Publication 1746-UM004A-US-P
Programming Overview 4-19
The SLC processor and module operate independently of each other. The
following CALLs allow the SLC processor and module to interrupt each other.
SLC Fault Codes
Fault codes are reported in word 6 of the SLC processor status file. The format of
the status word and applicable error codes are shown below:
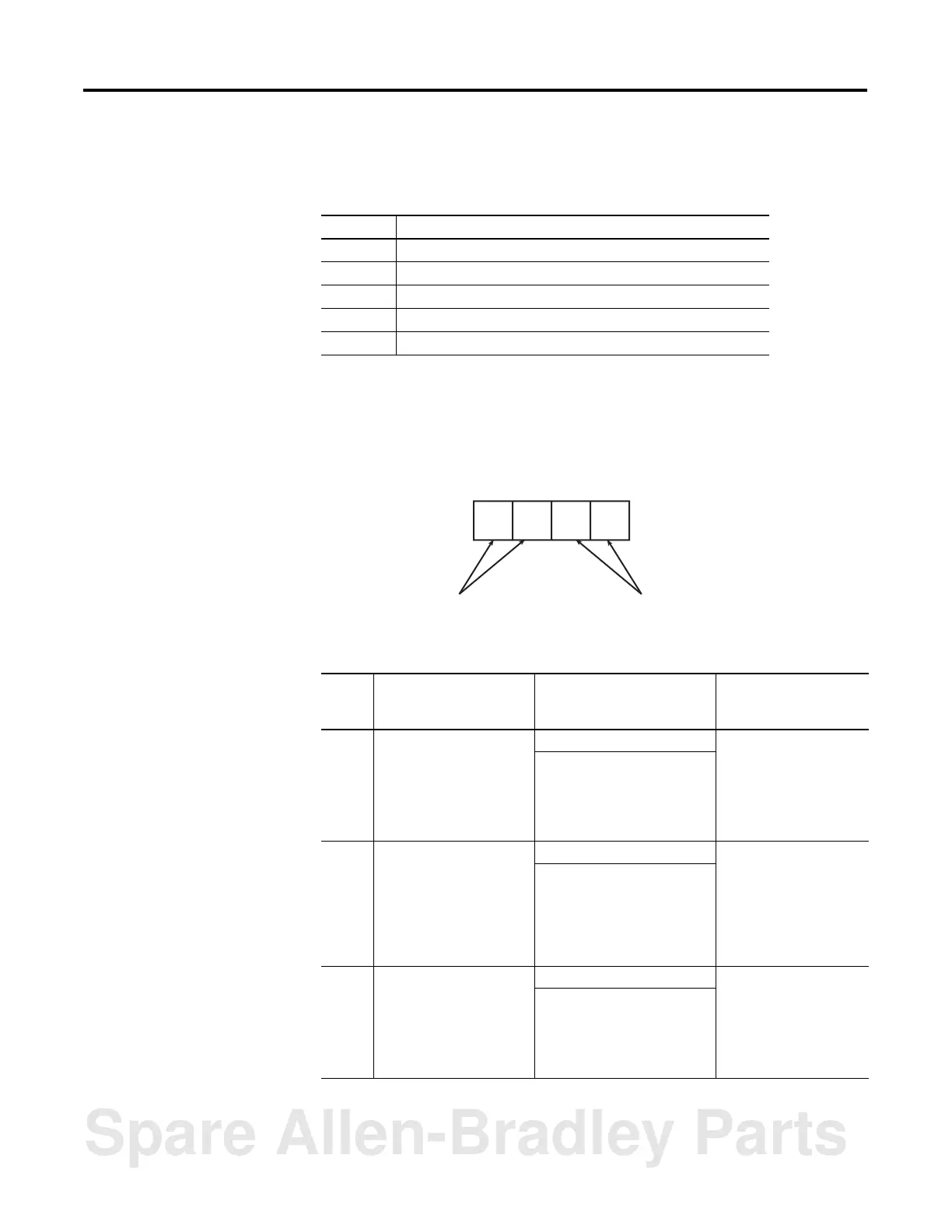
Figure 4.7 SLC Fault Code Placement
Table 4.17 Interrupt CALLs
CALL Purpose
CALL 16 Enables interrupt capability when a DF1 packet is received.
CALL 17 Disables the DF1 packet interrupt capability.
CALL 20 Enables SLC processor interrupt capability.
CALL 21 Disables SLC processor interrupt capability.
CALL 26 Generates an interrupt to the SLC processor.
4-digit Hex Number
Slot Number Fault Code
Table 4.18 SLC Fault Codes
SLC
Fault
Code
Description Possible Cause Recommended Action
57H Module has not
responded to a lock
shared memory command
within the required time
limit.
Module hardware problem. Cycle power to the
module to re-initialize
parameters and re-run
the program.
Module internal stacks,
pointers, etc. (if XBY
instructions are used) are
corrupted by the user
program.
58H Module generated a
generic fault.
Module hardware problem. Verify that module is
configured correctly
(correct I/O and M files).
Cycle power to the
module to re-initialize
parameters and re-run
the program.
Module internal stacks,
pointers, etc. (if XBY
instructions are used) are
corrupted by the user
program.
59H Module did not complete
a command within the
required time limit.
Module hardware problem. Cycle power to the
module to re-initialize
parameters and re-run
the program.
Module internal stacks,
pointers, etc. (if XBY
instructions are used) are
corrupted by the user
program.
Spare Allen-Bradley Parts

 Loading...
Loading...











