Si30-408 Points of Refrigerant Control of VRV System
Basic Information 25
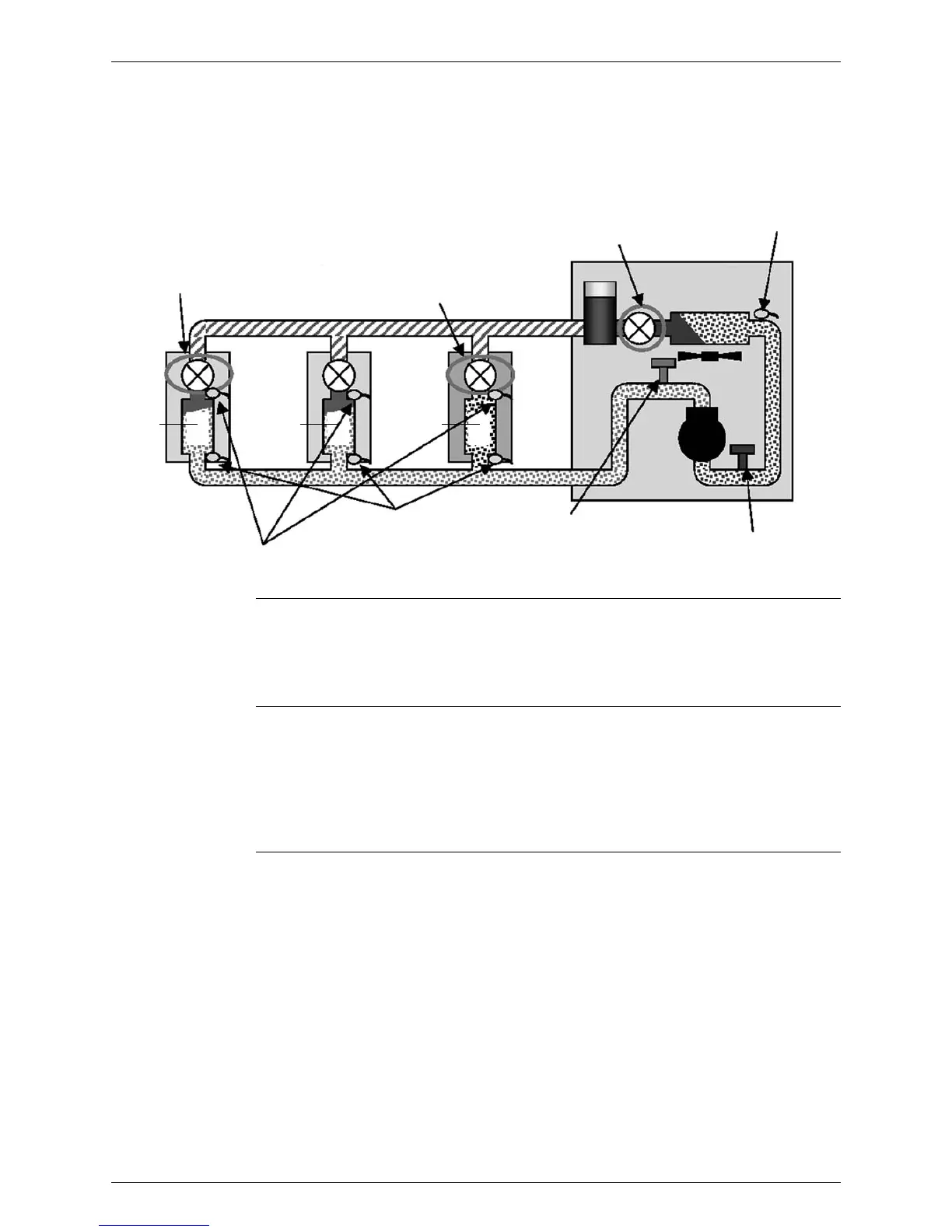
3.2 Heating Operation
Subject to change of the number of operation (thermostat-on) units, capacity, air flow rate,
suction temperature, of indoor units
Load on total system changes.
Loads on every indoor unit are different.
Compressor
Capacity Control
In order to maintain the heating capacity against condenser capacity and load fluctuation, based
on the pressure detected by high-pressure sensor control (Pc), compressor capacity is so
controlled to put the high pressure equivalent saturation temperature (condensing temperature
= Tc) close to target value.
Superheated
Degree Control of
Outdoor
Electronic
Expansion Valve
In order to maintain the superheated degree in evaporator, based on the pressure detected by
the low pressure sensor (Te) and the temperature detected by the thermistor of suction pipe,
outdoor electronic expansion valve is so controlled as to put superheated degree at evaporator
outlet close to target value.
• Superheated degree SH = (outdoor suction pipe temperature – outdoor evaporating
temperature)
Subcooled
Degree Control of
Indoor Electronic
Expansion Valve
In order to distribute proper refrigerant flow rate in spite of different loads on every indoor unit,
based on the pressure detected by the high pressure sensor of outdoor unit (Tc) and the
temperature detected by the thermistor of indoor liquid pipes, indoor electronic expansion valve
is so controlled as to put subcooled degree at condenser outlet close to target value.
• Subcooled degree SC = (outdoor condensing temperature – indoor liquid pipe
temperature)
Subcooled degree control
Superheated degree control
Suction pipe thermistor
Heating
Compressor
Low pressure sensor
Receiver
High pressure sensor
Gas pipe thermistor
Liquid pipe thermistor
As to stopping unit and thermostat-off unit, electronic
expansion valve should be minute-closed (approx.
200 pls) in order to prevent refrigerant from collection
in indoor heat exchanger.
Operation
Operation Stop

 Loading...
Loading...