Application examples
4.3 Example 3: Path control
4−10
l
EDSVS9332P−EXT DE 2.0
4.3 Example 3: Path control
Path control is an interesting solution for warehousing and complex transport tasks. These motion
sequences often require complicated and expensive control systems.Thanks to the different function
blocks, such as AND, OR, NOR elements, the servo position controller is able to perform a variety
of functions and features.
For a multi−axis application, the individual stations can be linked e.g. via the InterBus fieldbus. A
higher−level control is required in these cases.
X5
RFR
28
E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 A1 A2 A3
A4 59
L3L2L1
39
+UG -UG
93XX
WVU
HI LO
GND
X4
24V
=
+
-
S4,X
S4,X
S1,X
S2,X
X7
S2,X
S1,X
X
X5
28 E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 A1 A2 A3
A4 59
L3L2L1
39
+UG
-UG
93XX
WVU
HI LO
GND
X4
SB
RFR
24V
=
+
-
S4,Y
S4,Y
S1,Y
S2,Y
X7
S2,Y
S1,Y
Y
X5
28 E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 A1 A2 A3
A4 59
L3L2
L1
39
+UG -UG
93XX
WVU
HI LO
GND
X4
RFR
24V
=
+
-
S4,Z
S4,Z
S2,Z
S1,Z
X7
S2,Z
S1,Z
Z
X
Y
Z
SPS
39
39
3
9
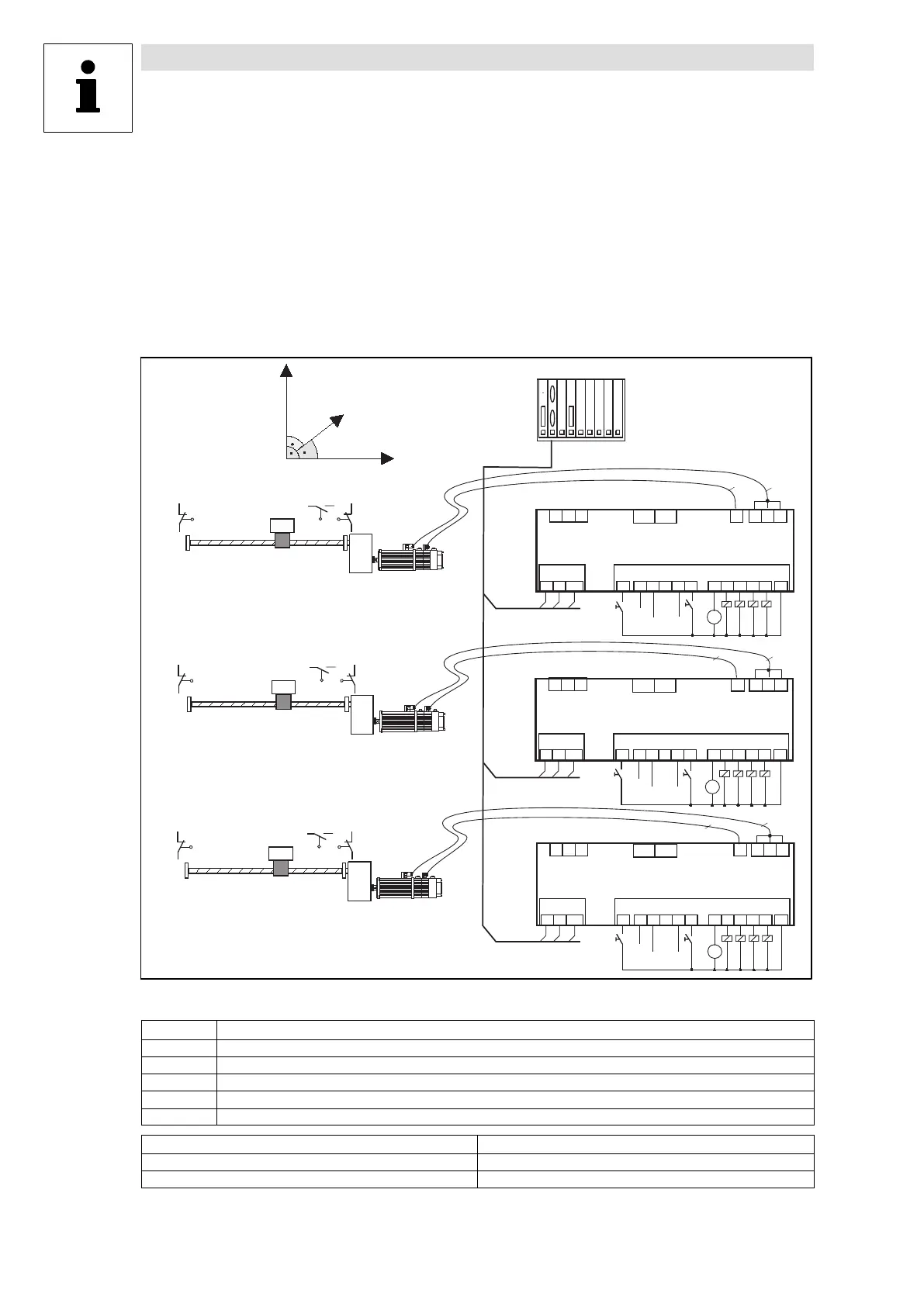
Fig. 4−4 Example of a multi−axis positioning
Input
Function
E1 Limit switch (S1X, S1Y, S1Z) negative traversing direction
E2 Limit switch (S2X, S2Y, S2Z) positive traversing direction
E3 Not assigned
E4 Reference switch (S4X, S4Y, S4Z)
E5 Changeover manual jog / program mode
Abbreviations Meaning
PLC Programmable logic controller
SB System bus (CAN)

 Loading...
Loading...