Base Conversions and Arithmetic
10–5
File name 33s-E-Manual-1008-Publication(1st).doc Page : 386
Printed Date : 2003/10/8 Size : 13.7 x 21.2 cm
Range of Numbers
The 36-bit word size determines the range of numbers that can be represented in
hexadecimal (9 digits), octal (12 digits), and binary bases (36 digits), and the
range of decimal numbers (11 digits) that can be converted to these other bases.
Range of Numbers for Base Conversions
Base Positive Integer
of Largest Magnitude
Negative Integer
of Largest Magnitude
Hexadecimal 7FFFFFFFF 800000000
Octal 377777777777 400000000000
Binary 0111111111111111111111
11111111111111
1000000000000000000000
00000000000000
Decimal 34,359,738,367 –34,359,738,368
When you key in numbers, the calculator will not accept more than the maximum
number of digits for each base. For example, if you attempt to key in a 10–digit
hexadecimal number, digit entry halts and the
â
annunciator appears.
If a number entered in decimal base is outside the range given above, then it
produces the message
in the other base modes. Any operation using
causes an overflow condition, which substitutes the largest positive or
negative number possible for the too–big number.
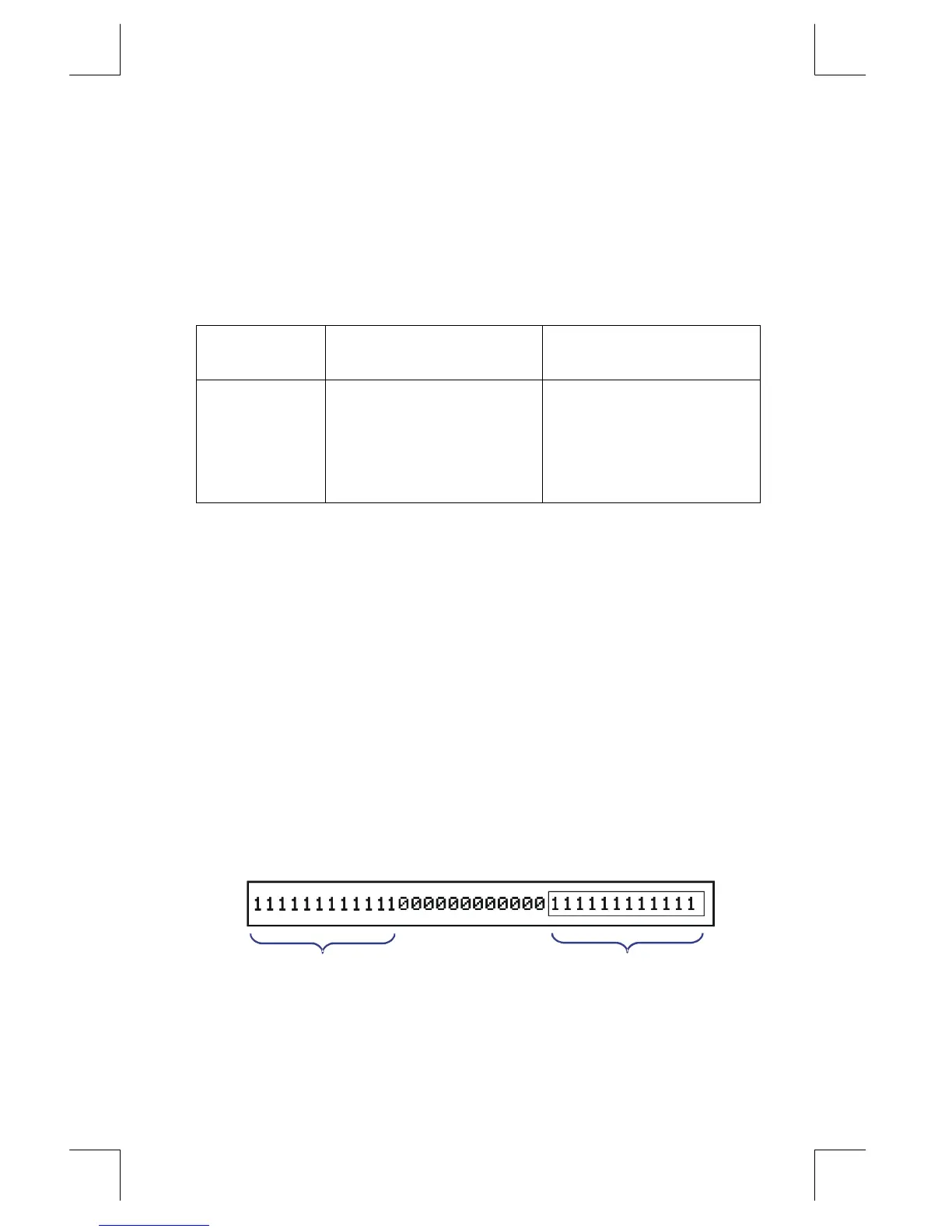
Windows for Long Binary Numbers
The longest binary number can have 36 digits — three times as many digits as fit
in the display. Each 12–digit display of a long number is called a window.
36 - bit number
Highest window
Lowest window
(displayed)

 Loading...
Loading...





