Parameterization and Commissioning
BC9000 and BC9100 29Version: 4.0.0
4.4.7 Subnet mask
The subnet mask is subject to the control of the network administrator, and specifies the structure of the
subnet.
Small networks without a router do not require a subnet mask. The same is true if you do not use registered
IP numbers. A subnet mask can be used to subdivide the network with the aid of the mask instead of using a
large number of network numbers.
The subnet mask is a 32-bit number:
• Ones in the mask indicate the subnet part of an address space.
• Zeros indicate that part of the address space which is available for the host IDs.
Description Binary representation Decimal representation
IP address 10101100.00010000.00010001.11001000 172.16.17.200
Subnet mask 11111111.11111111.00010100.00000000 255.255.20.0
Network ID 10101100.00010000.00010000.00000000 172.16.16.0
Host ID 00000000.00000000.00000001.11001000 0.0.1.200
Standard subnet mask
Address class Standard subnet mask (decimal) Standard subnet mask (hex)
A 255.0.0.0 FF.00.00.00
B 255.255.0.0 FF.FF.00.00
C 255.255.255.0 FF.FF.FF.00
Subnets and host number
Neither subnet 0 nor the subnet consisting only of ones may be used. Neither host number 0 nor
the host number consisting only of ones may be used!
If the IP address is set using the KS2000 configuration software, it is necessary for the subnet mask
also to be changed with the KS2000 configuration software.
If ARP addressing is used, the associated standard subnet mask, based on the IP address, is en-
tered.
Under BootP or DHCP the subnet mask is transmitted also by the server.
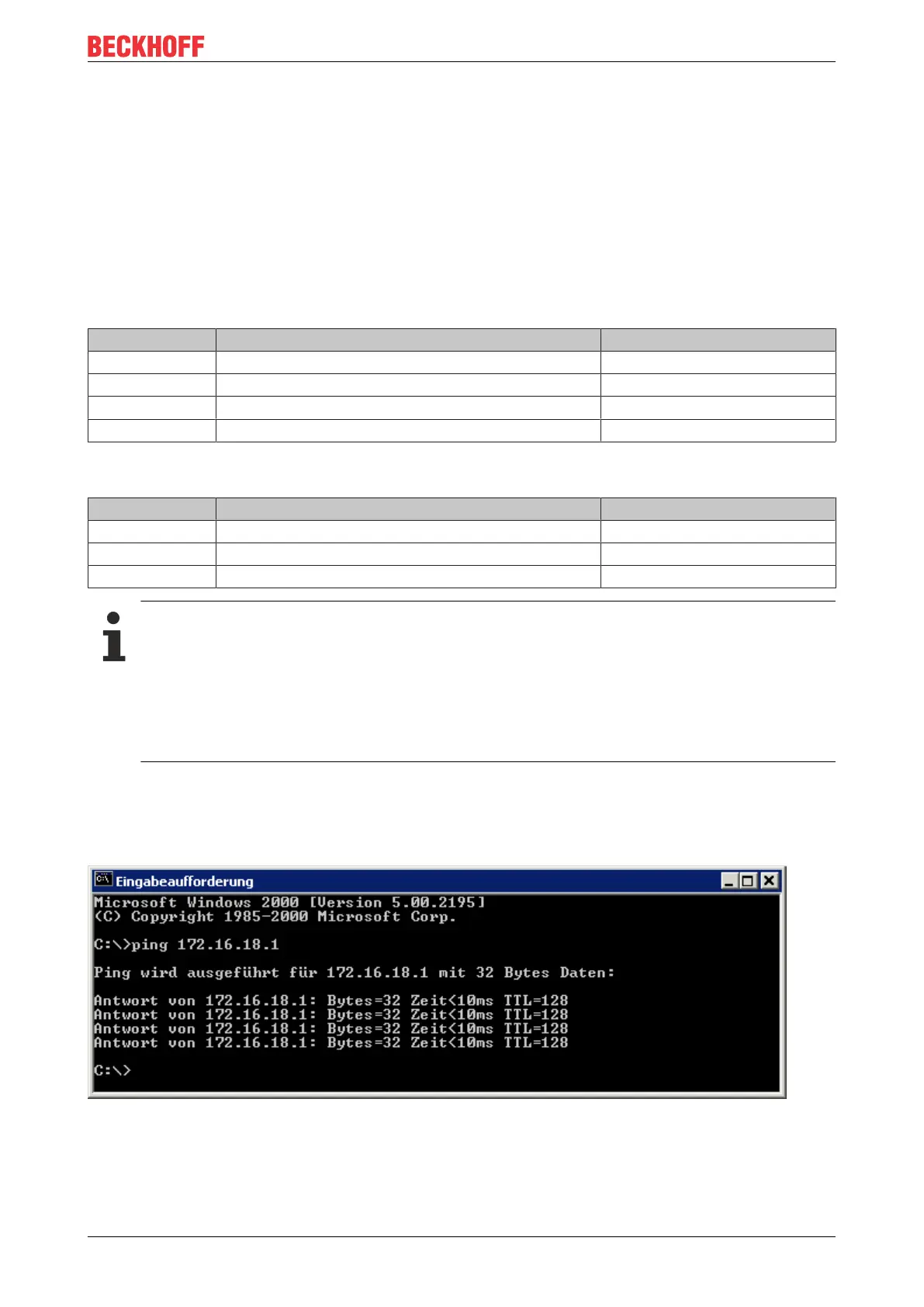
4.4.8 Testing the IP address
To test the IP address you can use the Ping command in a Windows prompt.
Fig.16: Testing the IP address using the Ping command

 Loading...
Loading...