6-22
Cisco ASA Series Firewall CLI Configuration Guide
Chapter 6 ASA and Cisco TrustSec
Guidelines for Cisco TrustSec
Layer 2 Security Group Tagging Imposition
Cisco TrustSec identifies and authenticates each network user and resource and assigns a 16-bit number
called a Security Group Tag (SGT). This identifier is in turn propagated between network hops, which
allows any intermediary devices such as ASAs, switches, and routers to enforce polices based on this
identity tag.
SGT plus Ethernet Tagging, also called Layer 2 SGT Imposition, enables the ASA to send and receive
security group tags on Ethernet interfaces using Cisco proprietary Ethernet framing (EtherType 0x8909),
which allows the insertion of source security group tags into plain-text Ethernet frames. The ASA inserts
security group tags on the outgoing packet and processes security group tags on the incoming packet,
based on a manual per-interface configuration. This feature allows inline hop-by-hop propagation of
endpoint identity across network devices and provides seamless Layer 2 SGT Imposition between each
hop.
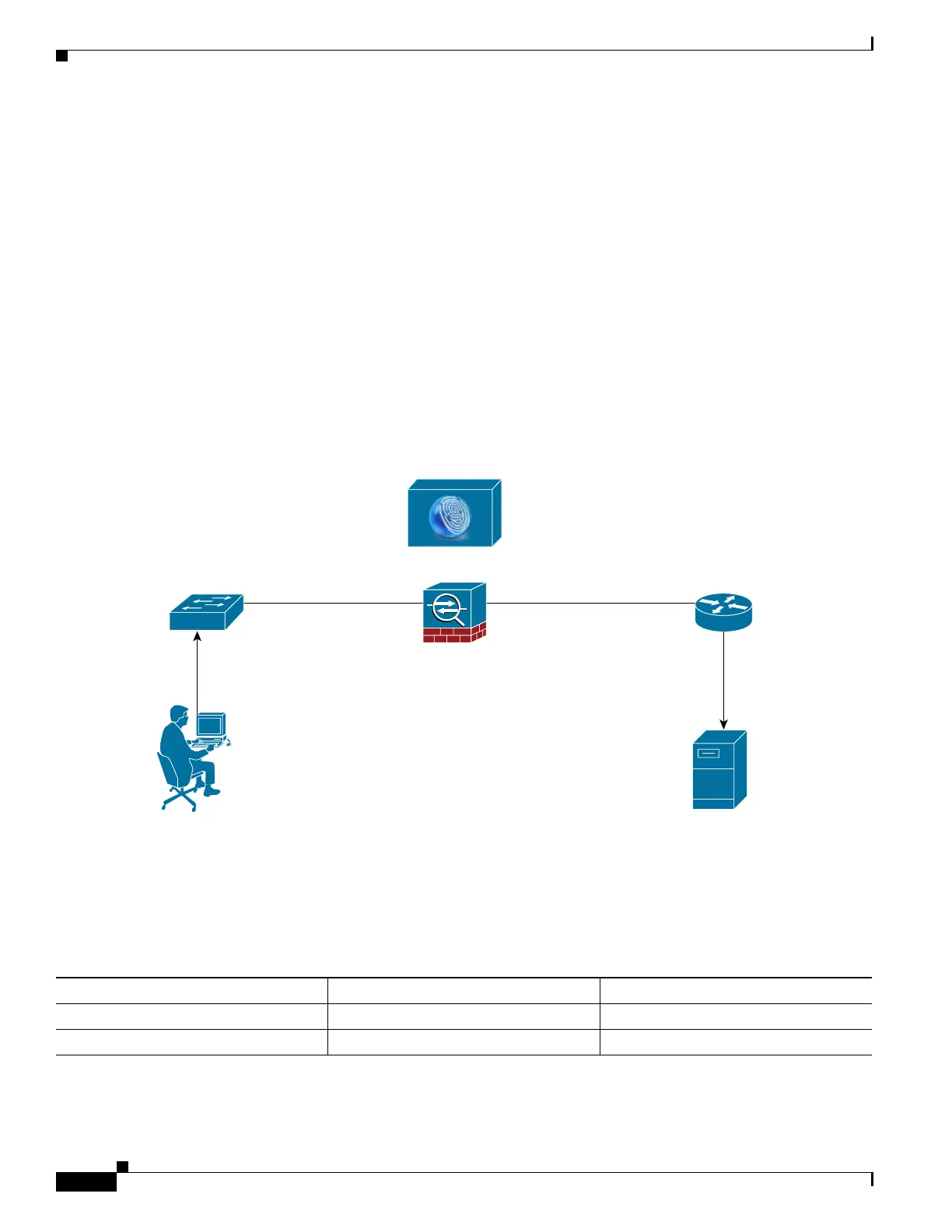
The following figure shows a typical example of Layer 2 SGT Imposition.
Figure 6-3 Layer 2 SGT Imposition
Usage Scenarios
The following table describes the expected behavior for ingress traffic when configuring this feature.
User 1
Untagged
Switch Router
ISE
ASA
Server
Inline Tagged
SGT 100
SGT 100 = User 1
ACL: Allow User 1
to access server
Inline Tagged
SGT 100
Untagged
372270
Table 6-3 Ingress Traffic
Interface Configuration Tagged Packet Received Untagged Packet Received
No command is issued. Packet is dropped. SGT value is from the IP-SGT Manager.
The cts manual command is issued. SGT value is from the IP-SGT Manager. SGT value is from the IP-SGT Manager.
 Loading...
Loading...















