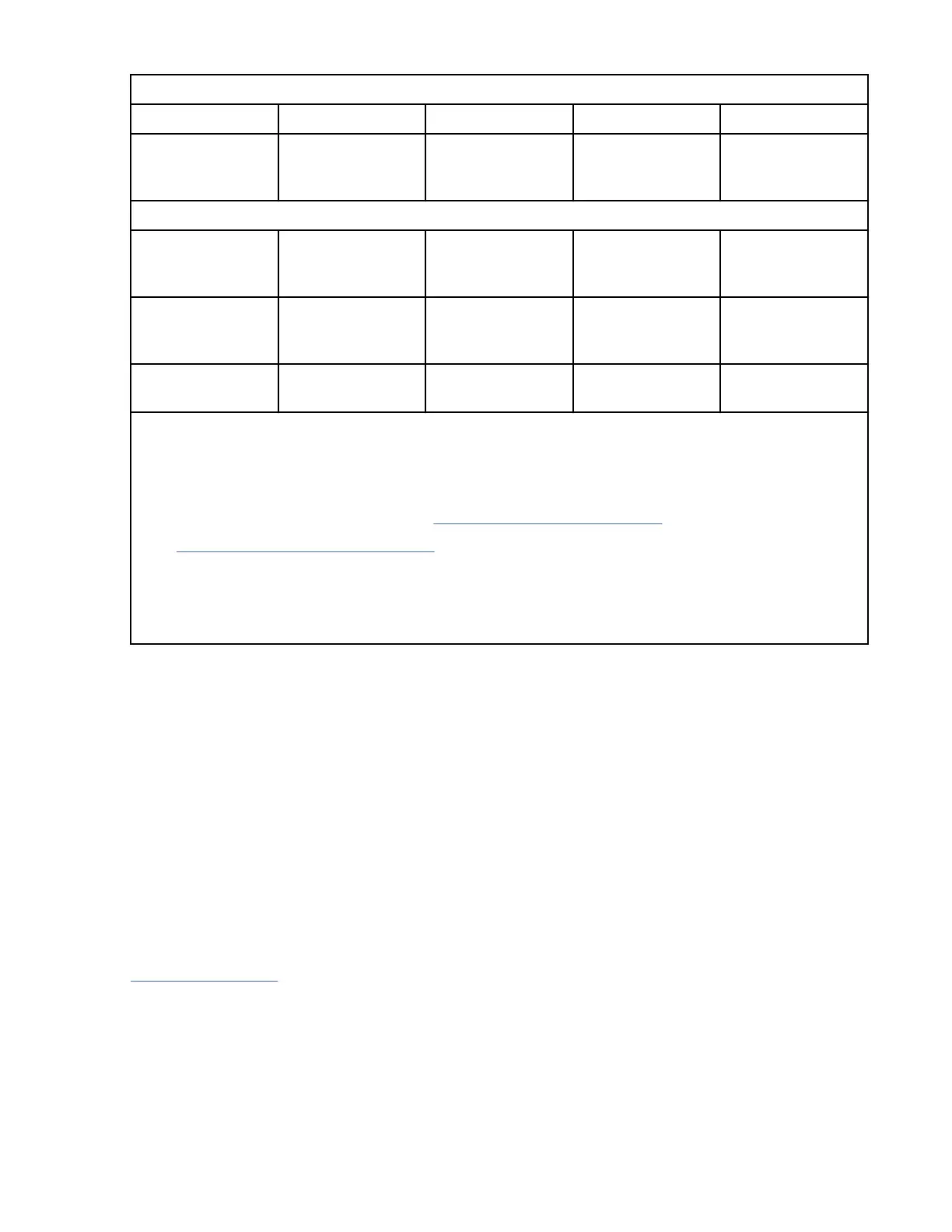
Table 7. Drive information and performance specication for half-height drives (continued)
Generation LTO 9 LTO 8 LTO 7 LTO 6
Average rewind
time (REWIND
command)
62 seconds 59 seconds 60 seconds NA
Average rewind time (part of UNLOAD command, dependent on mount activity)
3
Less than 5 Gb
of contiguous data
transferred
62 seconds 59 seconds 60 seconds NA
5 Gb to 50 Gb
of contiguous data
transferred
124 seconds 59 seconds 60 seconds NA
All other types of
mount activity
186 seconds 59 seconds 60 seconds NA
1
By using the buil
t-in data-compression capability of the tape drive, greater data rates than the native
data transfer rate are achieved. However, the actual throughput is a function of many components, such
as the host system processor, disk data rate, block size, data compression ratio, SAS bus capabilities,
and system or application software.
2
Cartridge initialization time can vary. See “Media optimization” on page 17
for more information.
3
See “Archive mode unthread” on page 18 for more information.
Remember:
• All sustained data rates depend on the capabilities of the interconnect.
• Drive performance varies with media generation and drive interface (SAS/FC).
Control path drives
A control path is a logical path to the library.
A control path is the path for SCSI Medium Changer commands that are sent by a server to control a
specic logical library. The library has no direct SCSI connection to a host server. When a software host
server communicates with the library, it sends the communication by way of a tape drive. The tape drive is
designated as a control path drive.
Mixed drives
All supported generations of LTO tape drives and cartridges can be in the same physical library and within
a single module.
This library supports a mixture of LTO drive types in a logical library. Some independent software vendors
(ISVs) support mixed drive types within a logical library and other do not. Some ISVs that support mixed
drive types might have restrictions. For details, contact your ISV.
Figure 13 on page 14 shows examples of methods for mixing LTO drive types in a logical library.
IBM Condential
Chapter 1. Overview13

 Loading...
Loading...