26
VRD: safety func-
tion
A Voltage Reduction Device (VRD) is an optional safety device for reducing the voltage. It
is recommended for environments in which the risk of an electric shock or electrical acci-
dent is increased considerably during arc welding:
- Due to a low human body resistance of the welder
- If the welder is exposed to a clear risk of touching the workpiece or other parts of the
welding circuit
A low human body resistance is possible when there is:
- water in the area
- humidity
- heat, particularly ambient temperatures in excess of 32°C (89.6°F)
In wet, damp or hot locations, humidity or sweat can significantly reduce the skin resistance
and the insulation resistance of protective equipment and clothing.
Such environments can include:
- Temporary dams for draining certain areas of a site during construction work (coffer-
dams)
- Trenches
- Mines
- Rain
- Areas partly submerged by water
- Spraywater areas
The VRD option reduces the voltage between the electrode and the workpiece. In safe
conditions, the indicator for the currently selected welding process is permanently lit. A
safe condition is defined as follows:
- The output voltage in an open circuit is limited to 35 V.
For as long as the welding operation is active (welding circuit resistance < 200 Ohm), the
indicator of the currently selected welding process flashes and the output voltage may ex-
ceed 35 V.
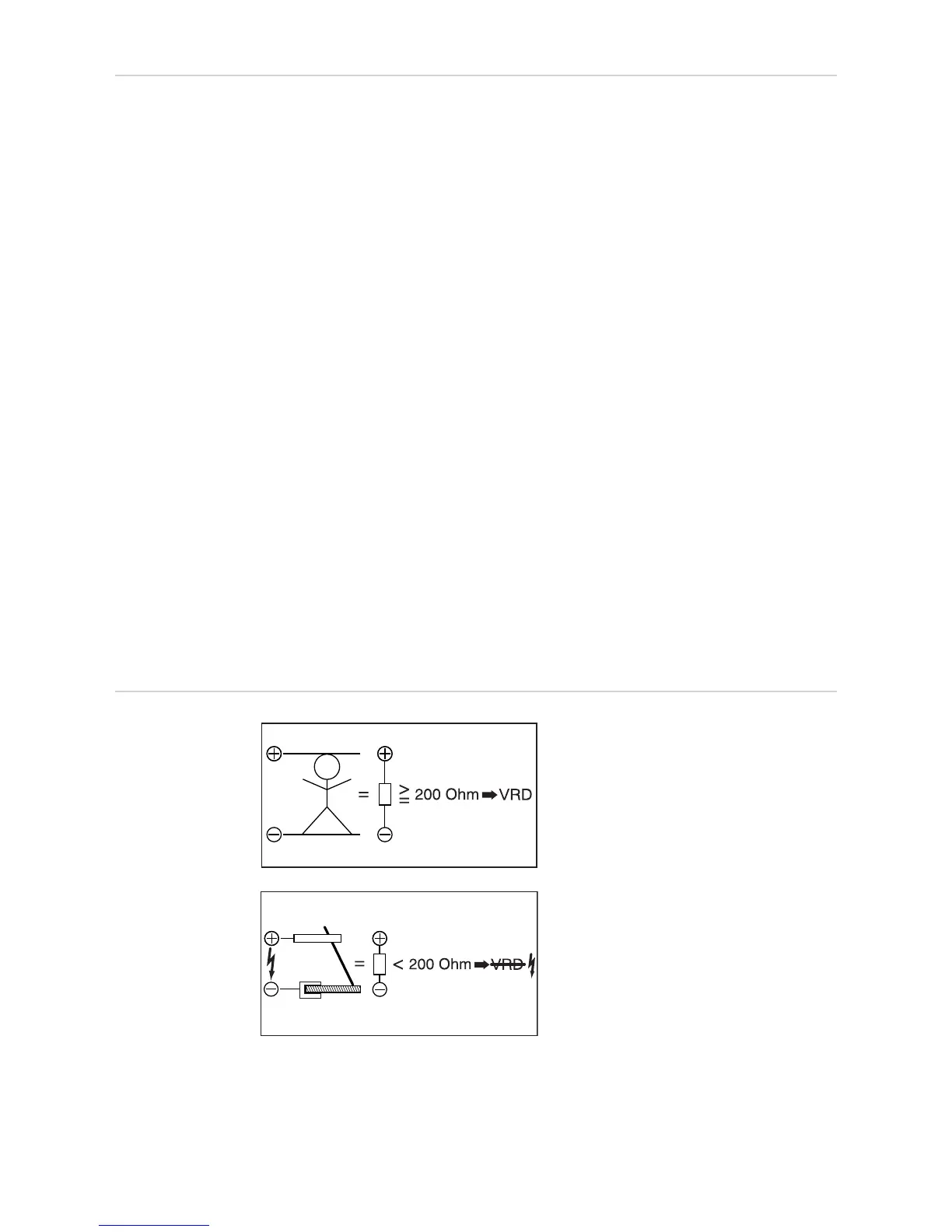
VRD: safety prin-
ciple
The welding circuit resistance is greater
than the minimum human body resistance
(greater than or equal to 200 Ohm):
- VRD is active
- Open circuit voltage is limited to 35 V
- Unintentional contact with the output
voltage does not put the welder at risk
The welding circuit resistance is less than
the minimum human body resistance (less
than 200 Ohm):
- VRD is inactive
- Output voltage not restricted in order to
ensure sufficient welding power
- Example: Welding starts
In MMA welding mode:
Within 0.3 seconds of end of welding:
- VRD is active again
- The output voltage is limited to 35 V once more

 Loading...
Loading...











