6 Basic Control Functions
6 - 2
G5-series Linear Motors/Servo Drives With Built-in EtherCAT Communications
6-1 Cyclic Synchronous Position Mode
In this mode of operation, the controller has a path generation function (an operation profile calculation
function) and it gives the target position to the Servo Drive using cyclic synchronization. Position
control, speed control, and force control are performed by the Servo Drive.
The Velocity offset (60B1 hex) and Torque offset (60B2 hex) can be used as speed feed-forward and
force feed-forward amounts.
Precautions for Correct UsePrecautions for Correct Use
According to the CiA 402 Drive Profile, the object names between 6000 hex and 6999 hex may
be represented using the word “torque,” instead of force. Read it as “force” when using this
function.
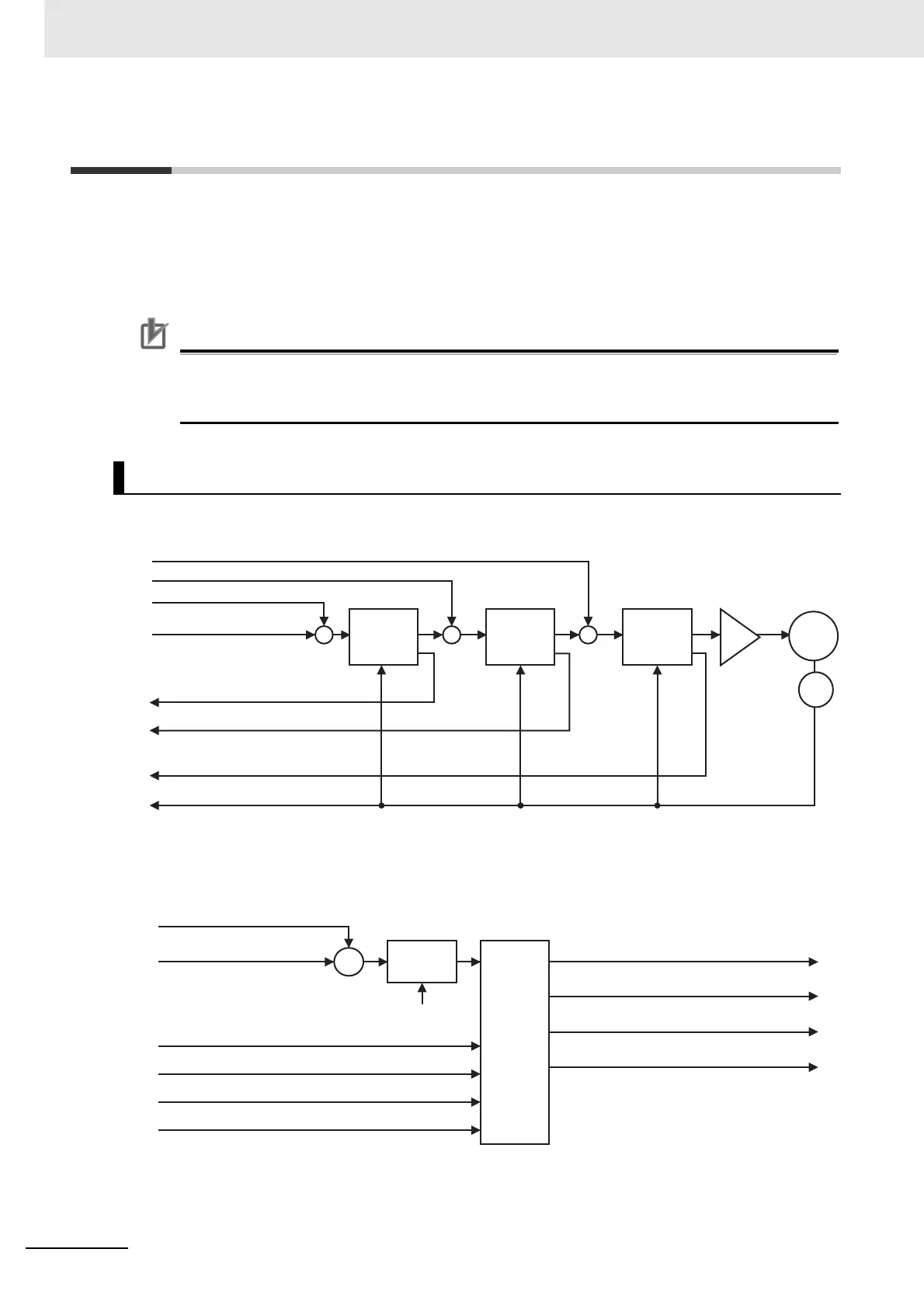
The following diagram shows the configuration of the Cyclic synchronous position mode.
The following diagram shows the configuration of the control function of the Cyclic synchronous position
mode.
Cyclic Synchronous Position Mode Configuration
Target position (607A hex)
S
M
Following error actual value (60F4 hex)
Position actual value (6064 hex)
Torque actual value (6077 hex)
(=Torque demand)
+
+
Position offset (60B0 hex)
+
+
+
+
Velocity offset (60B1 hex)
Torque offset (60B2 hex)
Velocity actual value (606C hex)
Position
Control
Speed
Control
Force
Control
Target position (607A hex)
Following error window (6065 hex)
Position actual value (6064 hex)
Following error actual value (60F4 hex)
Torque actual value (6077 hex) (=Torque demand)
Velocity actual value (606C hex)
Software position limit (607D hex)
+
+
Position offset (60B0 hex)
Velocity offset (60B1 hex)
Torque offset (60B2 hex)
Max torque (6072 hex)
Control
Function
Limit
Function

 Loading...
Loading...











