Configuring Secure Shell (SSH)
Overview
Overview
Feature Default Menu CLI Web
Generating a public/private key pair on the switch No n/a page 7-10 n/a
Using the switch’s public key n/a n/a page 7-12 n/a
Enabling SSH Disabled n/a page 7-15 n/a
Enabling client public-key authentication Disabled n/a pages 7-19, n/a
7-22
Enabling user authentication Disabled n/a page 7-18 n/a
The switches covered by this guide use Secure Shell version 1 or 2 (SSHv1 or
SSHv2) to provide remote access to management functions on the switches
via encrypted paths between the switch and management station clients
capable of SSH operation.
SSH provides Telnet-like functions but, unlike Telnet, SSH provides encrypted,
authenticated transactions. The authentication types include:
■ Client public-key authentication
■ Switch SSH and user password authentication
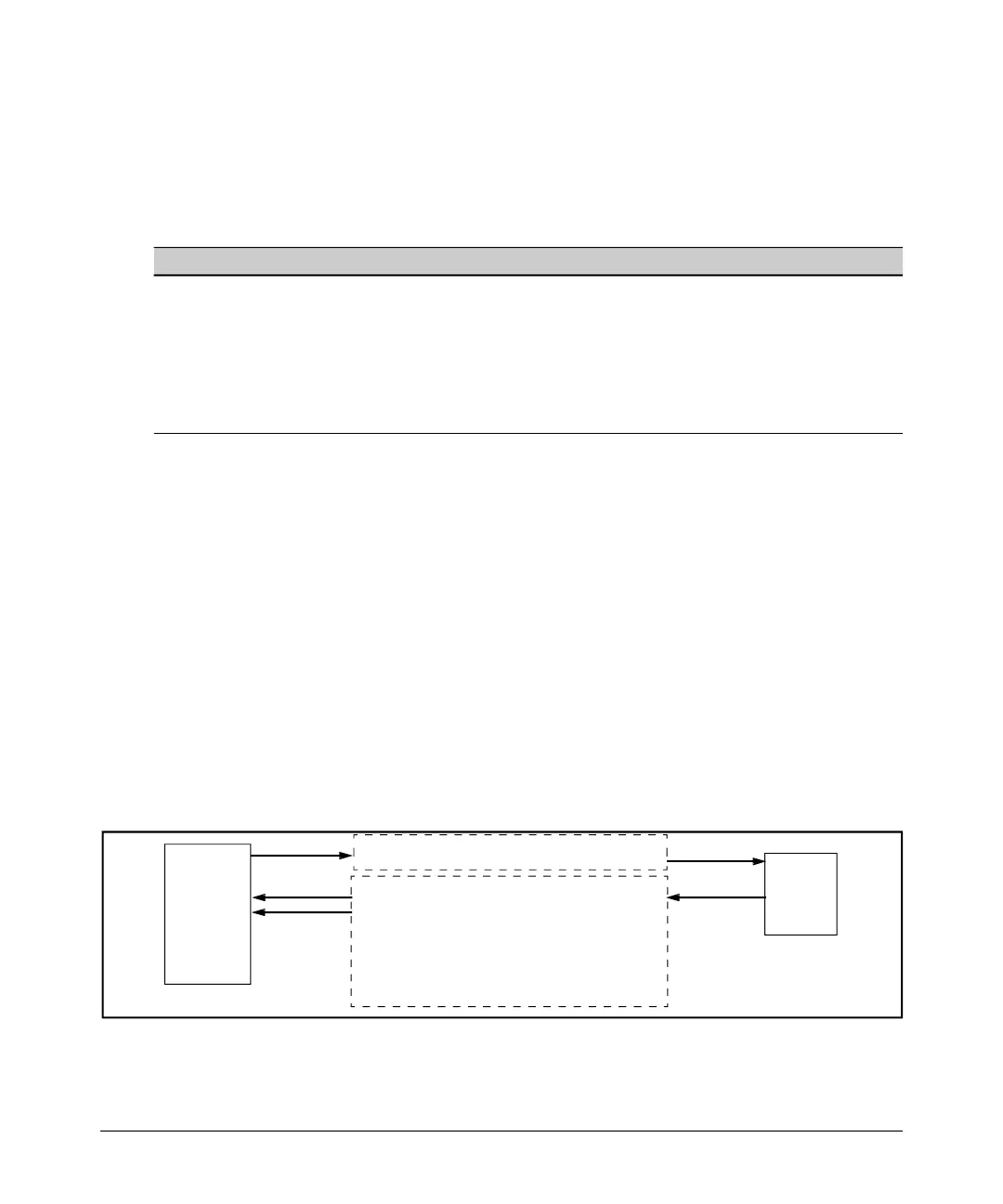
Client Public Key Authentication (Login/Operator Level) with User
Password Authentication (Enable/Manager Level).
This option uses
one or more public keys (from clients) that must be stored on the switch. Only
a client with a private key that matches a stored public key can gain access
to the switch. (The same private key can be stored on one or more clients.)
Switch
(SSH
Server)
(
l i
–
SSH
Client
Station
ProCurve
1. Switch-to-Client SSH authentication.
2. Client-to-Switch login rsa) authentication
3.User-to-Switch (enab e password) authenticat on
options:
Local
–TACACS+
–RADIUS
–None
Work-
Figure 7-1. Client Public Key Authentication Model
7-2

 Loading...
Loading...











