10
+F/B compensation +Learning compensation +Low speed
compensation) x battery voltage compensation x Water temperature compensation
Described below is how control is done at each time.
(1) When the engine is at a stop
The ISC solenoid valve remains OFF or completely closed.
COOLANT TEMPERATURE
COMPENSATION
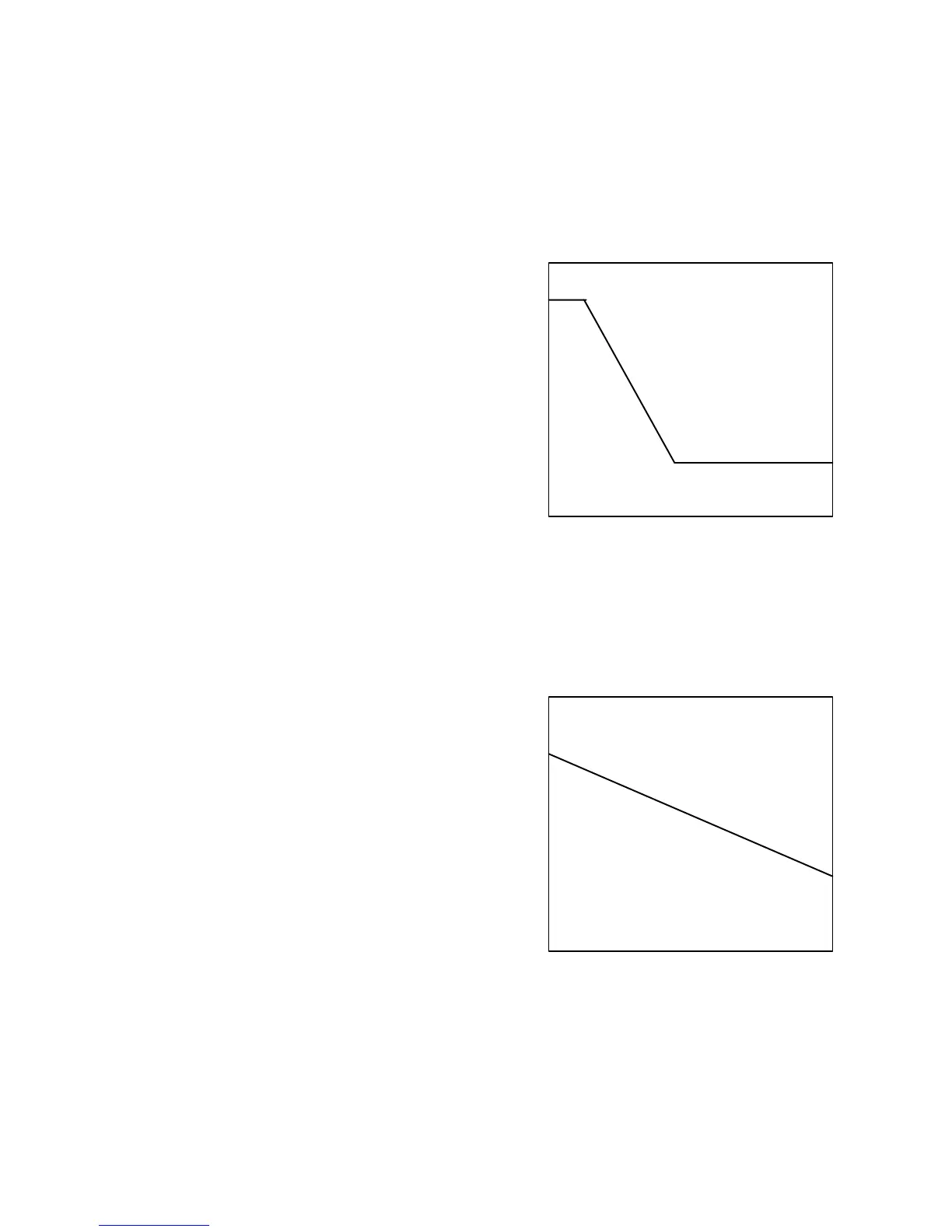
(2) When the engine is started (correction at engine
start)
Once the engine is started, the ISC solenoid valve opens
widely to increase the bypassing air for quicker
warm–up. At this time, the ISC duty ratio initially set
varies depending on the temperature of the cooling
water. The lower the temperature is, the higher value it is
set to.
(3) During the engine is warmed up
(Compensation at engine start)
(Basic value)
The ISC duty value set at the engine start as described in
(2) attenuates by a constant value to the basic duty value
which is determined only by the cooling water tempera-
ture.
(4) When a load is applied to the engine
When the D range signal (the select lever position, applicable to A/T vehicles only) turns ON, the ISC duty ratio is
increased by the amount of value stored in the ECM memory to prevent the idle speed from varying.
COOLANT TEMPERATURE
ENGINE SPEED (RPM)
(5) Feedback ( F/B) compensation
The ECM stores target speeds for different levels of the
cooling water temperature in memory. During idling,
the duty ratio is varied for compensation so that the
engine idle speed remains constantly at this target
speed (target idle speed). For example, when the idle
speed drops lower than the target speed, the duty ratio
is increased by increasing the feedback compensation
value. Then the amount of the bypassing air increases
and the engine idle speed increases. The target speed
varies depending on the shift position (for the A/T
vehicles).
 Loading...
Loading...