Publication 1747-UM011G-EN-P - June 2008
Selecting Your Hardware Components 33
• RS-232C (EIA-232) electrical specifications.
• modem support.
• built-in isolation.
Protocol Options
EtherNet TCP/IP Protocol - Standard Ethernet, utilizing the TCP/IP
protocol, is used as the backbone network in many office and
industrial buildings. Ethernet is a local area network that provides
communication between various devices at 10/100 Mbps. This
network provides the same capabilities as DH+ or DH-485 networks,
plus:
• SNMP support for Ethernet network management.
• optional dynamic configuration of IP addresses by using a
BOOTP/DHCP utility.
• SLC 5/05 Ethernet data rate up to 40 times faster than SLC 5/04
DH+ messaging.
• ability to message entire SLC 5/05 data files.
• much greater number of nodes on a single network possible
compared to DH-485 (32) and DH+ (64).
Data Highway Plus (DH+) Protocol - The Data Highway Plus protocol
is used by the PLC-5 family of processors and the SLC 5/04 processor.
This protocol is similar to DH-485, except that it can support up to 64
devices (nodes) and runs at faster communication (baud) rates.
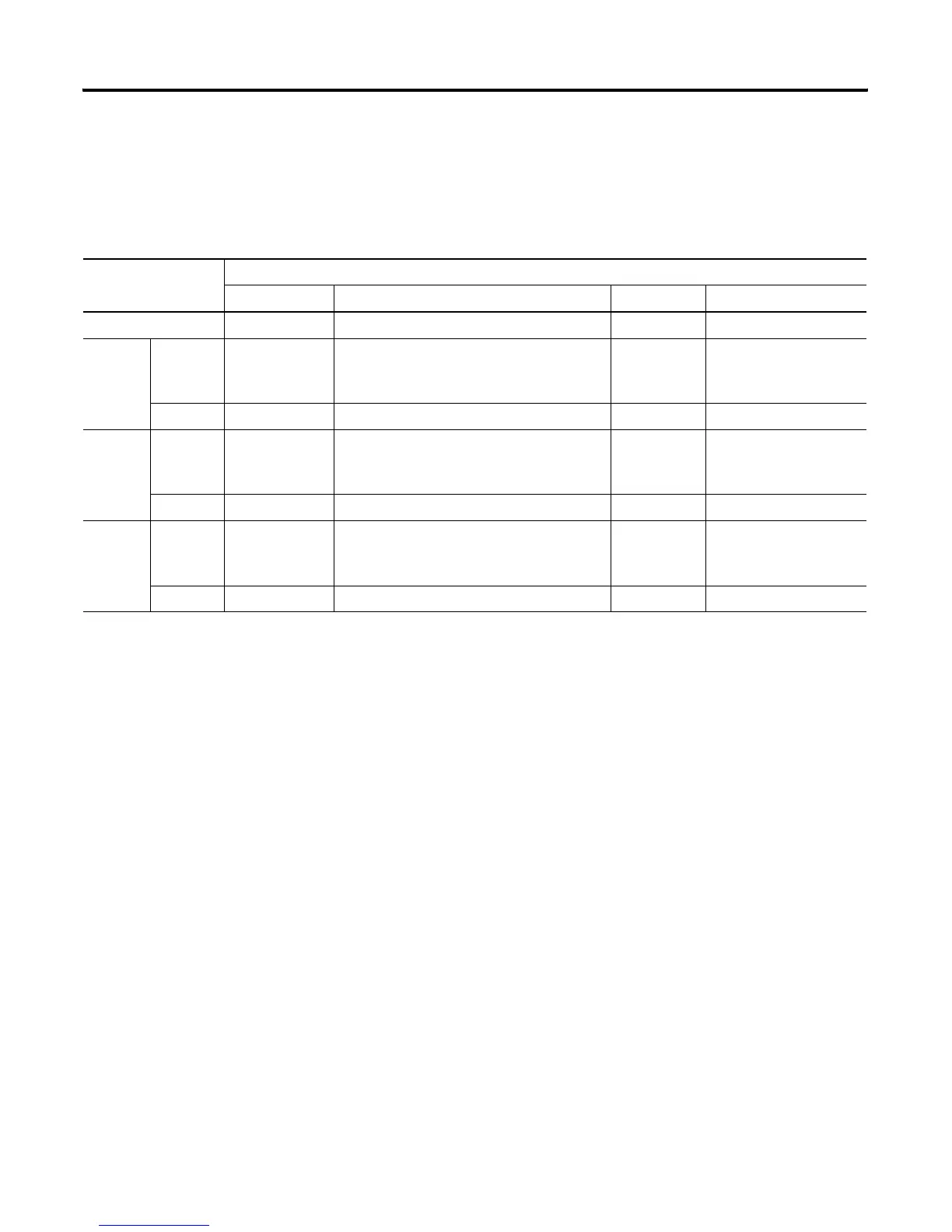
Processor Channel Connections
Processor Physical Communication Channel
DH-485 RS-232 DH+ Ethernet
SLC 5/01 and SLC 5/02 DH-485 protocol — — —
SLC 5/03 channel 0
—
DH-485
(1)
, DF1 full-duplex, DF1 half-duplex
master/slave, ASCII, DF1 radio modem, and
Modbus RTU Master protocols
——
channel 1 DH-485 protocol — — —
SLC 5/04 channel 0
—
DH-485
(1)
, DF1 full-duplex, DF1 half-duplex
master/slave, ASCII, DF1 radio modem, and
Modbus RTU Master protocols
——
channel 1 — — DH+ protocol —
SLC 5/05 channel 0
—
DH-485
(1)
, DF1 full-duplex, DF1 half-duplex
master/slave, ASCII, DF1 radio modem, and
Modbus RTU Master protocols
——
channel 1 — — — EtherNet TCP/IP protocol
(1)
An 1761-NET-AIC interface is required when connecting to a DH-485 network.

 Loading...
Loading...