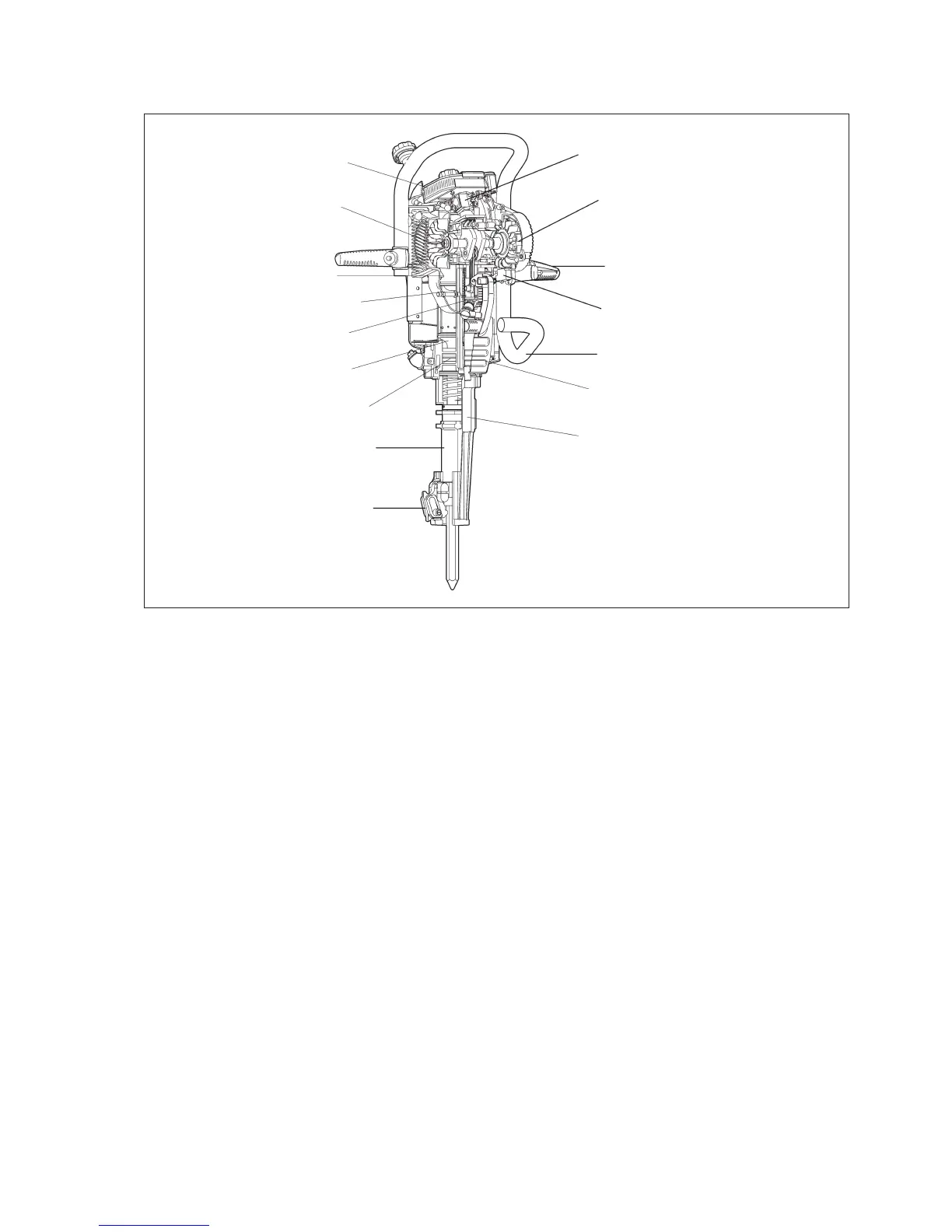
Design and function
Engine
The machine is powered by a single-cylinder,
air-cooled two-stroke engine. The engine is
equipped with a diaphragm carburettor, which is con-
trolled by changes in pressure inside the crankcase.
The carburettor feeds the fuel mixture into the cylin-
der via a diaphragm valve. The engine is automati-
cally lubricated by the oil in the fuel mixture.
The speed of the engine can be varied by the hand
throttle, which is connected to the carburettor butter-
fly valve.
The maximum speed of the engine is restricted by an
electronic speed restrictor, which is incorporated in
the breakerless ignition system.
The power transmission between the engine and
hammer mechanism is via a gear assembly.
Hammer mechanism
Before starting the engine, the hammer piston rests
on the tool shank. When the engine is started, the
drive piston commences to move up and down in the
hammer cylinder.
When the handles are pushed down, the tool raises
the hammer piston in the hammer cylinder and the
hammer mechanism is activated.
When the machine is lifted, the tool drops down onto
the tool latch. The hammer piston moves into its
lower position, where it stops, and the hammer
mechanism is disengaged.
This operational system also means that the ma-
chine can stand on a tool without engaging the ham-
mer piston.
7
Air Filter
Cooling Fan
Drive piston
Decompression valve
Engine cylinder
Hammer piston
Hammer piston guide
Tool chuck
Tool latch
Carburettor
Starter mechanism
Throttle
Electronic unit
Fuel tank
Muffler
Tool holder

 Loading...
Loading...











