197
Examples of Applied Control Types Section 5-2
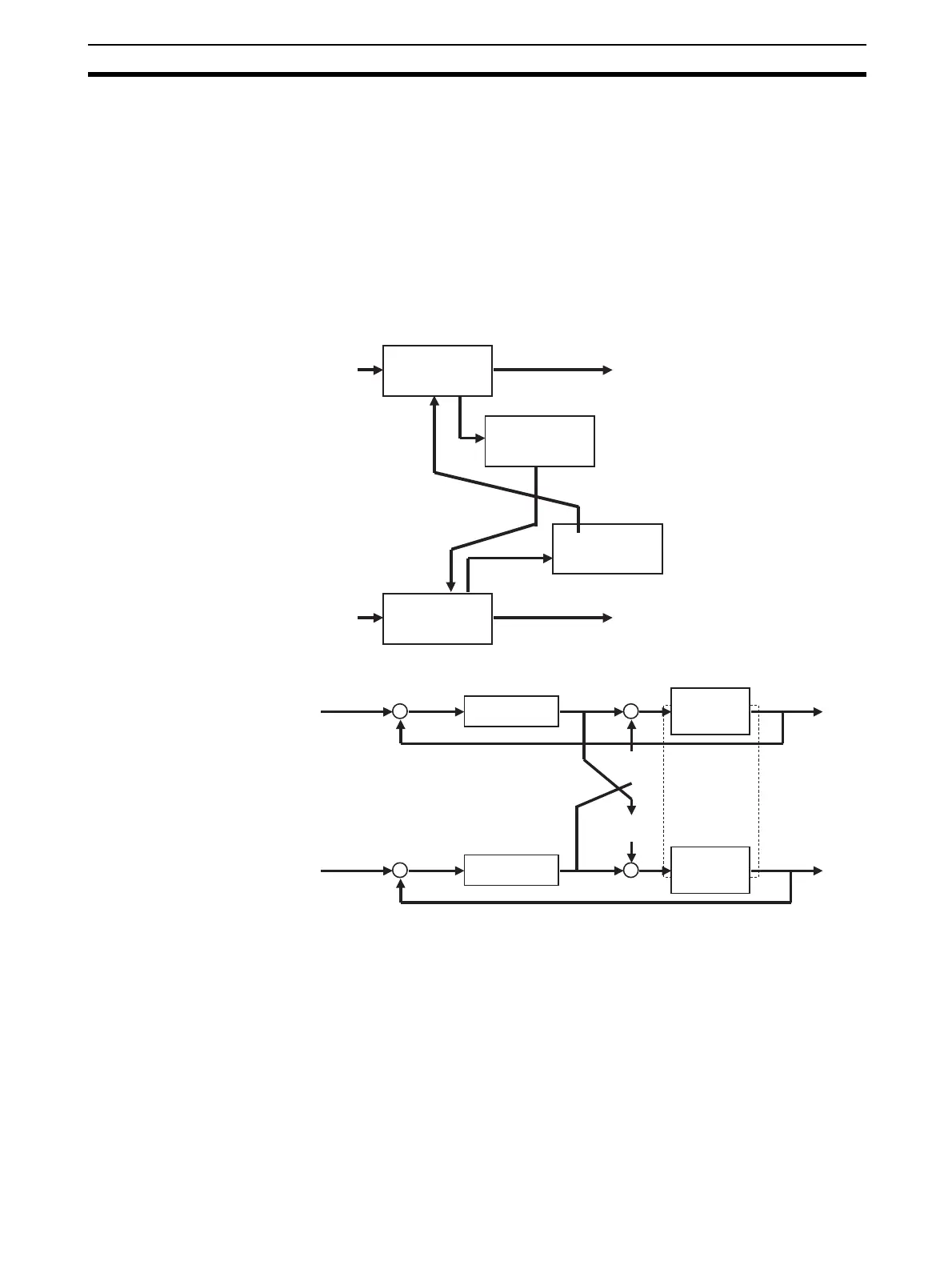
Note Noninteracting Control
Noninteracting control suppresses mutual action between processes, and
is the same as feedforward control. Influence caused by mutual action is
regarded as disturbance, and is controlled by noninteracting control to-
gether with feedforward control.
Function blocks used: Advanced PID (Block Model 012)
Lead/Delay (Block Model 147)
Processing by which the value after lead/delay operation is subtracted
from other MVs is enabled by the MV compensation function of advanced
PID.
Example
3. Noninteracting control elements generally are one cause of lag.
5-2-3 Sample PI Control
When processes with prolonged dead time or an ON/OFF measurement ana-
lyzer are taken as the control finite element, the next manipulated variable is
determined after the effect of having changed the manipulated variable has
sufficiently manifested itself.
PI control for time T1 is performed at every time T0, and resulting output is
held at a fixed value.
This is also called the “wait and see” method.
Lead/Delay Block
Model 147
Advanced PID
Block Model 012
MV
PV
Advanced PID
Block Model 012
MV
PV
Lead/Delay Block
Model 147
MV compensation:
Subtraction
Output for MV compensation
Output for MV compensation
MV compensation:
Subtraction
Set Point
SP
PID control
Process
characteristics
+
−
PV
+
Control output
Set Point
SP
PID control
Process
characteristics
Control output
Noninteracting
control
elements
Noninteracting
control
elements

 Loading...
Loading...











