INSPECTION AND REPAIR OF BASIC ENGINE
6-11
4. Inspecting and repairing cylinder block, crankshaft and piston
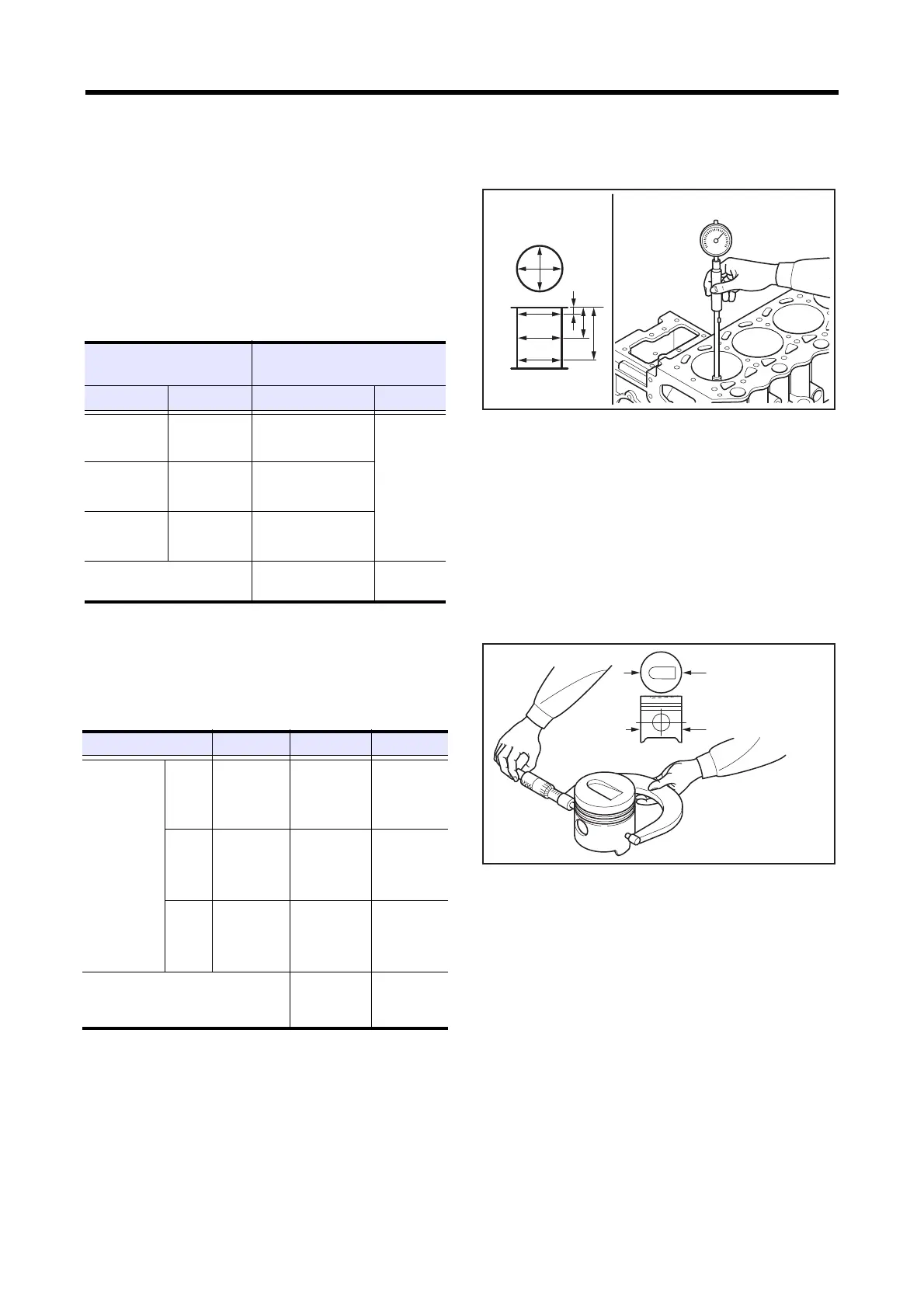
4.1 Measuring cylinder inside diameter
Use a cylinder gauge to measure the inside diameter and
cylindericity of the cylinder at three locations in the A and B
directions as shown in the illustration.
If any one of the cylinders exceeds the repair limit, bore all
the cylinders and replace the pistons and piston rings with
oversize ones.
Measuring cylinder inside diameter
4.2 Measuring piston outside diameter
Using a micrometer, measure the piston outside diameter at
the skirt perpendicular to the piston pins as shown in the
illustration.
Measuring piston outside diameter
Piston and piston ring
size
Cylinder inside diameter
Size Size mark Standard Limit
S.T.D STD
ø 78
+0.030
+0.060
mm
[3.0709
+0.012
+0.024
in.]
Standard
+0.2 mm
[0.008 in.]
0.25 mm O.S
[0.0098 in.]
25
ø 78.25
+0.030
+0.060
mm
[3.0807
+0.012
+0.024
in.]
0.50 mm O.S
[0.0197 in.]
50
ø 78.50
+0.030
+0.060
mm
[3.0905
+0.012
+0.024
in.]
Cylindericity of cylinder
± 0.01 mm
[0.0004 in.] or less
-
A
B
Measuring
points
Measuring
directions
Item Nominal Standard Limit
Piston outside
diameter
STD
78.00 mm
[3.0709 in.]
77.93 to
77.95 mm
[3.0681 to
3.0689 in.]
77.80 mm
[3.0630 in.]
0.25
OS
78.25 mm
[3.0807 in.]
78.18 to
78.20 mm
[3.0779 to
3.0787 in.]
78.05 mm
[3.0728 in.]
0.50
OS
78.50 mm
[3.0905 in.]
78.43 to
78.45 mm
[3.0878 to
3.0886 in.]
78.30 mm
[3.0827 in.]
Weight difference per piston
±5g
[0.18 oz.]
or less
-
Measuring point
Direction at right
angles to piston pin

 Loading...
Loading...











