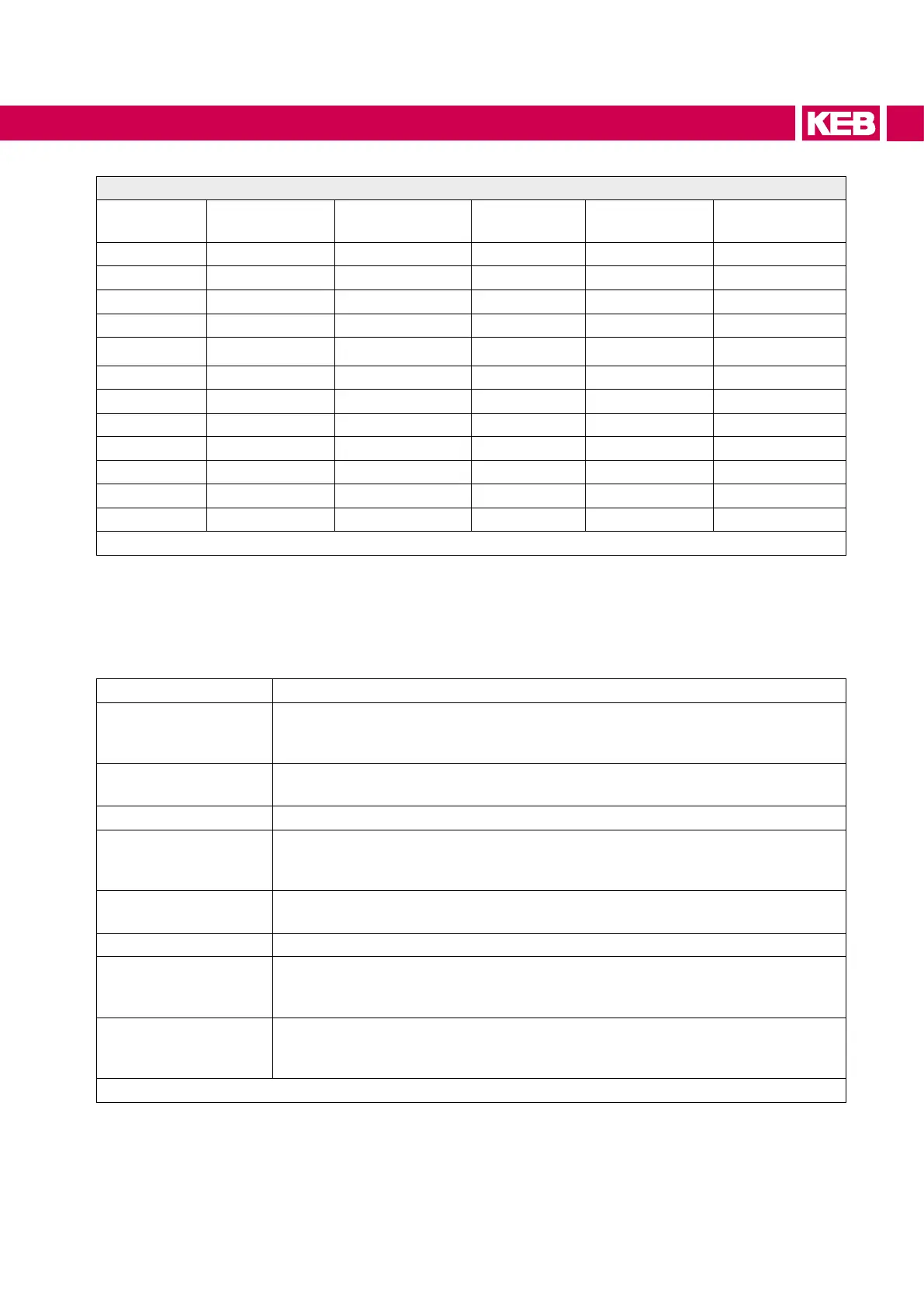
Electrochemical series / standard potentials against hydrogen
Material Generated Ion
Standard
potential
Material Generated Ion
Standard
potential
Lithium Li
+
-3.04 V Cobald Co
2+
-0.28 V
Potassium K
+
-2.93 V Nickel Ni
2+
-0.25 V
Calcium Ca
2+
-2.87 V Tin Sn
2+
-0.14 V
Sodium Na
+
-2.71 V Lead Pb
3+
-0.13 V
Magnesium Mg
2+
-2.38 V
Iron Fe
3+
-0.037 V
Titan Ti
2+
-1.75 V Hydrogen 2H
+
0.00 V
Aluminium Al
3+
-1.67 V Copper Cu
2+
0.34 V
Manganese Mn
2+
-1.05 V Carbon C
2+
0.74 V
Zinc Zn
2+
-0.76 V Silver Ag
+
0.80 V
Chrome Cr
3+
-0.71 V Platinum Pt
2+
1.20 V
Iron Fe
2+
-0.44 V Gold Au
3+
1.42 V
Cadmium Cd
2+
-0.40 V Gold Au
+
1.69 V
Table 22: Electrochemical series / standard potentials against hydrogen
10.1.3 Requirements on the coolant
The requirements on the coolant are depending on the ambient conditions, as well as
from the used cooling system. General requirements on the coolant:
Standards TrinkwV 2001, DIN EN 12502 part 1-5, DIN 50930 part 6, DVGW work sheet W216
VGB
Cooling water guideline
The VGB cooling water guideline (VGB R 455 P) contains instructions about com-
mon process technology of the cooling. Particulary the interactions between cool-
ing water and components of the cooling system are described.
pH-value Aluminum is particularly corroded by lixiviums and salts. The optimal pH value for
aluminum should be in the range of 7.5… 8.0.
Abrasive substances Abrasive substances as used in abrasive (quartz sand), clogging the cooling circuit.
Copper cuttings Copper cuttings can attach the aluminum and this leads to a galvanic corrosion.
Copper should not be used together with aluminum due to electro-chemical voltage
dierence.
Hard water Cooling water may not cause scale deposits or loose excretions. It shall have a low
total hardness (<20°dH) especially carbon hardness.
Soft water Soft water (<7°dH) corrodes the material.
Frost protection An appropriate antifreeze must be used for applications when the heat sink or the
coolant is exposed temperatures below zero. Use only products of one manufac-
turer for a better compatibility with other additives.
Corrosion protection Additives can be used as corrosion protection. In connection with frost protec-
tion the antifreeze must have a concentration of 20…25 Vol%, in order to avoid a
change of the additives.
Table 23: Requirements on the coolant
63
COOLING SYSTEM
 Loading...
Loading...











