v
About This Guide
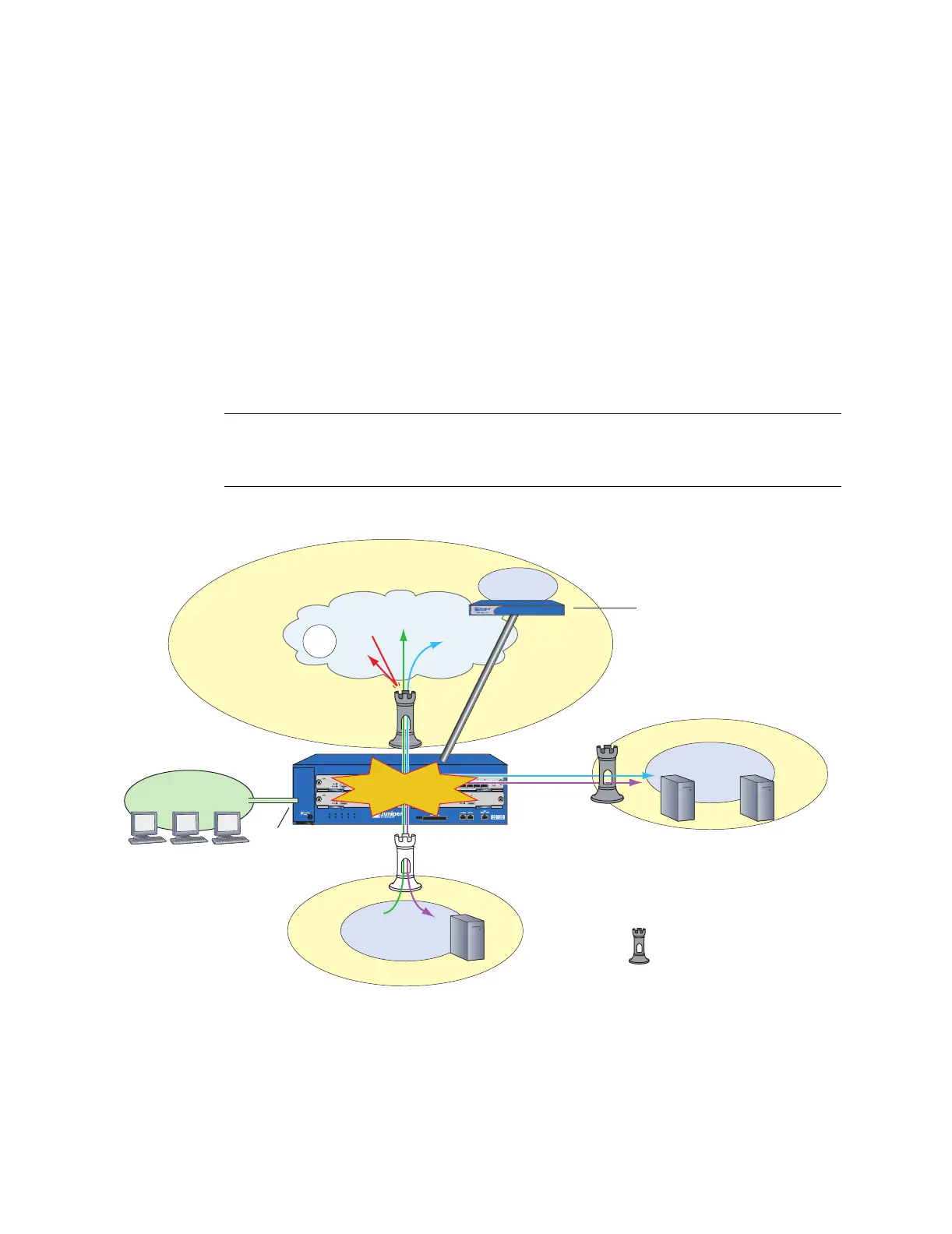
This guide describes how to install, configure, and service the ISG 2000. It presents
an example of a basic installation and configuration that secures resources in the
Trust and DMZ security zones, sets up a MGT zone for device administrators, and
defines a route-based VPN tunnel between the ISG 2000 and a remote peer (see
Figure 1). You can use this example as a reference as you perform similar tasks.
Figure 1: Example Configuration
This guide makes the following assumptions:
You are adding the ISG 2000 to an existing network.
You have an account with an Internet service provider (ISP) that has provided
you with two sets of IP addresses:
An outside address in the ISP’s domain (1.1.1.1 in our example)
A range of addresses in your domain (such as 1.2.2.1–1.2.2.6)
You have a registered domain name (such as “jnpr.net”).
NOTE:
Intrusion Detection and Prevention (IDP) requires the installation of at least one
security module, an advanced license key, and an IDP license key. To configure
IDP on the ISG 2000, you must use NetScreen-Security Manager.
HA
FLASH
PWR
FAN
ALARM
MOD1
TEMP
MOD2
STATUS
MOD3
ISG 2000
®
POWER STATUS
1 2 3 4
LINK/ACTIVITY
10/100
UNTRUSTED
DMZ
ISP
Untrust Zone
Internet
LAN
10.2.2.0/24
VPN
Tunnel
Policies
ethernet1/1
1.1.1.1/30
ethernet2/1
10.1.1.1/24
NAT mode
LAN
10.1.1.0/24
Trust Zone
MGT Zone
10.2.2.0/28
ethernet1/2
1.2.2.1/29
LAN
1.2.2.0/29
HTTP Server
www.jnpr.net
1.2.2.2:80
Mail Relay Server
smtp.jnpr.net
1.2.2.3:25
Remote Peer
ISP
Default GW: 1.1.1.2
DNS #1: 2.2.2.5
DNS #2: 2.2.2.6
MGT
10.2.2.1/28
Note: The rook icon represents
a security zone interface.

 Loading...
Loading...