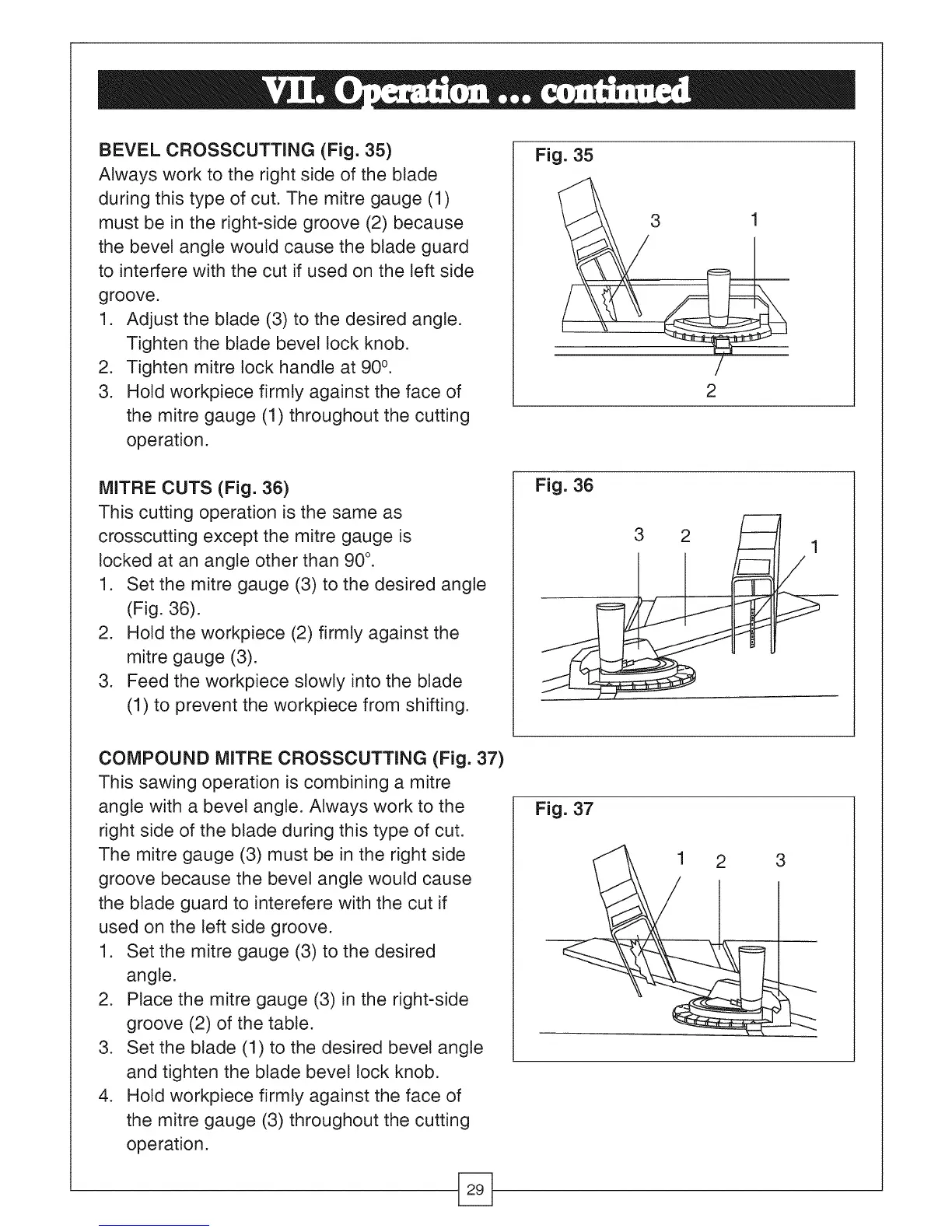
BEVEL CROSSCUTTING (Fig. 35)
Always work to the right side of the btade
during this type of cut. The mitre gauge (1)
must be in the right-side groove (2) because
the bevel angte would cause the blade guard
to interfere with the cut if used on the left side
groove.
1. Adjust the blade (3) to the desired angte.
Tighten the btade bevel lock knob.
2. Tighten mitre lock handle at 90 °.
3. Hold workpiece firmly against the face of
the mitre gauge (1) throughout the cutting
operation.
Fig. 35
3 1
2
MITRE CUTS (Fig. 36)
This cutting operation is the same as
crosscutting except the mitre gauge is
locked at an angle other than 90 °.
1. Set the mitre gauge (3) to the desired angle
(Fig. 36).
2. Hold the workpiece (2) firmly against the
mitre gauge (3).
3. Feed the workpiece slowly into the blade
(1) to prevent the workpiece from shifting.
Fig. 36
3 2
/
COMPOUND MITRE CROSSCUTTING (Fig. 37)
This sawing operation is combining a mitre
angle with a bevel angle. Always work to the
right side of the blade during this type of cut.
The mitre gauge (3) must be in the right side
groove because the bevel angle would cause
the blade guard to interefere with the cut if
used on the left side groove.
1. Set the mitre gauge (3) to the desired
angle.
2. Place the mitre gauge (3) in the right-side
groove (2) of the table.
3. Set the blade (1) to the desired bevel angle
and tighten the blade bevel lock knob.
4. Hold workpiece firmly against the face of
the mitre gauge (3) throughout the cutting
operation.
Fig. 37
1 2 3

 Loading...
Loading...