3-10
Chapter 3
KNOW YOUR VEHICLE
Children should be restrained at all times and tted with a child restraint appropriate to
their size when travelling in a vehicle. The following outlines guidelines about selecting
the appropriate restraint.
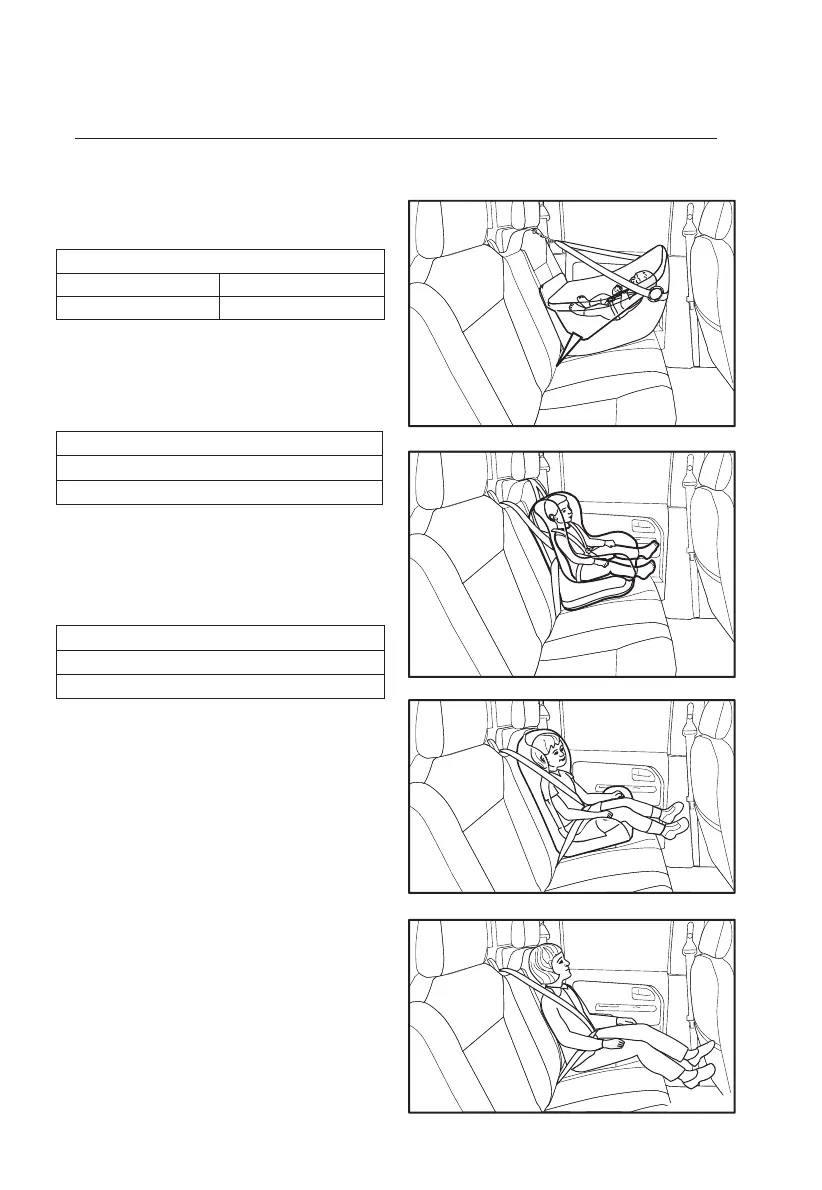
Infants
Designed so that in the event of a collision,
impact forces will be evenly spread over
the baby’s back, with minimal jarring to
the vulnerable head and neck area.
Young children
For use when the child is able to sit and
easily hold his or her head upright. It is
also possible to purchase convertible
seats which can be used as a rearward
facing infant restraint or converted to a
forward facing child seat.
When children outgrow a typical forward-
facing child seat but they are still too small
for lap/sash seat belts. A booster seat raises
the child so the knees bend comfortably,
the lap/sash seat belt is correctly positioned
and the child can see out the window. A
rigid booster seat with a back, side wings
and sash guide gives the best protection. In
assessing the range of children who would
benet from booster seats, height is a better
indicator than age or weight.
Older children
A child should use a normal lap/sash seat
belt only when:
• he/she can sit against the back of the
rear seat with knees bent comfortably
at the edge of the seat,
• lap belt rests low and snug across the
hips – not across the stomach,
• sash belt is centred on shoulder and
chest,
• he/she is able to stay seated like this
for the entire trip.
*
According to AS/NZ 1754:2004
Rearward facing infant capsule
Forward facing child seat
Booster seat with lap/sash seat belt
Adult lap/sash seat belt
WHICH TYPE OF CHILD RESTRAINT FOR YOUR CHILD?
Rearward facing infant capsule
Weight Height
Up to 9 kg* Up to 70 cm*
Forward facing child seat
Weight
8 to 18 kg*
Booster seat with lap/sash seat belt
Weight
14 to 26 kg*
CAPTIVA BOOK.indb 10 30/05/2007 12:49:19 PM

 Loading...
Loading...











