4-12 Real–Number Functions
Example: Conversion with Vectors.
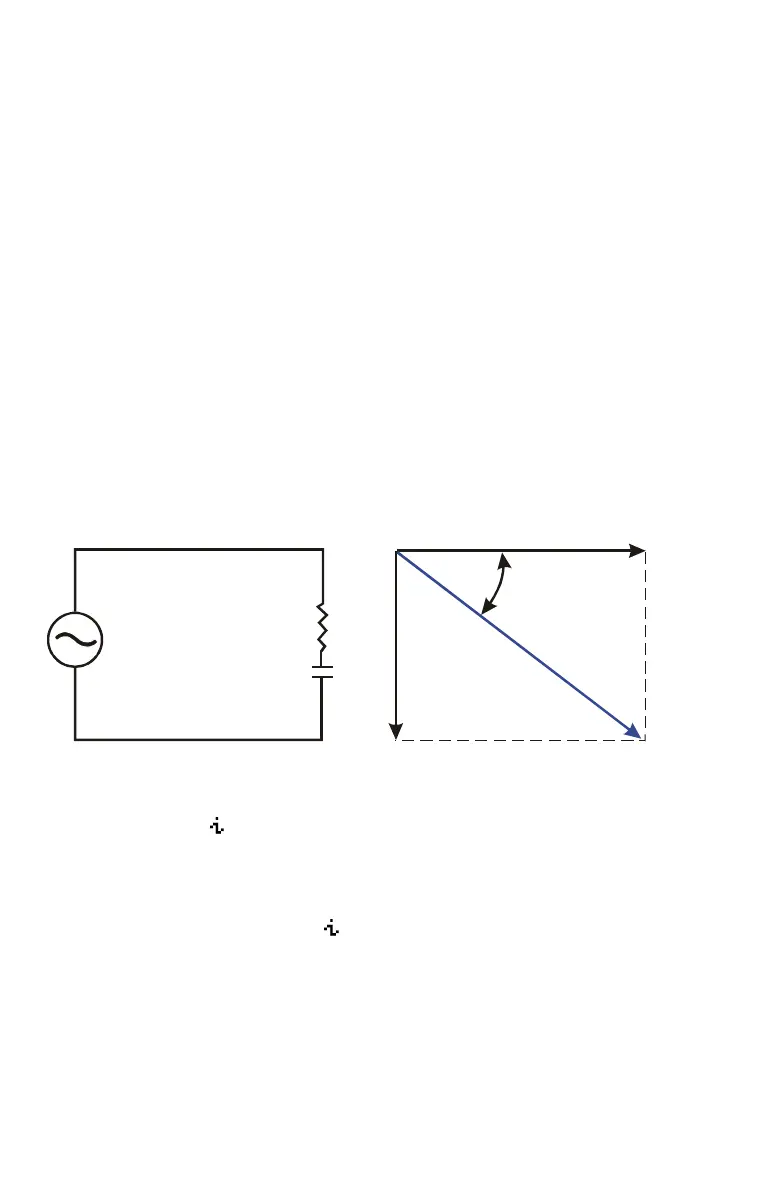
Engineer P.C. Bord has determined that in the RC circuit shown, the total impedance
is 77.8 ohms and voltage lags current by 36.5º. What are the values of resistance R
and capacitive reactance X
C
in the circuit?
Use a vector diagram as shown, with impedance equal to the polar magnitude, r,
and voltage lag equal to the angle,
θ
, in degrees. When the values are converted
to rectangular coordinates, the x–value yields R, in ohms; the y–value yields X
C
, in
ohms.
8
()
θ
Sets complex coordinate
mode.
6
θ
Convert xiy (rectangular) to
r
θ
a (polar).
Keys: Display: Description:
9()
¹8 ( )
Sets Degrees and complex
coordinate mode.
?
θ
Enters
θ
, degrees of voltage lag.
Enters r, ohms of total
impedance.
Calculates x, ohms
resistance, R.
Calculates y, ohms
reactance, X
C
R
C
R
X
c
36.5
o
77.8 ohms
θ

 Loading...
Loading...





