10.3.3.3 Power supply quality
M13853-15 v3
The setting must be above the highest occurring "normal" residual voltage and below
the highest acceptable residual voltage, due to regulation, good practice or other
agreements.
10.3.3.4
High impedance grounded systems
M13853-18 v10
In high impedance
grounded systems, ground faults cause a neutral voltage in the
feeding transformer neutral. Two step residual overvoltage protection ROV2PTOV
(59N) is used to trip the transformer, as a backup protection for the feeder ground fault
protection, and as a backup for the transformer primary ground fault protection. The
setting must be above the highest occurring "normal" residual voltage, and below the
lowest occurring residual voltage during the faults under consideration. A metallic
single-phase ground fault causes a transformer neutral to reach a voltage equal to the
nominal phase-to-ground voltage.
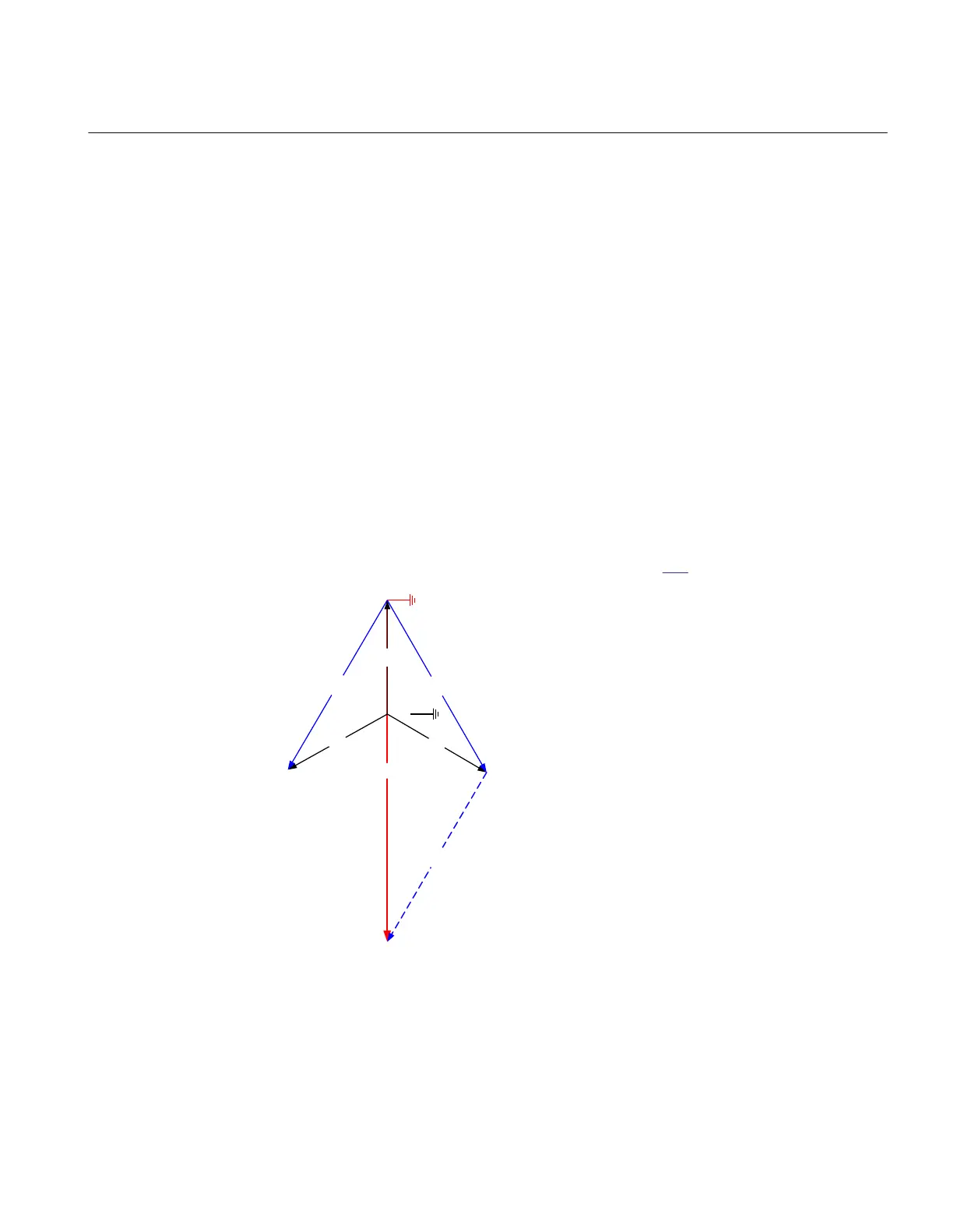
The voltage transformers measuring the phase-to-ground voltages measure zero
voltage in the faulty phase. The two healthy phases will measure full phase-to-phase
voltage, as the faulty phase will be connected to ground. The residual overvoltage will
be three times the phase-to-ground voltage. See figure
295.
3V
0
V
_
A
V_B
V
_
C
V
_
B
F
V
_C
F
V
_
C
F
ANSI07000190-1-en.vsd
ANSI07000190 V1 EN-US
Figure 295: Ground fault in Non-effectively grounded systems
1MRK 504 163-UUS A Section 10
Voltage protection
Transformer protection RET670 2.2 ANSI 623
Application manual

 Loading...
Loading...











