Which Method Is Best?
This depends on the frequency to be measured, the rate at which you want to monitor the
frequency and the accuracy you desire. Take for example, measuring a 50 kHz signal.
Assuming that the measurement times for the sample clocked (with averaging) and two
counter frequency measurements are configured the same, the following table summarizes the
results.
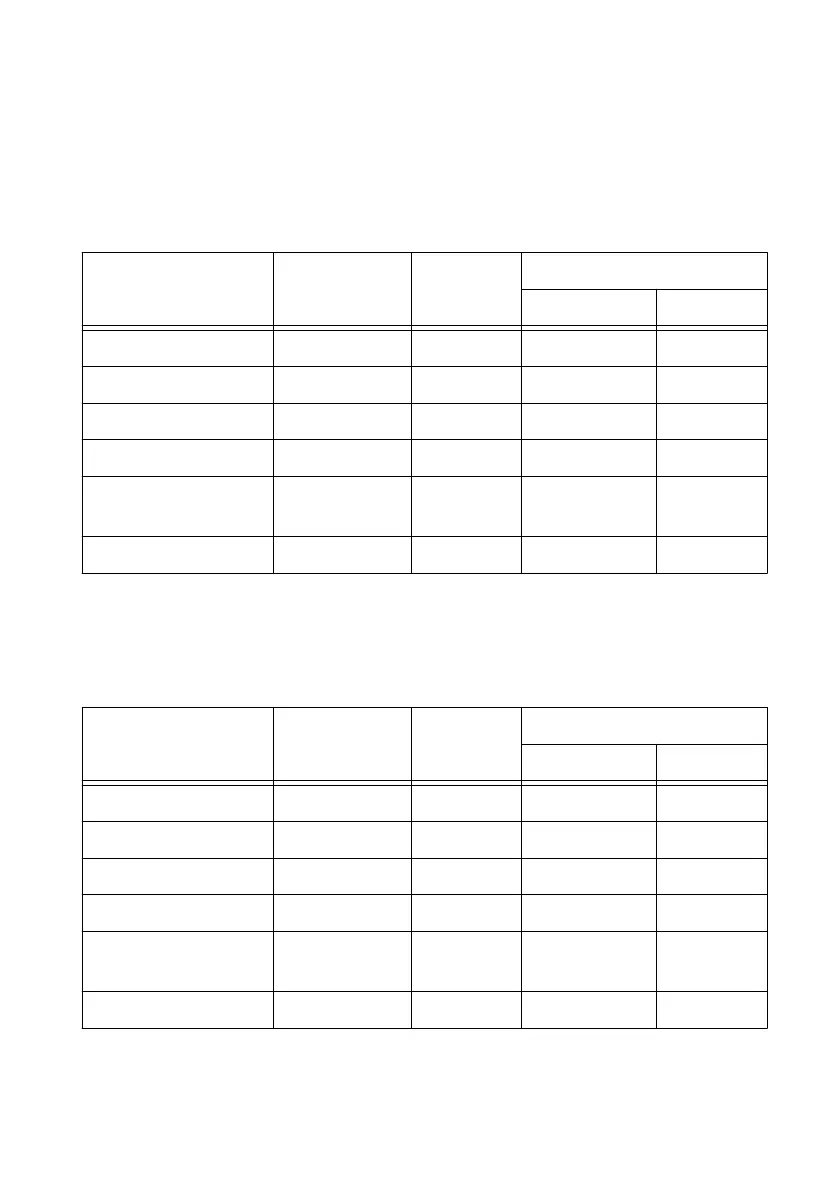
Table 22. 50 kHz Frequency Measurement Methods
Variable Sample Clocked One Counter Two Counters
High Frequency Large Range
fx 50,000 50,000 50,000 50,000
fk 80 M 80 M 1,000 80 M
Measurement time (ms) 1 .02 1 1
N — — — —
Max. frequency error
(Hz)
.638 31.27 1,000 .625
Max. error % .00128 .0625 2 .00125
From this, you can see that while the measurement time for one counter is shorter, the
accuracy is best in the sample clocked and two counter large range measurements. For another
example, the following table shows the results for 5 MHz.
Table 23. 5 MHz Frequency Measurement Methods
Variable Sample Clocked One Counter Two Counters
High Frequency Large Range
fx 5 M 5 M 5 M 5 M
fk 80 M 80 M 1,000 80 M
Measurement time (ms 1 .0002 1 1
N — — — 5,000
Max. frequency error
(Hz)
62.51 333 k 1,000 62.50
Max. error % .00125 6.67 .02 .00125
Again, the measurement time for the one counter measurement is lowest but the accuracy is
lower. Note that the accuracy and measurement time of the sample clocked and two counter
90 | ni.com | cRIO-904x User Manual

 Loading...
Loading...