parameter was illegal - and hence not even the state of the execution could be specied.
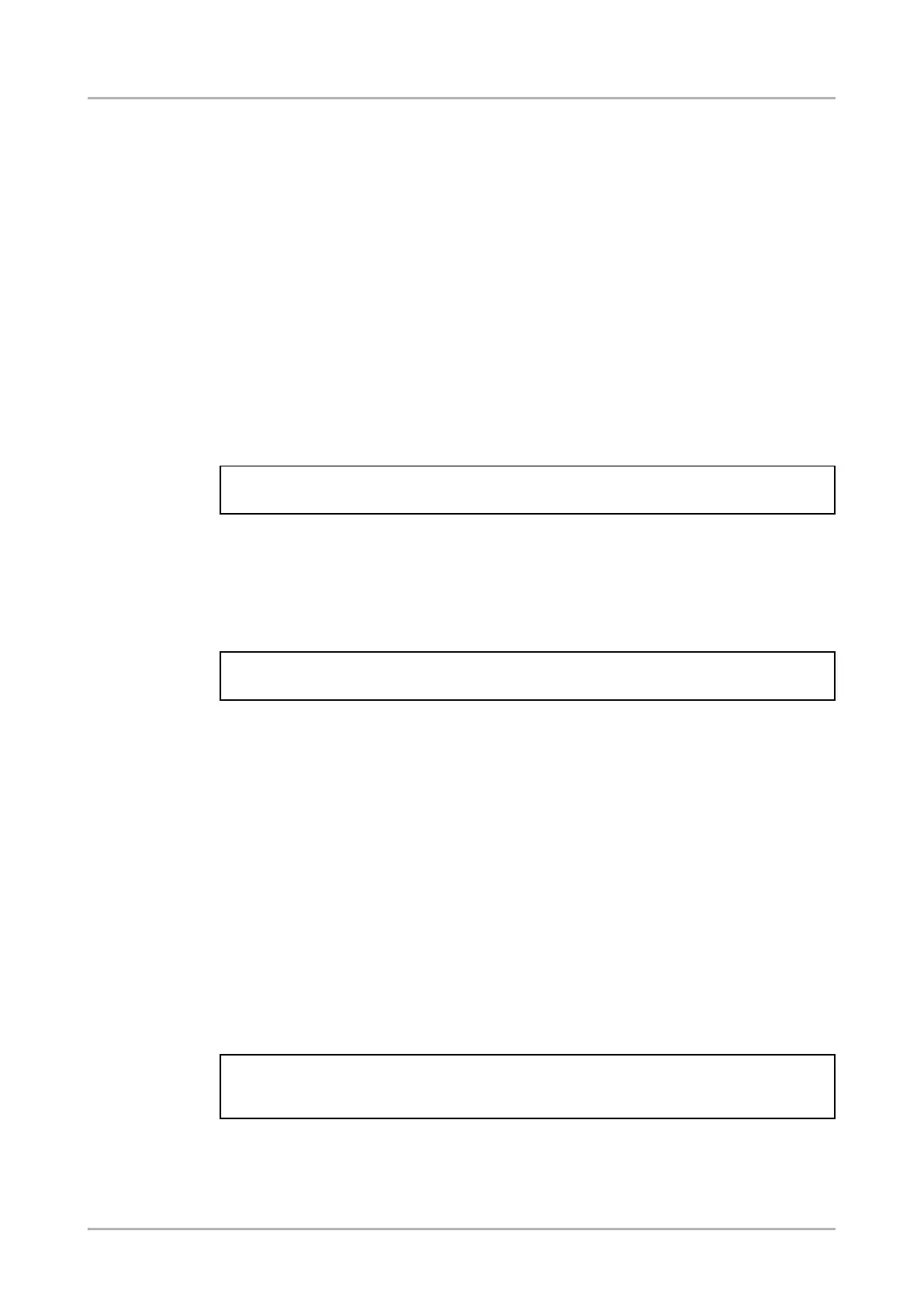
mX●[nodePath]:[methodName]=Y
Legend:
X can be:
‘O’: if the execution is successful.
‘F’: if the execution is failed, but the method could be
executed.
‘E’: if the method could not be executed: e.g. illegal
parameter count.
Y can be:
▪ The return value of the method if any.
▪ It is valid that a method does not have any return value. In this case,
the equal sign (‘=‘) can be omitted.
Example:
˃ CALL /EDID:switch(D1:E1)
˂ mO /EDID:switch
Error response format:
If there were errors during the execution, an error message is received, which follows the
method name.
mE●[nodePath]:[methodName]●%EXXX:Error message
Example:
˃ CALL /EDID:switch(D1:R1)
˂ mE %E001:Syntax error
8.3.4. Manual
For every node, property and method in the tree there is a manual. The manual is a human
readable text that describes the syntax and provides a hint for how to use the primitives.
Command format:
for nodes: MAN●[nodePath]
for property: MAN●[nodePath].[propertyName]
for method: MAN●[nodePath]:[methodName]
Response format:
The human readable manual is separated by a space (‘ ‘) character from the primitives.
for nodes: nm●[nodePath]●Human readable manual
for property: pm●[nodePath].[propertyName]●Human readable manual
for method: mm●[nodePath]:[methodName]●Human readable manual
Example: (for a property)
˃ MAN /SYS/MB/RS232/Local.ActiveProtocol
˂ pm /SYS/MB/RS232/Local.ActiveProtocol ["LW2" | "LW3"] Active
Protocol
HDMI-3D-OPT-TX200 series
User’s manual
LW3 programmers' reference Page 69 / 106
 Loading...
Loading...











