4-3
Cisco ASA Series Firewall CLI Configuration Guide
Chapter 4 Access Rules
Controlling Network Access
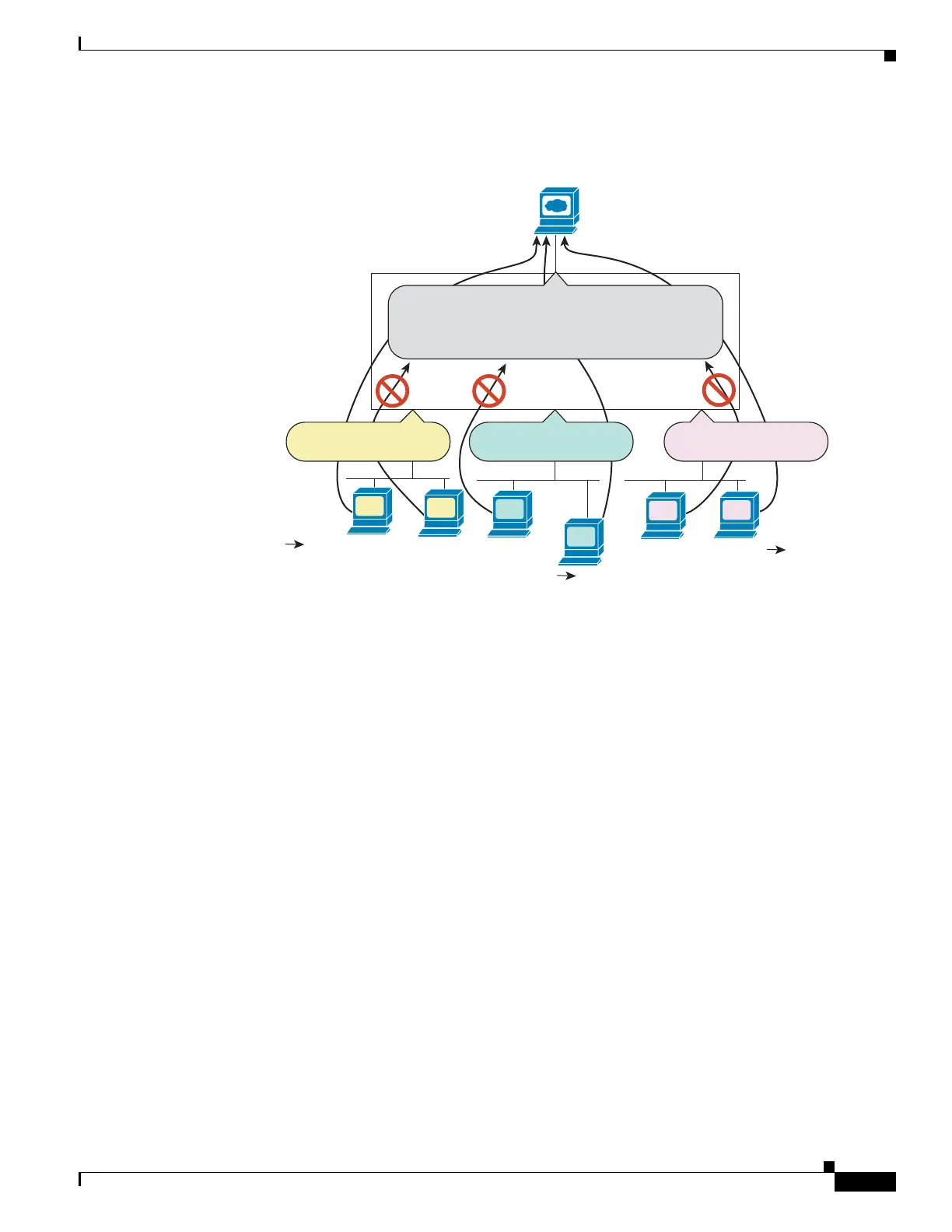
Figure 4-1 Outbound ACL
See the following commands for this example:
hostname(config)# access-list OUTSIDE extended permit tcp host 10.1.1.14
host 209.165.200.225 eq www
hostname(config)# access-list OUTSIDE extended permit tcp host 10.1.2.67
host 209.165.200.225 eq www
hostname(config)# access-list OUTSIDE extended permit tcp host 10.1.3.34
host 209.165.200.225 eq www
hostname(config)# access-group OUTSIDE out interface outside
Rule Order
The order of rules is important. When the ASA decides whether to forward or drop a packet, the ASA
tests the packet against each rule in the order in which the rules are listed in the applied ACL. After a
match is found, no more rules are checked. For example, if you create an access rule at the beginning
that explicitly permits all traffic for an interface, no further rules are ever checked.
Implicit Permits
For routed mode, the following types of traffic are allowed through by default:
• Unicast IPv4 and IPv6 traffic from a higher security interface to a lower security interface.
Web Server:
209.165.200.225
Inside
HR
Eng
Outside
Static NAT
209.165.201.410.1.1.14
Static NAT
209.165.201.610.1.2.67
Static NAT
209.165.201.810.1.3.34
ACL Outbound
Permit HTTP from 10.1.1.14, 10.1.2.67,
and 10.1.3.34 to 209.165.200.225
Deny all others
ACL Inbound
Permit from any to any
ACL Inbound
Permit from any to any
ACL Inbound
Permit from any to any
ASA
333823

 Loading...
Loading...



