_____ _
User Guide Electrical Line Shaft for ADV200 Page 54 of 72
7 Application example – Calculation of Ratio
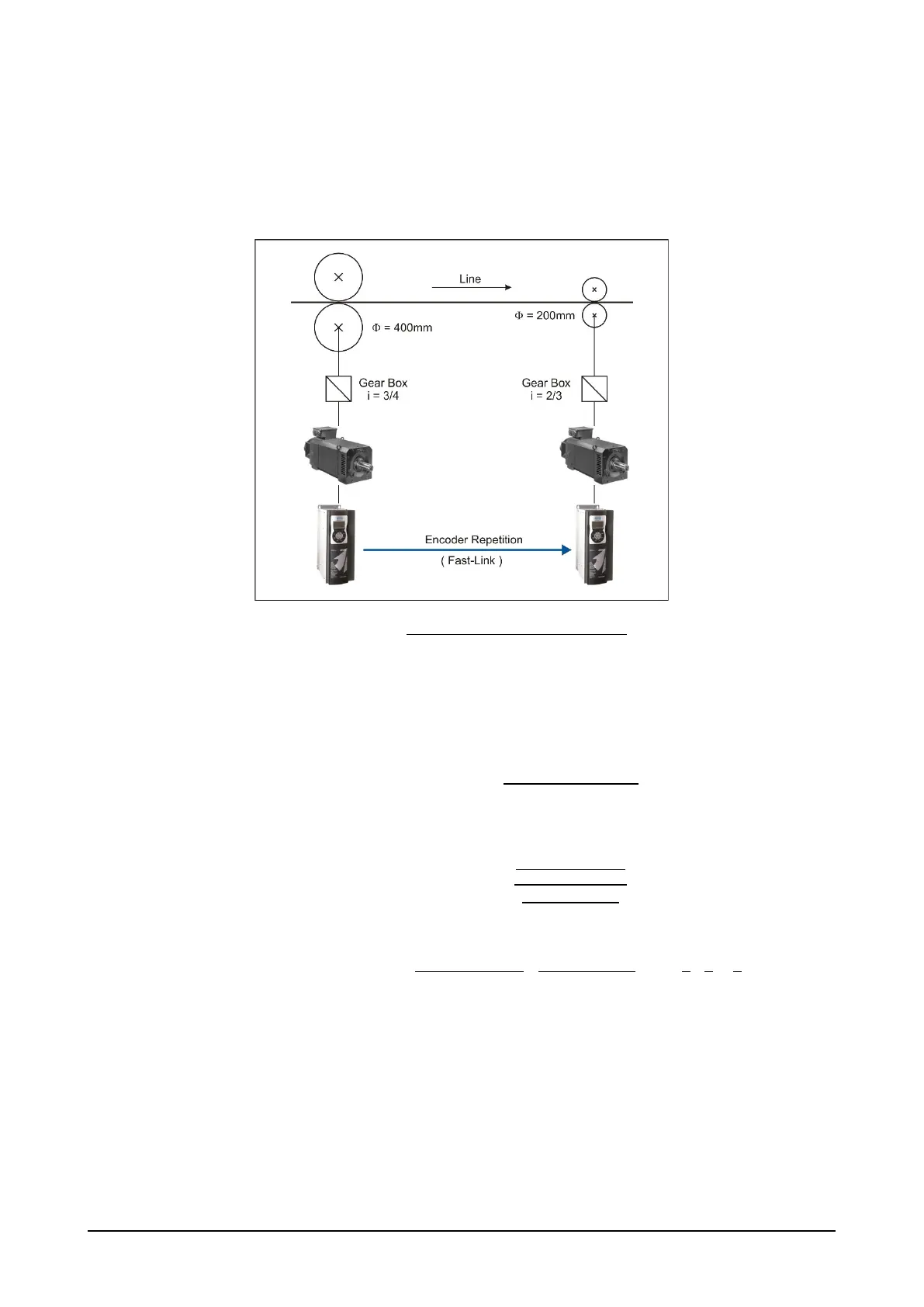
The following example shows two pairs of rollers commanded by two different kinematic chains.
The material conveyed by the Master system to the Slave must not be stretched; therefore the space traveled
by the rollers must be the same.
Figure 22. Example of electric line shaft application
Premise:
the mechanical ratio (Mech ratio) between rotations of the Master and Slave motor shafts (fast shafts) is
calculated so that the slow shafts (downstream of the gearboxes) will rotate at the same speed.
The mechanical ratio is expressed by the following base formula:
=
In the presence of gearboxes, the base formula becomes:
=
= =
= 1
4
3
2
3
=
8
9
Therefore, we have:
Els Mech Ratio Mul = 8;
Els Mech Ratio Div = 9;
Els Mech Ratio = 1;
The ratio between the speeds is now calculated in order to keep the rims speeds of the rollers the same.
If the plate has a linear speed of 100 m/min, we calculate the ratio between the angular velocities in rpm of
the slow shafts:
 Loading...
Loading...















