Si30-408 Concept of Basic Refrigeration Cycle
Basic Information 23
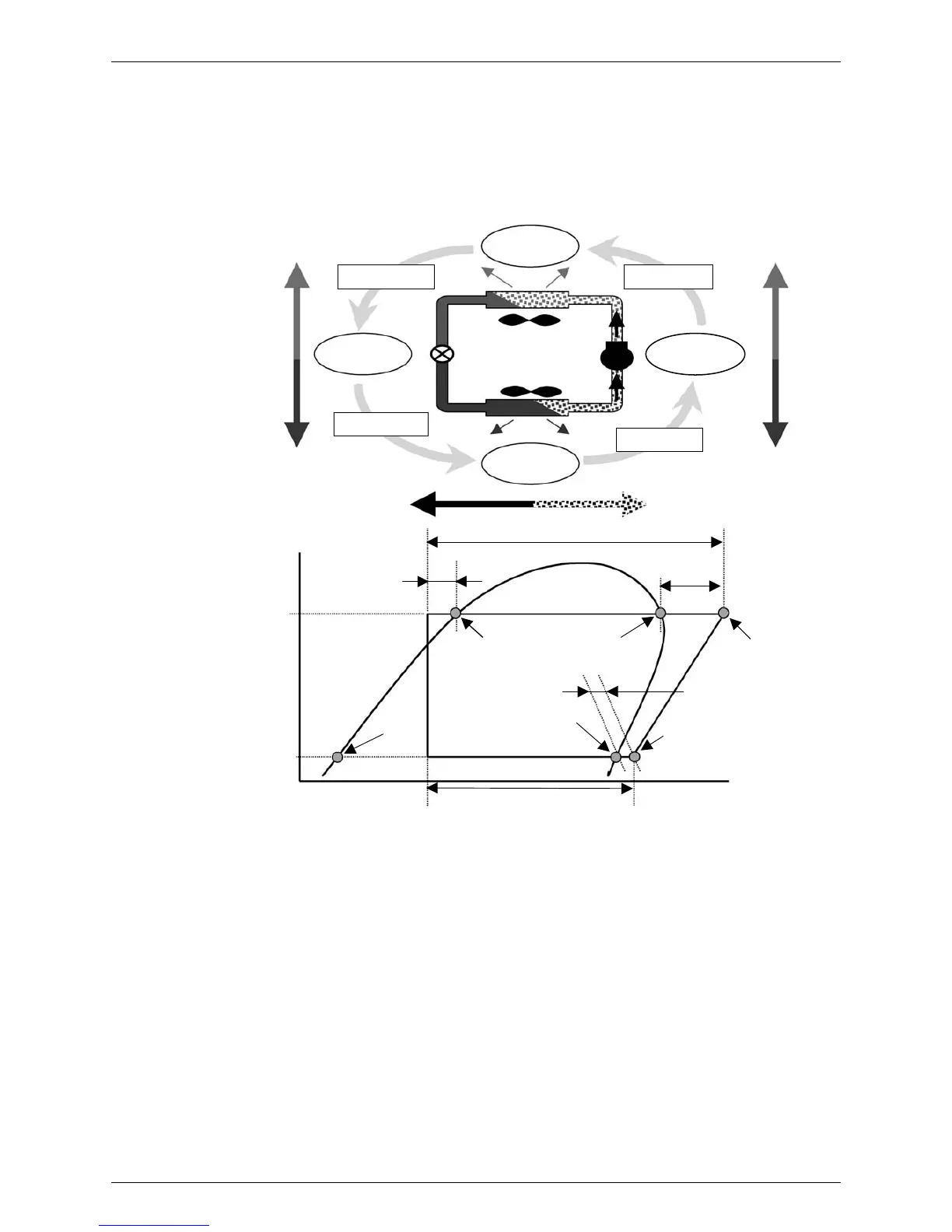
2. Concept of Basic Refrigeration Cycle
The refrigeration cycle is composed of repetition of the following process.
"Compression
→ Condensation → Expansion → Evaporation"
The refrigerating machine conducts above cycle with compressor, condenser, expansion valve
and evaporator.
Theoretic refrigeration cycle neglecting pressure loss, etc. drawn on P-H diagram is shown as
above.
The difference between "temperature" and "pressure equivalent saturation temperature" is
called superheated degree.
The difference between discharging pipe temperature and condensation temperature is
called discharging superheated degree(DSH).
The difference between suction pipe temperature and evaporating temperature is called
suction superheated degree (SH).
(Generally, superheated degree means suction superheated degree)
The difference between "temperature" and "pressure equivalent saturation temperature" in
subcooled liquid is called subcooled degree (SC).
In order to prevent wet operation (*), the superheated degree is made at evaporator outlet and
refrigerant flow rate into evaporator is regulated with expansion valve, so that the superheated
vapor can be sucked by compressor.
* Wet operation is a state of operation, where wet vapor due to the vapor not completely
vaporized in the evaporator, wet vapor is sucked by compressor.
(Wet operation may cause damage of compressor due to liquid compression, dilution of
refrigeration oil, etc..)
Condenser
Hot air
Cold air
P
Pc
Pe
Tcl
Tcg
h
Tel
Teg
High pressure liquid
Low pressure liquid
Subcooled degree
(SC)
Discharge superheated degree
(DSH)
Discharge pipe temperature
Suction superheated degree (SH)
Suction pipe temperature
Cooling effect (Evaporating capacity)
GasLiquid
Heating effect (Condensing capacity)
High
Low
High pressure
Low pressure
Temperature
Low pressure gas
Compressor
High pressure gas
Evaporator
Expansion valve

 Loading...
Loading...