RADIUS Authentication and Accounting
Configuring a RADIUS Server To Specify Per-Port CoS and Rate-Limiting Services
Note The order in which an ACE occurs in an ACL is significant. For example, if an
ACL contains six ACEs, but the first ACE is a “permit IP any”, then the ACL
permits all IP traffic, and the remaining ACEs in the list do not apply, even if
they specify criteria that would make a match with any of the traffic permitted
by the first ACE.
For example, suppose you want to configure a RADIUS-based ACL to invoke
these policies in the 11.11.11.0 network:
1. Permit inbound client traffic with a DA of 11.11.11.42.
2. Permit inbound Telnet traffic for DA 11.11.11.101.
3. Deny inbound Telnet traffic for all other IP addresses in the 11.11.11.0
network.
4. Permit inbound HTTP traffic for any IP address in the 11.11.11.0 network.
5. Deny all other inbound traffic.
The following ACL model, when invoked by a client authenticating with the
credentials configured in the RADIUS server for this ACL, supports the above
case:
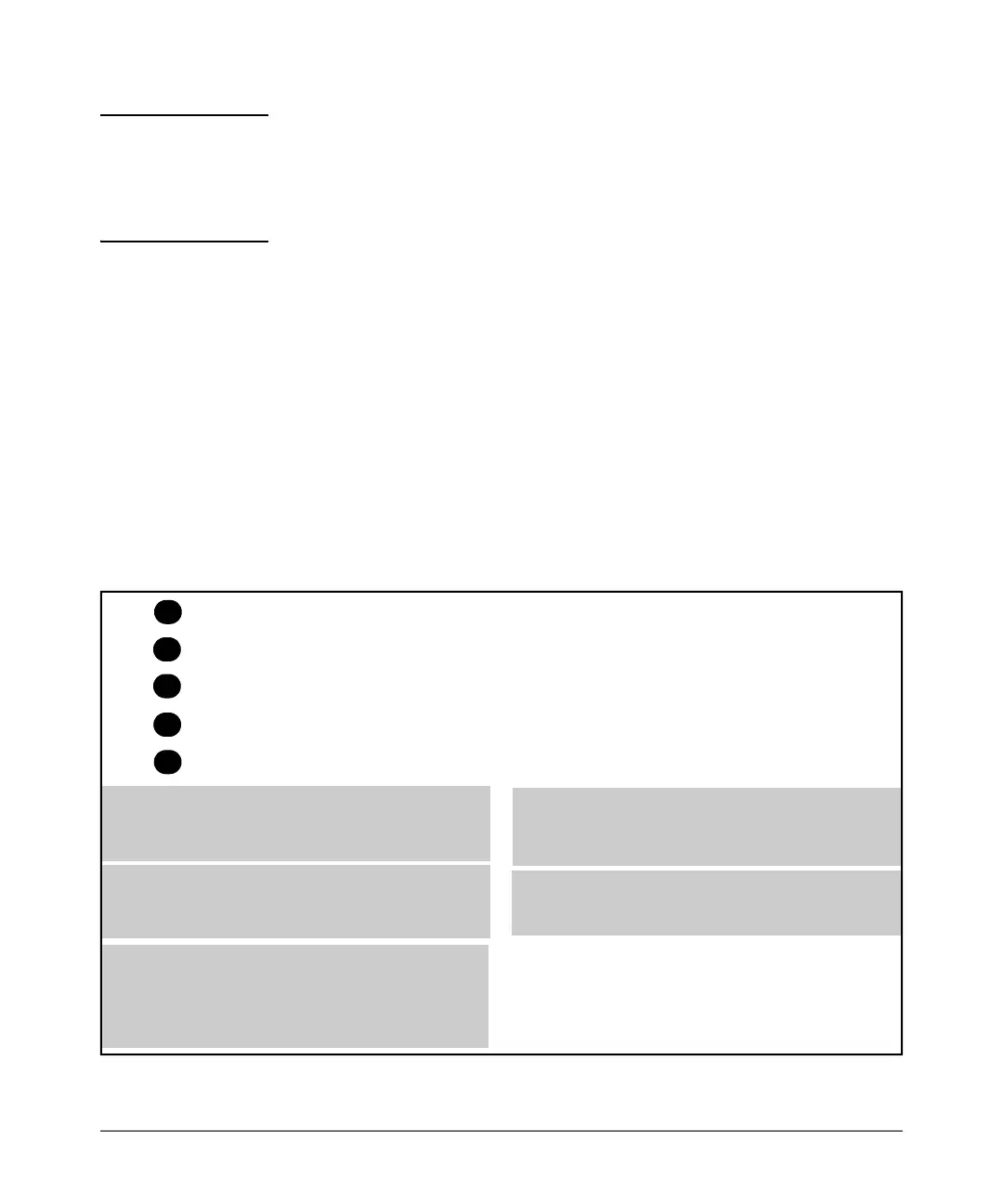
4
2. i
to the next entry in the list.
1. i
ion will
i
4. li
i
i i i
ist.
l i
i
i
l
1
2
3
5
( )
3. i
l
l
li
ist.
Permits nbound Telnet traffic from the authenticated client to
the destination address 11.11.11.101. Packets matching this
criterion are forwarded and are not compared to any later ACE
in the list. Packets not matching this criterion will be compared
Permits inbound IP traffic from the authenticated cl ent to the
destination address 11.11.11.42. Packets matching this criterion
are forwarded and are not compared to any later ACE in the list.
Packets not matching this criter be compared to the next
entry n the list.
Permits inbound HTTP traffic from the authenticated c ent to
any address in the 11.11.11.1 network. Packets match ng this
criterion are permitted and are not compared to any later
criteria n the list. Packets not match ng this cr terion are
compared to the next entry in the l
5. This entry does not appear in an actua ACL, but is implic t as
the last entry n every ACL. Any inbound traffic from the
authenticated client that does not match any of the cr teria in
the ACL’s preceding ACE entries wil be denied (dropped).
Permit in ip from any to 11.11.11.42
Permit in tcp from any to 11.11.11.101 23
Deny in tcp from any to 11.11.11.0/24 23
Permit in tcp from any to 11.11.11.1/24 80
implicit deny in ip any to any
Denies nbound Telnet traffic from the authenticated client to
any IP address in the 11.11.11.0 network. Since packets
matching entry “2” wil never reach this ACE, the Telnet traffic
permitted by entry “2” will not be affected. Packets matching
this criterion will be denied and wil not be compared to any
later criteria in the st. Packets not matching this criterion will
be compared to the next entry in the l
Figure 6-12. Example of How a RADIUS-Based ACL Filters Packets
6-32
 Loading...
Loading...











