4
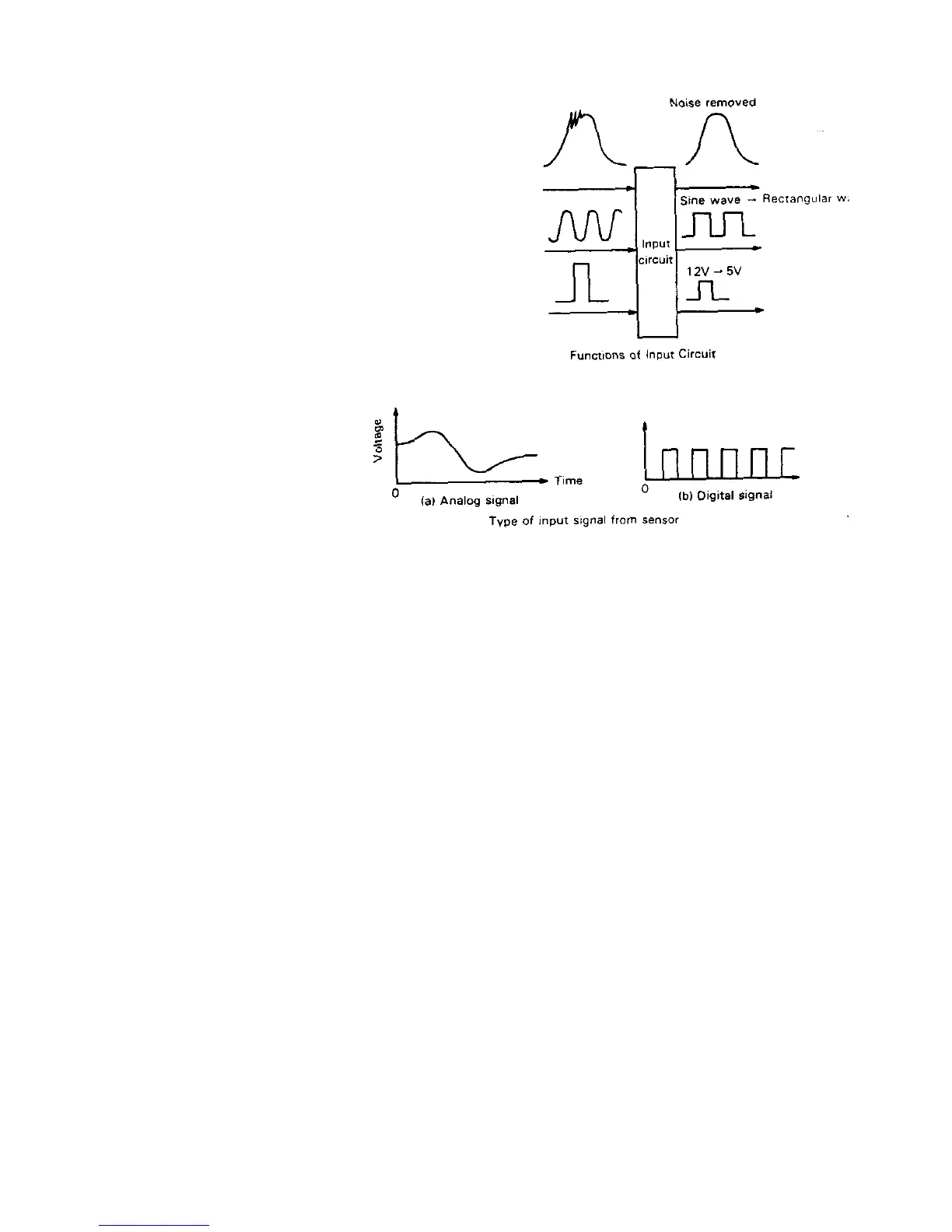
Input circuit
When a signal from each sensor enters ECM, it first passes
through the input circuit, where any noise on each signal is
removed and a sine wave signal such as a crank angle signal is
converted to a pulse signal (rectanglar wave). Another function of
the input circuit is to convert the voltage level of the digital signal
to such voltage level that can be processed by the microcom-
puter which operates at a 5V voltage.
A/D Converter
The analog signal received by the ECM
must be converted into a digital signal
for microcomputer processing and this
conversion is done by the A/D con-
verter.
Microcomputer
The microcomputer accepts signals from the sensors as necessary, processes them by using programs and data written
in it and then sends the results to the output circuit as fuel injection signals, ignition signals, etc. Here each of its compo-
nents is described.
(1) CPU
CPU is the brain of the microcomputer. It processes the input data by using the processing program stored in the ROM.
In the CPU, simultaneous processing of a large amount of data is not expected, for the data is processed one by one
within each unit time. However, as the processing speed is as high as to handle over one million operations per second, it
can process a large amount of data very quickly.
(2) Memory (ROM, RAM)
The ROM (Read–Only Memory) is where programs and data necessary for control are stored. Once stored in it, they are
retained as they are, even if power has been turned OFF and no change can be made to them.
The RAM (Random Access Memory) is where input data and processed results are temporarily stored. They will be
erased if power is turned OFF.
(3) Input/output interface
The input/output interface controls receiving and sending signals according to the command from CPU. As CPU cannot
process a large amount of data simultaneously as described above, inputting/ outputing of signals is executed according
to the programmed sequence.
Output circuit
As the output signal from the microcomputer is a digital signal, it cannot operate the actuator. The output circuit has a
function to operate the actuator, based on the output signal from the microcomputor.
 Loading...
Loading...