GPIB
4-6 370B User Manual
Interface Capabilities
IEEE Standard 488 defines a variety of possible interface capabilities for
differing needs among various controllers and instruments.
Table 4–1 summarizes the capabilities realized in the 370B. The abbreviations
are detailed in the IEEE standard.
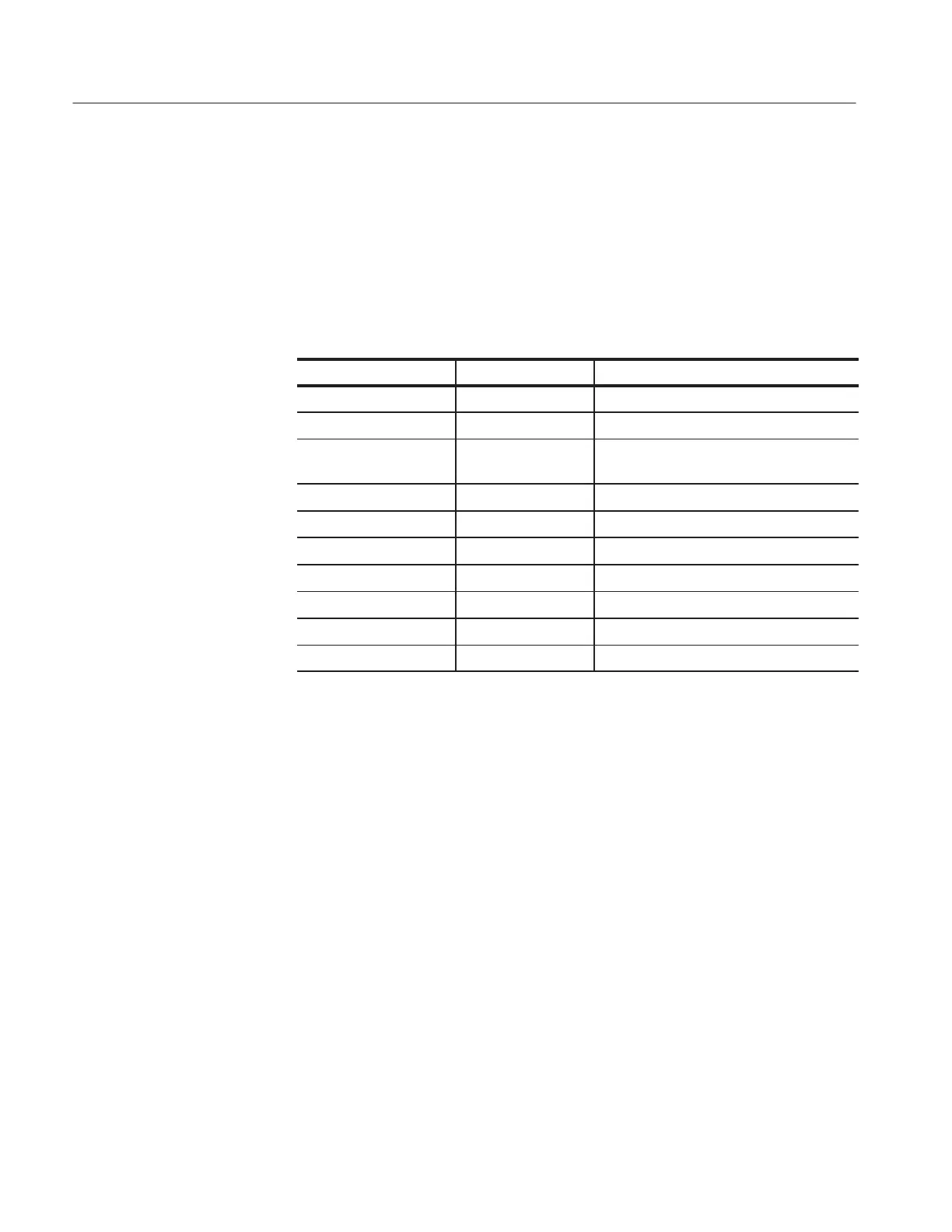
Table 4-1: GPIB Interface Specifications
Function Implemented As Note
Source Handshake SH1 Complete Capability
Acceptor Handshake AH1 Complete Capability
Talker
T6
Basic Talker, Serial Poll, Talk Only,
Unaddress if MLA
Listener L4 Basic Listener, Unaddress if MTA
Service Request SR1 Complete Capability
Remote / Local RL2 Complete Capability
Parallel Poll PP0 Not Capability
Device Clear DC1 Complete Capability
Device Trigger DT0 Not Capability
Controller C0 Not Capability
The following explains how the curve tracer reacts to standard interface
messages. Abbreviations are from IEEE Standard 488, As noted before, a
uni-line message is sent over a dedicated line and a multi-line message is sent
using the eight data lines while the ATN line is asserted. In the following
descriptions, uni-line messages are described as having the appropriate line
asserted . Multi-line messages are described with their respective ASCII code
and decimal value for the eight-bit byte expressed on the eight data lines.
Due to the set of interface functions required for the 370B, not all of the possible
interface messages would be meaningful. The 370B does not respond to the
following:
GET Group execute trigger
PPC Parallel poll configure
PPU Parallel poll unconfigure
TCT Take control
It does respond to or use the following interface messages, as described.
Interface Messages
 Loading...
Loading...