4-3SectionWiring
72
4-3 Wiring
4-3-1 Terminal Arrangement
The signal names corresponding to the connecting terminals are as shown in the
following diagram.
Voltage output 2 (+) B0
Voltage/current output 2 (–) B1
Current output 2 (+) B2
NC B3
NC B4
NC B5
Current input 2 B6
Voltage input 2 (+) B7
Voltage input 2 (–) B8
COM (analog 0 V) B9
NC B10
NC B11
NC B12
NC B13
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
Voltage output 1 (+)
Voltage/current output 1 (–)
Current output 1 (+)
NC
NC
NC
Current input 1
Voltage input 1 (+)
Voltage input 1 (–)
COM (analog 0 V)
NC
NC
NC
NC
Note 1. The analog I/O numbers that can be used are set in the Data Memory (DM).
2. The I/O signal ranges for individual inputs and outputs are set in the Data
Memory (DM). They can be set in units of analog I/O numbers.
3. The COM terminal (A9, B9) is connected to the 0-V analog circuit in the Unit.
Connecting shielded input lines can improve noise resistance.
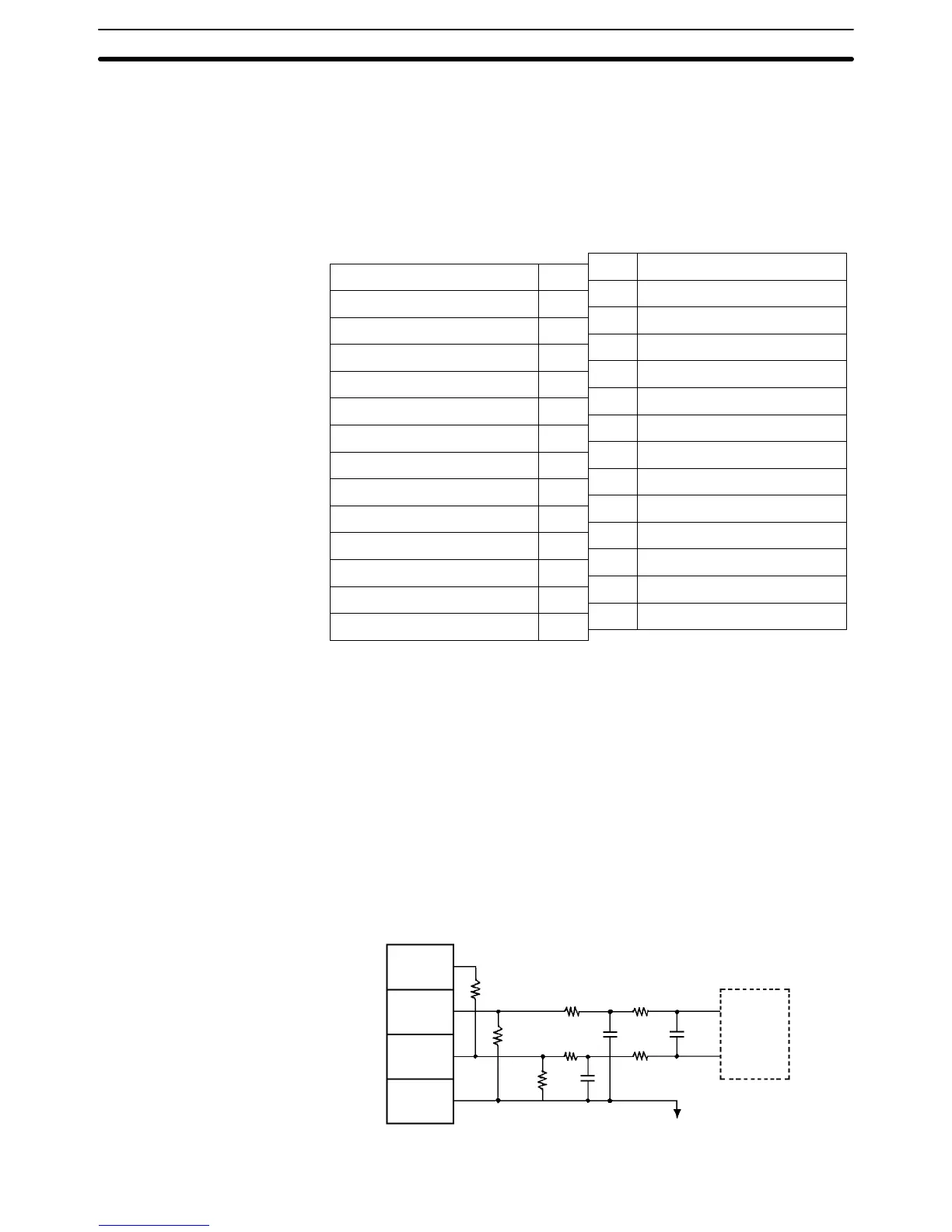
4-3-2 Internal Circuitry
The following diagrams show the internal circuitry of the analog I/O section.
Input Circuitry
250 Ω
1 MΩ
15 kΩ 15 kΩ
15 kΩ 15 kΩ
AG (common to all inputs)
Current
input (+)
Voltage
input (+)
Voltage
input (–)
COM
(analog
0 V)
Input circuit
and
conversion
circuit
1 MΩ

 Loading...
Loading...











