five minutes). Make sure all outdoor air
dampers are closed.
2- Compare the normal operating pressures (see table
14 through 21) to the pressures obtained from the
gauges. Check unit components if there are
significant differences.
3- Measure the outdoor ambient temperature and the
suction pressure. Refer to the appropriate circuit
charging curve to determine a target liquid
temperature.
Note - Pressures are listed for sea level applications.
4- Use the same thermometer to accurately measure the
liquid temperature (in the outdoor section).
If measured liquid temperature is higher than
the target liquid temperature, add refrigerant to
the system.
If measured liquid temperature is lower than
the target liquid temperature, recover some
refrigerant from the system.
5- Add or remove charge in increments. Allow the
system to stabilize each time refrigerant is added or
removed.
6- Continue the process until measured liquid
temperature agrees with the target liquid
temperature. Do not go below the target liquid
temperature when adjusting charge. Note that
suction pressure can change as charge is adjusted.
7- Example KG/KC 090: At 95°F outdoor ambient and
a measured suction pressure of 130psig, the target
liquid temperature is 99°F. For a measured liquid
temperature of 106°F, add charge in increments
until measured liquid temperature agrees with the
target liquid temperature.
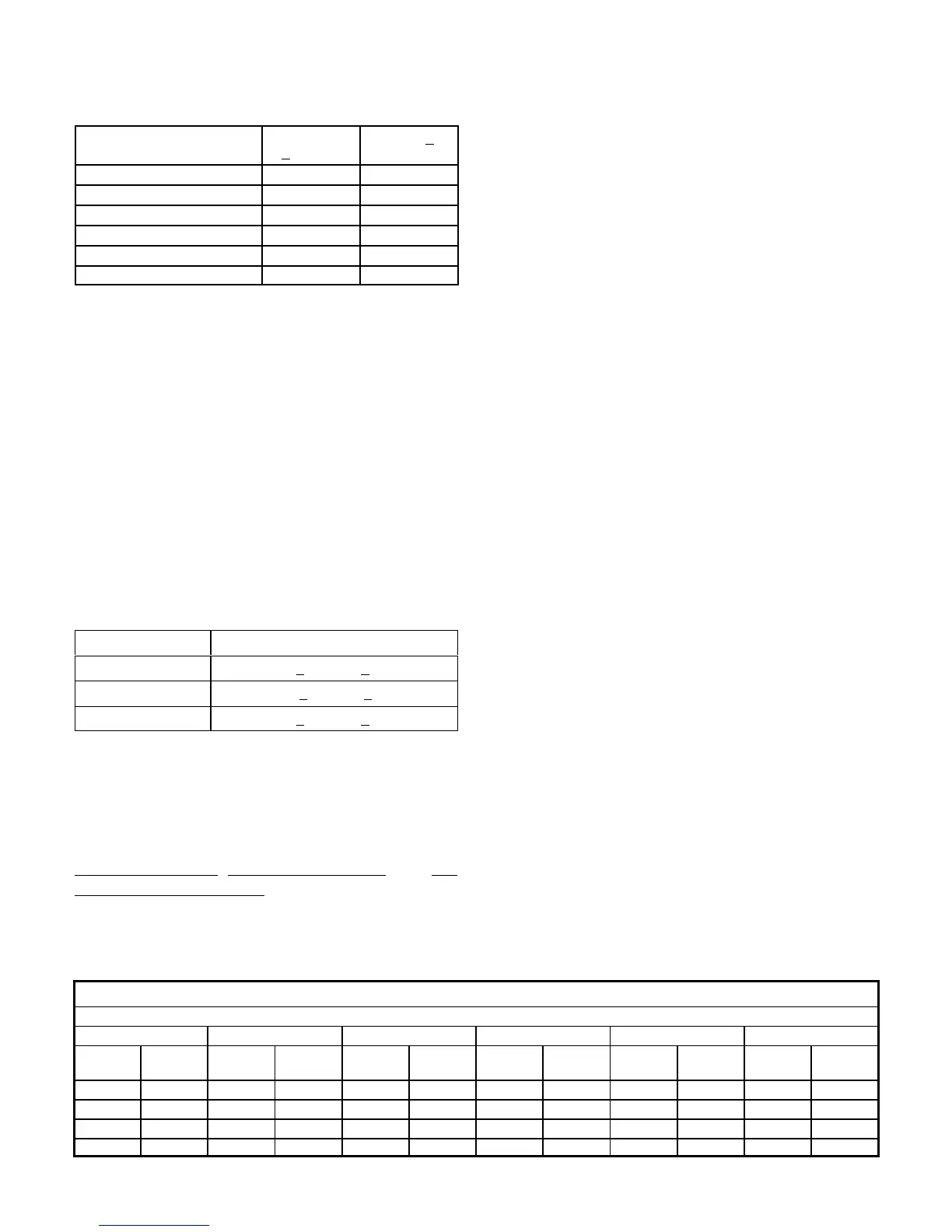
TABLE 14
KGB/KCB024 Normal Operating Pressures
Outdoor Coil Entering Air Temperature
65 °F 75 °F 85 °F 95 °F 105 °F 115 °F
Suct
(psig)
Disc
(psig)
Suct
(psig)
Disc
(psig)
Suct
(psig)
Disc
(psig)
Suct
(psig)
Disc
(psig)
Suct
(psig)
Disc
(psig)
Suct
(psig)
Disc
(psig)
118 224 119 259 121 297 121 342 122 390 124 442
125 227 127 262 129 301 130 343 131 391 134 441
141 232 144 267 149 306 151 347 153 393 154 444
159 236 164 273 168 311 171 354 173 400 176 449

 Loading...
Loading...