DES-3326S Layer 3 Fast Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
332 Understanding and Troubleshooting the Spanning Tree Protocol
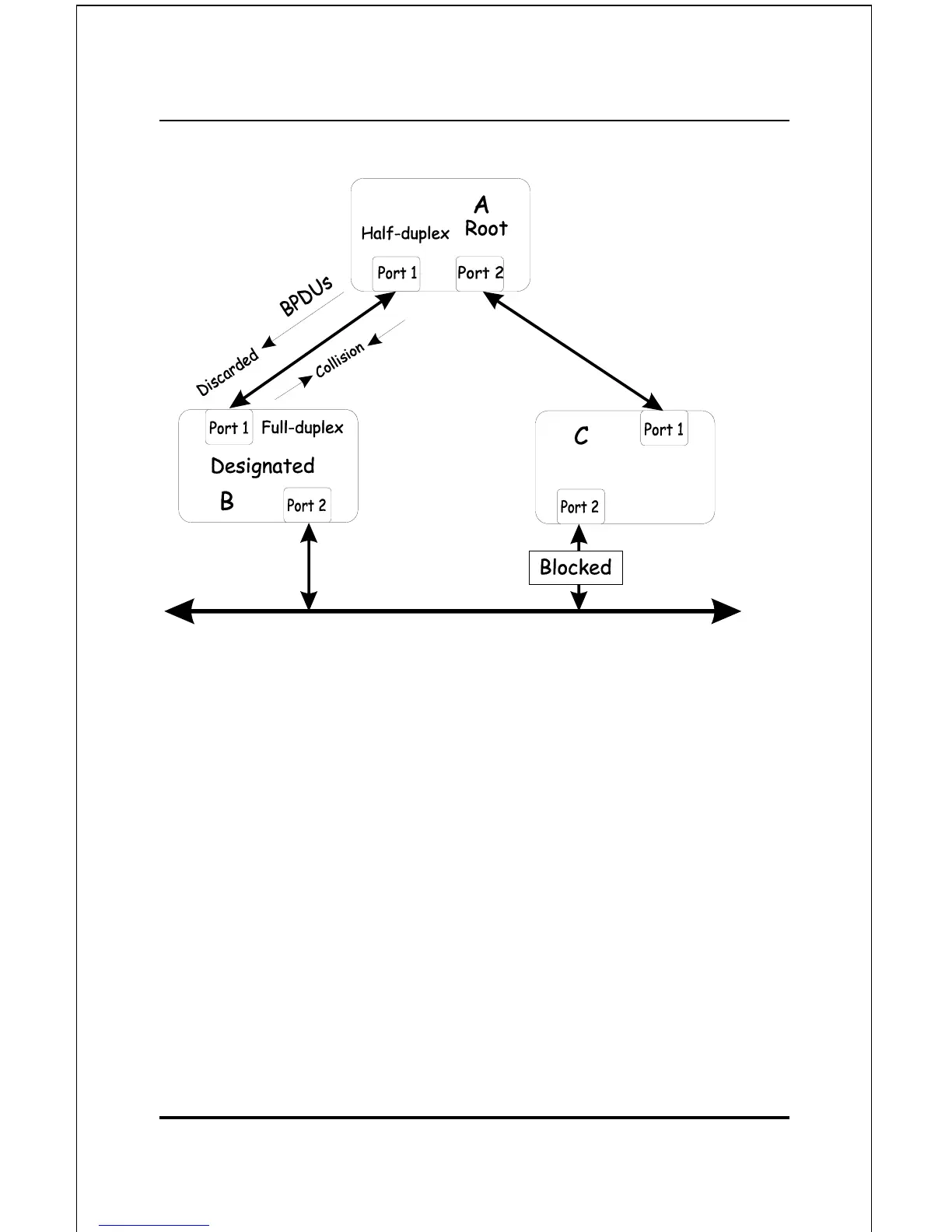
In the above example, port 1 on B is configured as a full-
duplex port and port 1 on A is either configured as a half-
duplex port, or left in auto-negotiation mode. Because port 1
on B is configured as a full-duplex port, it does not do the
carrier sense when accessing the link. B will then start
sending packets even if A is using the link. A will then detect
collisions and begin to run the flow control algorithm. If there
is enough traffic between B and A, all packets (including
BPDUs) will be dropped. If the BPDUs sent from A to B are
dropped for longer than the MAX AGE, B will lose its
connection to the root (A) and will unblock its connection to C.
This will lead to a data loop.
Unidirectional Link
Unidirectional links can be caused by an undetected failure in
one side of a fiber cable, or a problem with a ports transceiver.

 Loading...
Loading...











