Function library
Function blocks
3.5.56 Ramp function generator (RFG)
3−247
l
EDSVS9332P−EXT DE 2.0
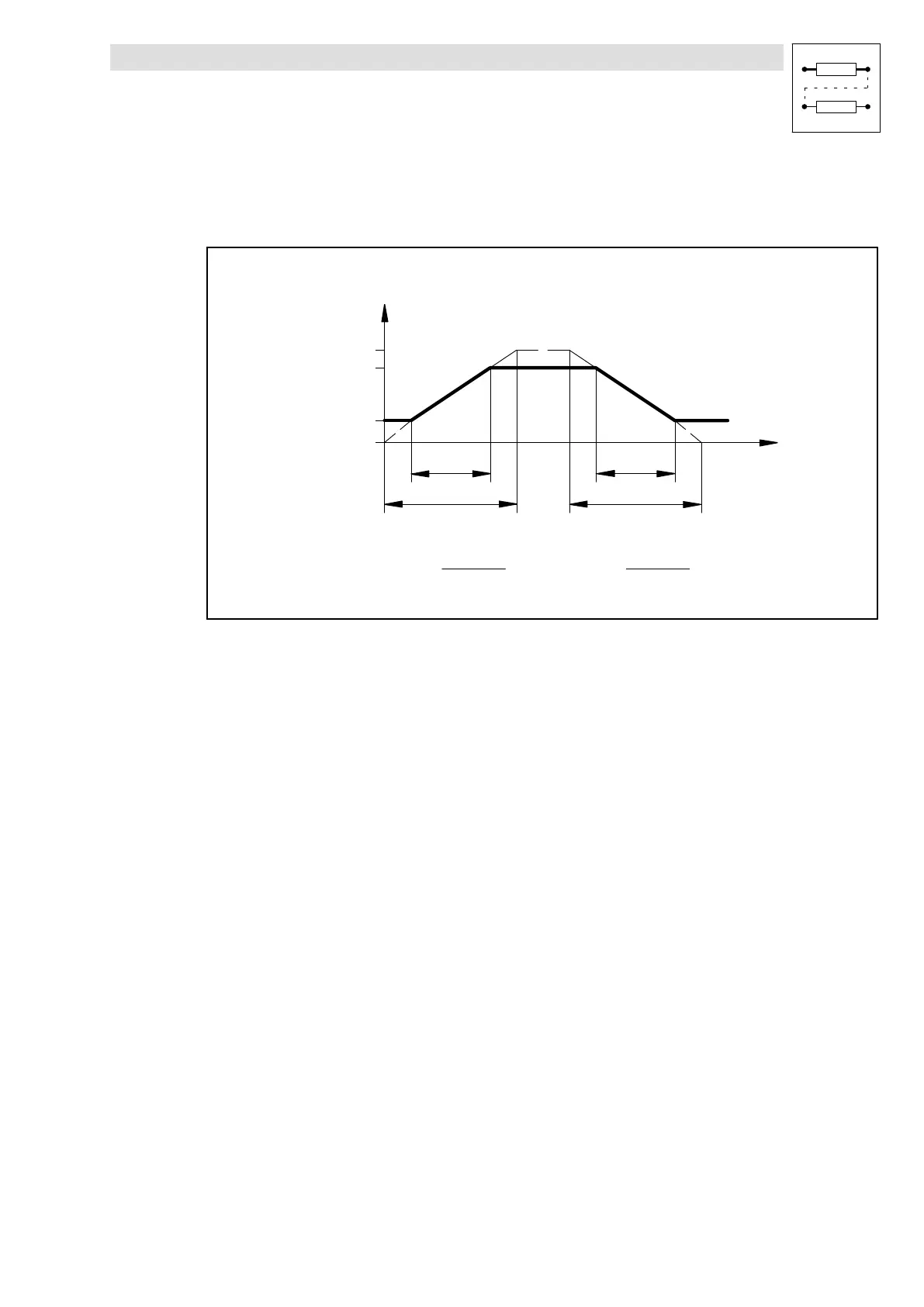
3.5.56.1 Calculation and setting of the times T
ir
and T
if
The acceleration time and deceleration time refer to a change of the output value from 0 to 100 %.
The times T
ir
and T
if
to be set can be calculated as follows:
100 %
0
t
ir
t
if
T
ir
T
if
t
RFG1−OUT
[%]
w1
w2
T
ir
+ t
ir
100%
w2 * w1
T
if
+ t
if
100%
w2 * w1
Fig. 3−195 Acceleration and deceleration times of the ramp function generator
t
ir
and t
if
are the times desired for the change between w
1
and w
2
.The values for T
ir
and T
if
can be
set under C0671 and C0672.
3.5.56.2 Loading of the ramp function generator
The ramp function generator can be initialised with defined values via the inputs RFG1−SET and
RFG1−LOAD.
l As long as the input RFG1−LOAD = HIGH, the input RFG1−SET is switched to the output.
l If the input RFG1−LOAD = LOW, the ramp function generator accelerates/decelerates from this
value to its input value within the set T
i
times.
 Loading...
Loading...











