64 | EdgeSync Manual rev 1 orolia.com
In current and next generation networks, there is need for time and not just frequency synchronization.
That is, a combination of frequency, phase and time-of-day synchronization is required and expected to
be delivered in a reliable and resilient fashion. Synchronous Ethernet can provide a stable frequency
and can also be used as a local short-term holdover clock for maintaining time.
The Synchronous Ethernet standard is specified in ITU-T G.8262 and ESMC message in ITU-T G.8264.
SyncE feature in EdgeSync
Synchronous Ethernet feature is a configurable option on EdgeSync that can be enabled or disabled
from the Home webpage, depending on the customer use-case and deployment. There are 4 main
modes of operation in which SyncE feature can be deployed as described below. The PHY’s used in
EdgeSync support SyncE in terms of supporting clock recovery on Ethernet Rx and being able to
provide 125MHz clock externally for Ethernet Tx. This is supported with native RJ45 (1000BASE-T)
PTP port interfaces and with optical 1GE SFP modules. SyncE is currently not supported on Copper
SFPs.
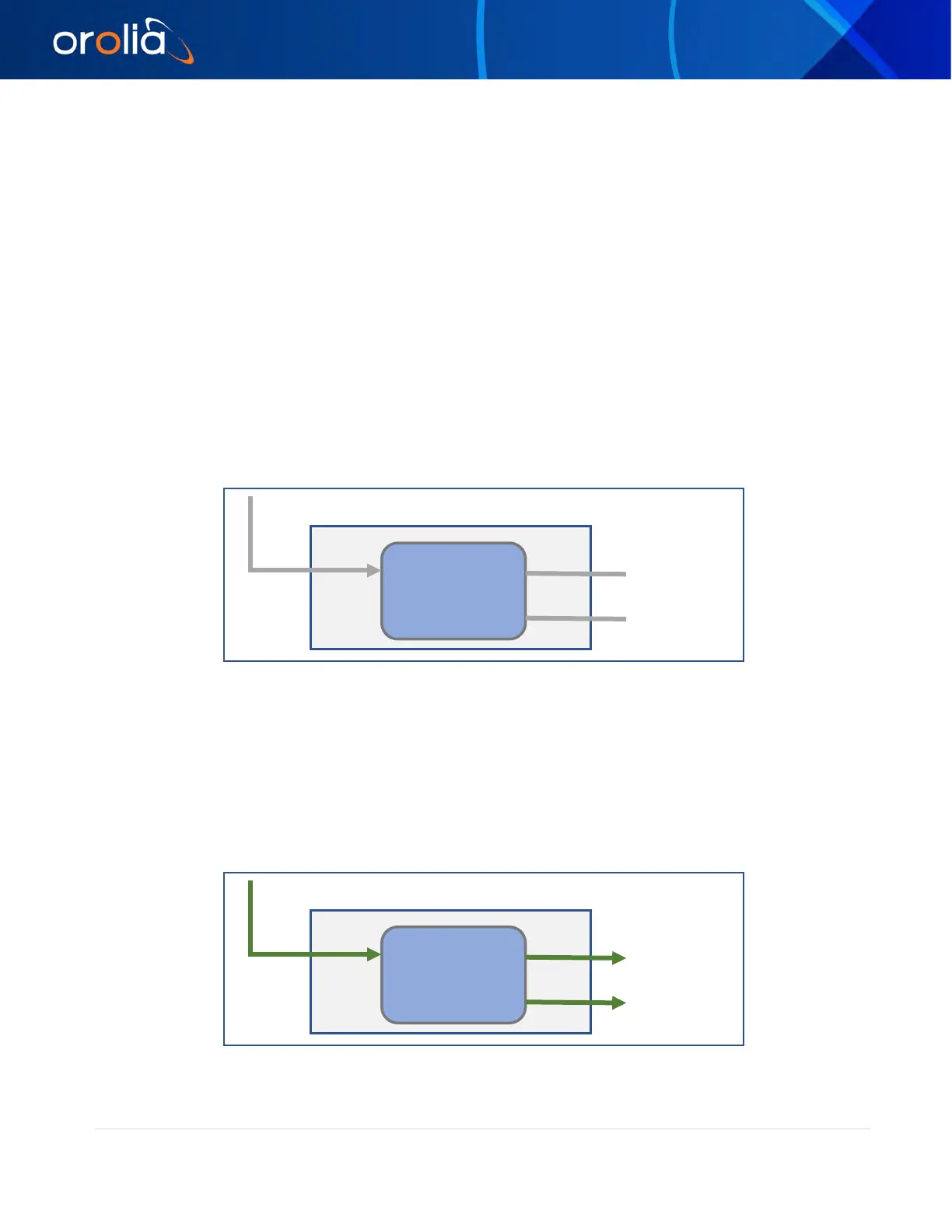
SyncE in OFF mode
Figure 40 SyncE OFF
In this mode of operation, Synchronous Ethernet feature is turned off completely. Any incoming ESMC
packets will be ignored and not processed, and no generation of outgoing ESMC packets. No clock
recovery is done on Ethernet Rx. Frequency, along with phase and time are extracted from GNSS or
PTP. This applies to both PTP ports.
SyncE in Master mode
Figure 41 SyncE in Master Mode
Managed
(optional)
Managed
ENABLED
 Loading...
Loading...