Alarm group configuration example
Network requirements
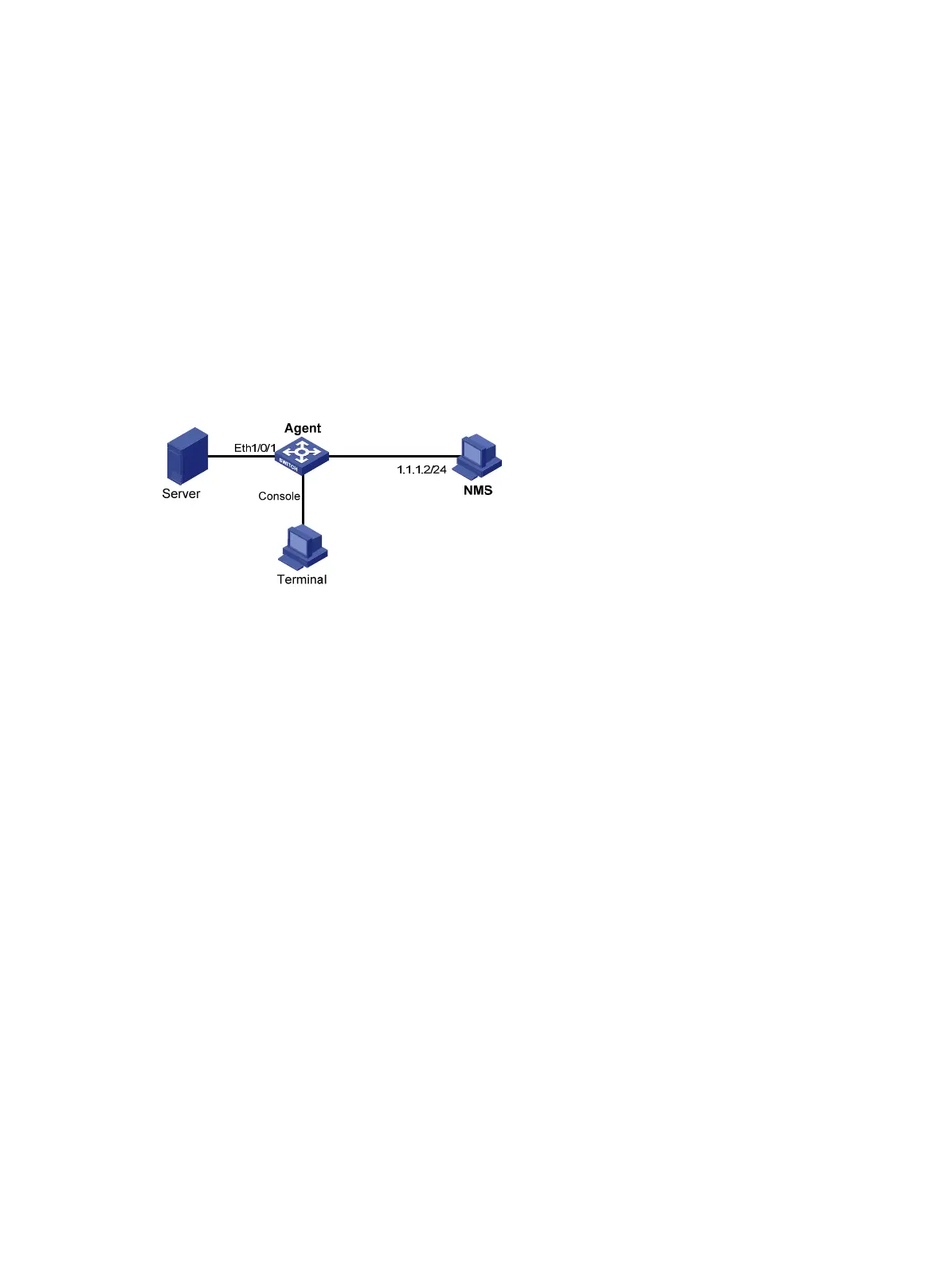
As shown in Figure 40, Agent is connected to a console terminal through its console port and to an NMS
across Ethernet.
Do the following:
• Connect Ethernet 1/0/1 to the FTP server. Gather statistics on traffic of the server on Ethernet
1/0/1 with the sampling interval being five seconds. When traffic is above or below the thresholds,
Agent sends the corresponding traps to the NMS.
• Execute the display rmon statistics command on Agent to display the statistics, and query the
statistics on the NMS.
Figure 40 Network diagram for RMON
Configuration procedure
# Configure the SNMP agent, and make sure that the SNMP settings are the same as on the NMS. This
example sets the SNMP version to SNMPv1, read community to public, write community to private, and
the trap destination to 1.1.1.2, the IP address of the NMS.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] snmp-agent
[Sysname] snmp-agent community read public
[Sysname] snmp-agent community write private
[Sysname] snmp-agent sys-info version v1
[Sysname] snmp-agent trap enable
[Sysname] snmp-agent target-host trap address udp-domain 1.1.1.2 params securityname
public
# Configure RMON to gather statistics for interface Ethernet 1/0/1.
[Sysname] interface Ethernet 1/0/1
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/1] rmon statistics 1 owner user1
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/1] quit
# Create an RMON alarm entry so when the delta sampling value of node 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.4.1 exceeds
100 or is lower than 50, event 1 is triggered to send traps.
[Sysname] rmon event 1 trap public owner user1
[Sysname] rmon alarm 1 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.4.1 5 delta rising-threshold 100 1
falling-threshold 50 1
# Display the RMON alarm entry configuration.
<Sysname> display rmon alarm 1
AlarmEntry 1 owned by null is Valid.
103
 Loading...
Loading...