Data Capture
124
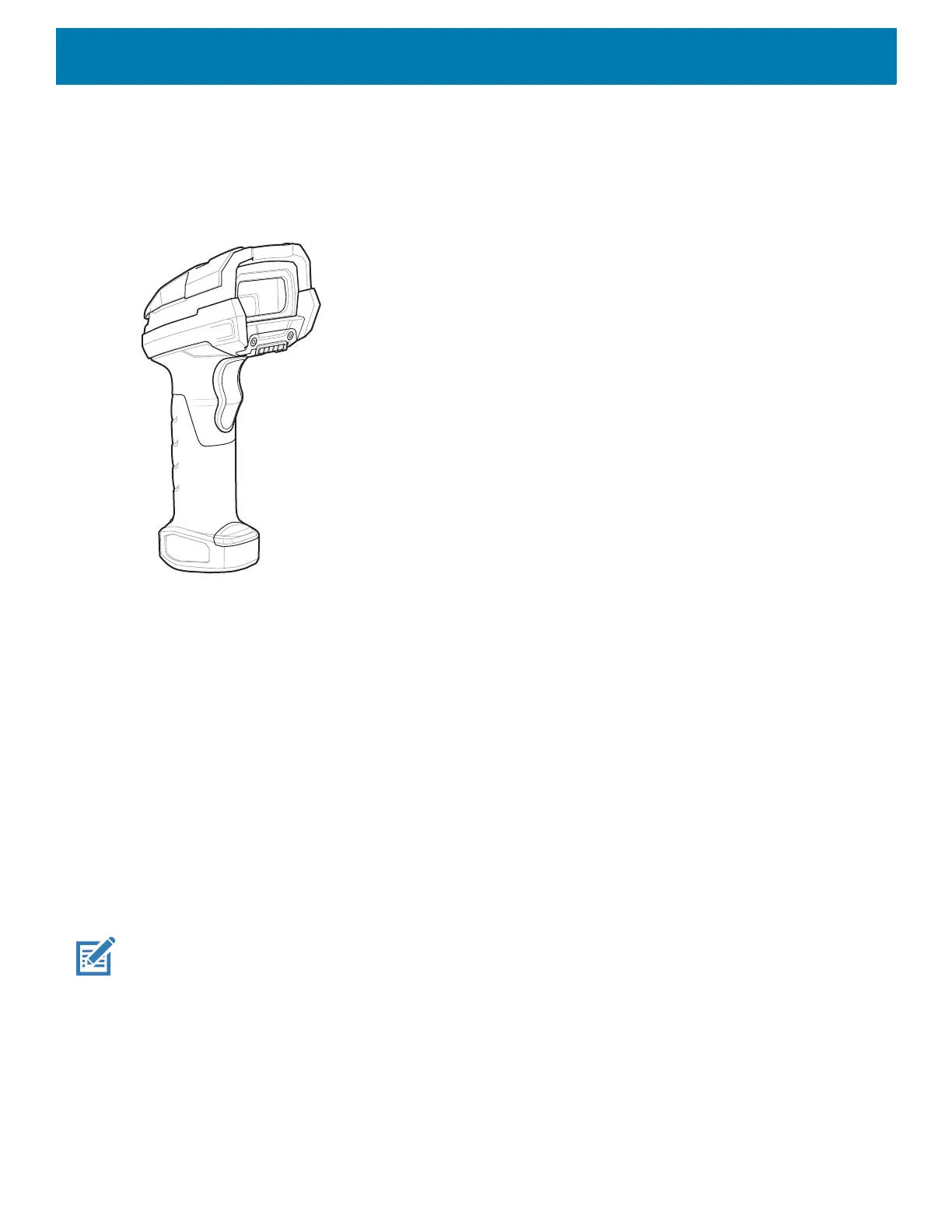
DS3678 Digital Scanner
The cordless DS3678 combines superior 1D and 2D omnidirectional barcode scanning performance and
advanced ergonomics in a lightweight design. See the DS36X8 Product Reference Guide for more information.
Figure 97 DS3678 Digital Scanner
Scanning Considerations
Typically, scanning is a simple matter of aim, scan, and decode, with a few quick trial efforts to master it.
However, consider the following to optimize scanning performance:
• Range: Scanners decode best over a particular working range — minimum and maximum distances from
the barcode. This range varies according to barcode density and scanning device optics. Scan within range
for quick and constant decodes; scanning too close or too far away prevents decodes. Move the scanner
closer and further away to find the right working range for the barcodes being scanned.
• Angle: Scanning angle is important for quick decodes. When the illumination/flash reflects directly back into
the imager, the specular reflection can blind/saturate the imager. To avoid this, scan the barcode so that the
beam does not bounce directly back. Do not scan at too sharp an angle; the scanner needs to collect
scattered reflections from the scan to make a successful decode. Practice quickly shows what tolerances to
work within.
• Hold the device farther away for larger symbols.
• Move the device closer for symbols with bars that are close together.
NOTE: Scanning procedures depend on the app and device configuration. An app may use different scanning
procedures from the one listed above.
Scanning with Internal Imager
To read a barcode, a scan-enabled app is required. The device contains the DataWedge app that allows the
user to enable the imager, decode the barcode data, and display the barcode content.
To scan with the internal imager:
1. Ensure that an app is open on the device and a text field is in focus (text cursor in text field).
 Loading...
Loading...