thefollowingtablecanhelpdeterminewhichoptionisbestfordifferent
situations.
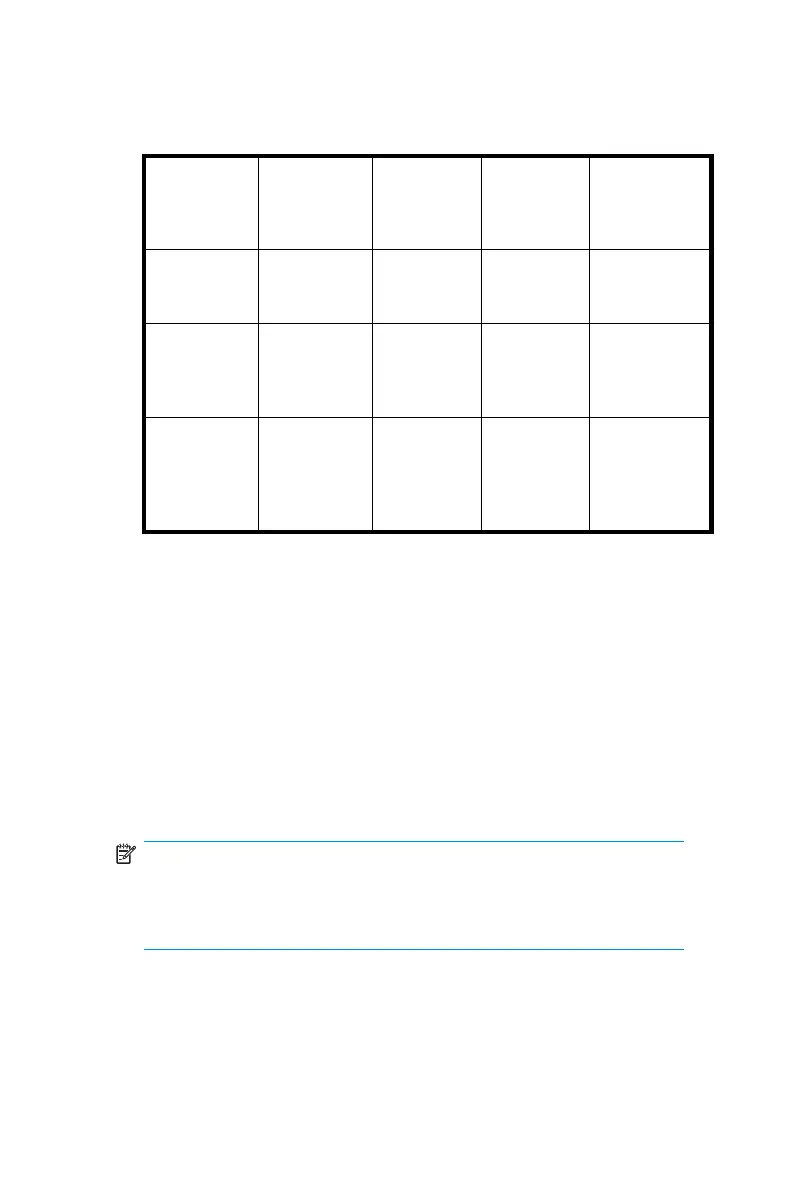
Ta ble 7 Summary of RAID methods
RAID 0
Striping
(no fault
tolerance)
RAID 1+0
Mirroring
RAID 5
Distributed
Data
Guarding
RAID ADG
Maximum
number of
hard drives
N/A N/A
14
Storage
system
dependent
Tolerant
of single
hard drive
failure?
No
Yes Yes Yes
Tolerant of
multiple si-
multaneous
hard drive
failure?
No
If the failed
drives
are not
mirrored to
each other
No
Yes (two
drives can
fail)
Online Spares
Further protection against data loss can be achieved by assigning an
online spare (or hot spare) to any configuration except RAID 0. This hard
drive contains no data and is contained within the same storage subsystem
as the other drives in the array. When a hard drive in the array fails, the
controller can then automatically rebuild information that was originally on
the failed drive onto the online spare. This quickly restores the system to
full RAID level fault tolerance protection. However, unless RAID Advanced
Data Gu arding (ADG) is being used, which can support two drive failures
in an array, in the unlikely event that a third drive in the array should fail
while data is b eing rewritten to the spare, the logical drive still fails.
NOTE:
For configurablestorageservers,storagelimitationsarebasedonthe
type of SAN to which the storage server is connected. See the individual
SAN documentation for limitations of Windows Storage Server 2003.
HPProLiantStorageServeruserguide
35

 Loading...
Loading...











