14–8 Financial Functions
82D362~1.DOC TI-83 international English Bob Fedorisko Revised: 10/26/05 1:42 PM Printed: 10/27/05 2:59
PM Page 8 of 14
Use the cash flow functions (menu items 7 and 8) to analyze the
value of money over equal time periods. You can enter unequal
cash flows, which can be cash inflows or outflows. The syntax
descriptions for
npv( and irr( use these arguments.
• interest rate is the rate by which to discount the cash flows
(the cost of money) over one period.
• CF0 is the initial cash flow at time 0; it must be a real
number.
• CFList is a list of cash flow amounts after the initial cash
flow CF0.
• CFFreq is a list in which each element specifies the
frequency of occurrence for a grouped (consecutive) cash
flow amount, which is the corresponding element of CFList.
The default is 1; if you enter values, they must be positive
integers < 10,000.
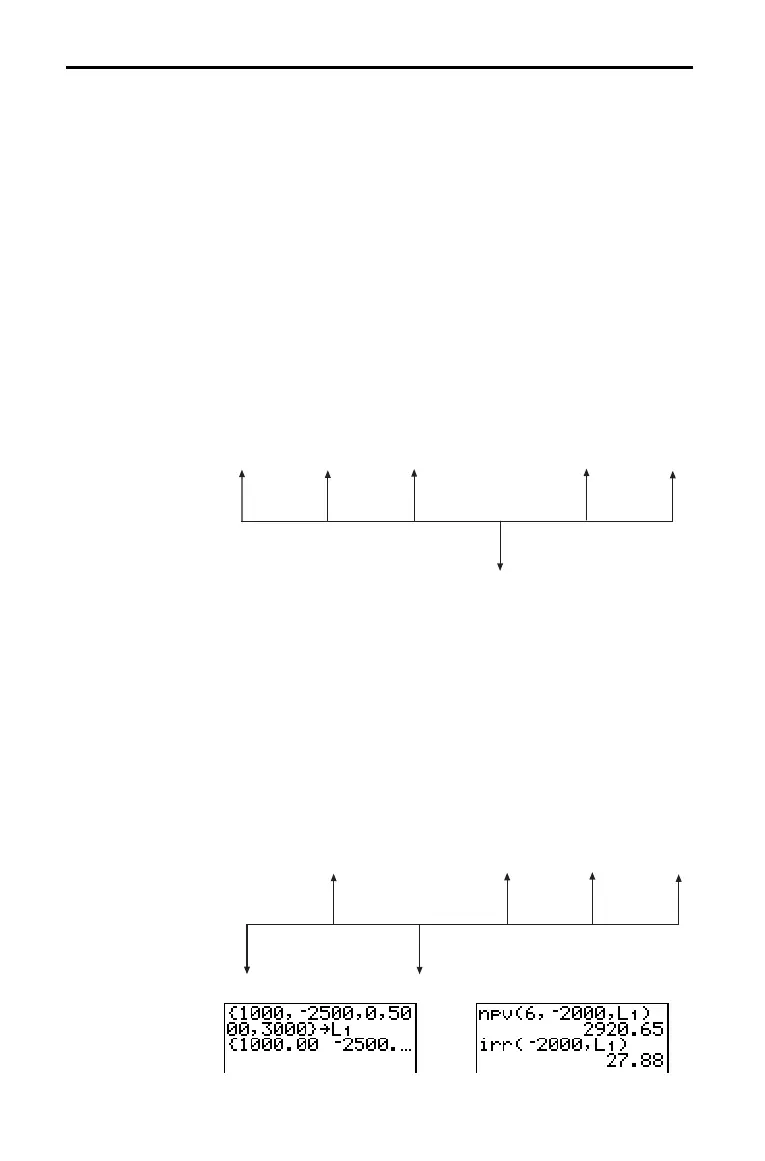
For example, express this uneven cash flow in lists.
2000
4000
2000
2000
- 3000
4000
CF0 = 2000
CFList = {2000,L3000,4000}
CFFreq = {2,1,2}
npv(
(net present value) is the sum of the present values for the
cash inflows and outflows. A positive result for
npv indicates a
profitable investment.
npv(interest rate,CF0,CFList[,CFFreq])
irr(
(internal rate of return) is the interest rate at which the net
present value of the cash flows is equal to zero.
irr(CF0,CFList[,CFFreq])
3000
5000
1000
- 2000
- 2500
0
Calculating Cash Flows
Calculating a
Cash Flow
npv(, irr(
 Loading...
Loading...











