122
Configuring FC tracert
Overview
In an FC SAN, use the fctracert command to obtain bidirectional routing information between source
and destination, and check the network connectivity.
You can use this feature to identify failed nodes and test network connectivity.
FC tracert includes the following processes:
• Uplink process—Beginning from the source, each switch along the path sends the Switch Trace
Route (STR) packet to its next hop until the STR packet reaches the destination switch. (If the
destination of FC tracert is a node, the destination switch refers to the FCF switch directly connected
to the node.) Each switch adds its uplink path information (including its WWN and domain ID) to
the STR packet. After the STR packet reaches the destination switch, the downlink process starts.
• Downlink process—Beginning from the destination switch, each switch along the path switch sends
the STR packet to its next hop until the STR packet reaches the source switch. Each switch adds its
downlink path information (with the same content as the uplink path information) to the STR packet.
When the source switch receives the STR packet, the FC tracert process ends. The source outputs
information (in the STR packet) about all uplink and downlink switches along the path.
If an FC switch fails to forward the STR packet, the switch performs the following operations:
• Sets an error reason in the packet.
• Sends the packet (containing information about switches the packet has passed through) directly to
the source switch.
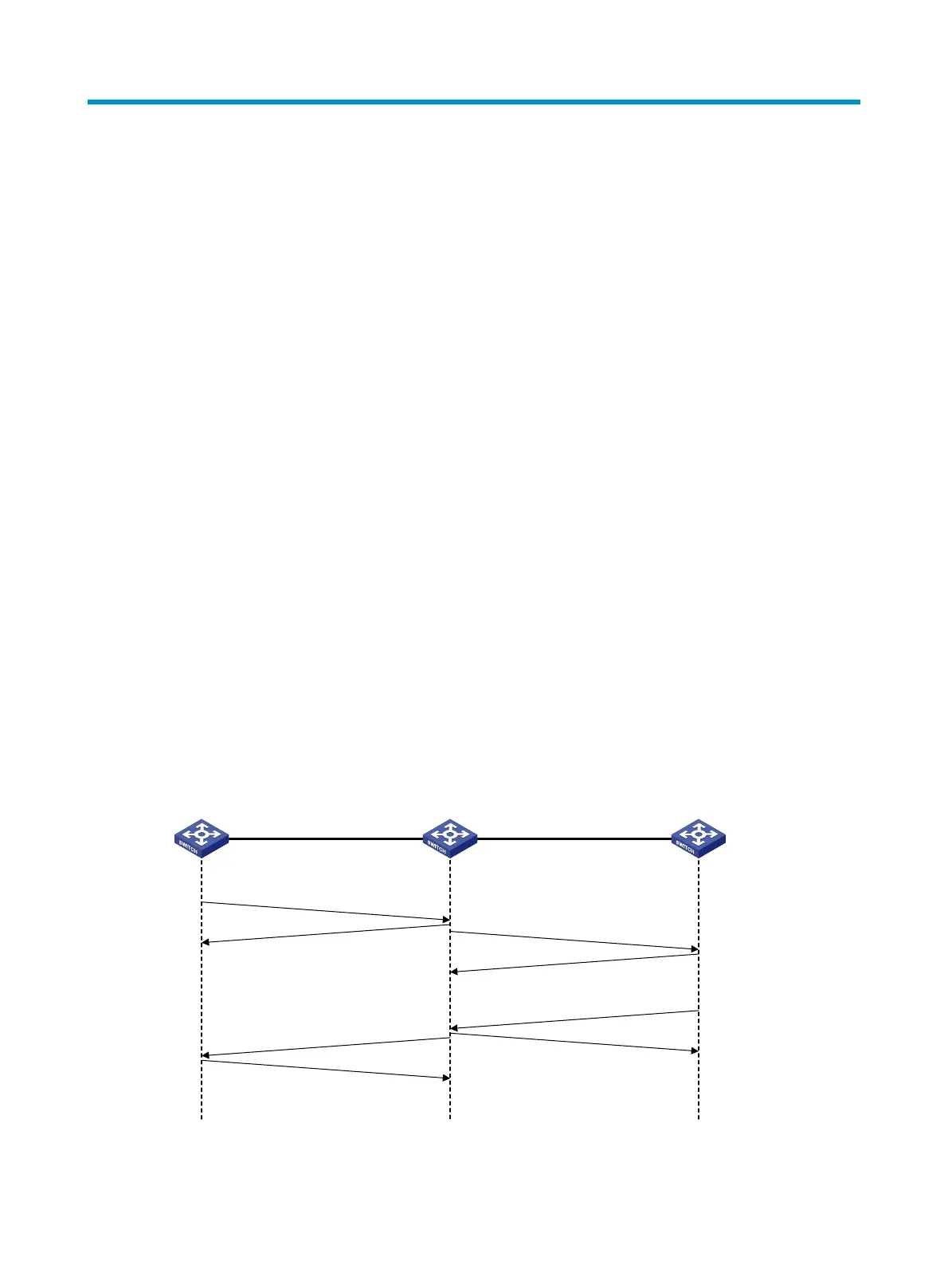
Figure 33 sh
ows the FC tracert process.
Figure 33 FC tracert flowchart
The following describes the process of an FC tracert operation from Switch A to Switch C.
Source switch
Switch A
Intermediate switch
Switch B
Destination switch
Switch C
STR Request
STR ACC
STR Request
STR ACC
STR Request
STR ACC
STR Request
STR ACC
 Loading...
Loading...











