2-25
• Inaccurate results and errors can be caused by the following:
- discontinuous points in
x values
- extreme changes in
x values
- inclusion of the local maximum point and local minimum point in
x values
- inclusion of the inflection point in
x values
- inclusion of undifferentiable points in
x values
- differential calculation results approaching zero
• Always use radians (Rad mode) as the angle unit when performing trigonometric differentials.
• You cannot use a differential, quadratic differential, integration, 3, maximum/minimum value,
Solve, RndFix or log
a
b calculation expression inside a differential calculation term.
• In the Math input/output mode, the tolerance value is fixed at 1
E–10 and cannot be changed.
I Quadratic Differential Calculations [OPTN]-[CALC]-[d
2
/dx
2
]
After displaying the function analysis menu, you can input quadratic differentials using the
following syntax.
*(CALC)*(
d
2
/dx
2
) f(x)atol * fx-7400GII: (CALC)
(
a: differential coefficient point, tol: tolerance)
Quadratic differential calculations produce an approximate differential value using the following
second order differential formula, which is based on Newton’s polynomial interpretation.
In this expression, values for “sufficiently small increments of
h” are used to obtain a value that
approximates f
"
(a).
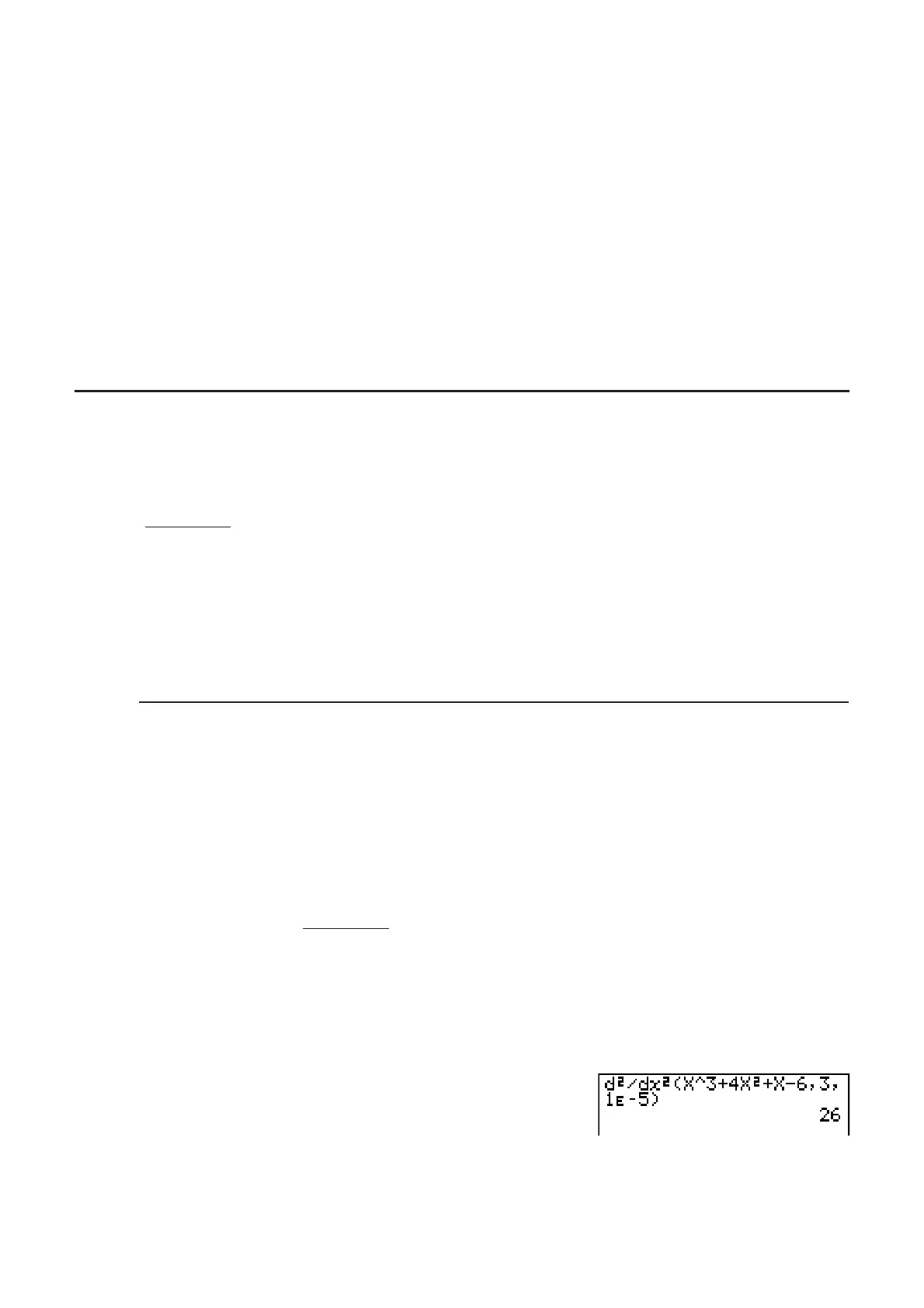
Example To determine the quadratic differential coefficient at the point where
x = 3 for the function y = x
3
+4x
2
+ x –6
Here we will use a tolerance tol =1E –5
Input the function
f(x).
*(CALC)* (
d
2
/dx
2
) T,BCTVTE
* fx-7400G
II: (CALC)
Input 3 as point
a, which is the differential coefficient point.
B
Input the tolerance value.
@$D
U
Quadratic Differential Calculation Precautions
• In the function f(x), only X can be used as a variable in expressions. Other variables (A
through Z excluding X, r, Ƨ) are treated as constants, and the value currently assigned to
that variable is applied during the calculation.
d
2
d
2
–– (
f
(
x
),
a
)
–––
f
(
a
)
dx
2
dx
2
d
2
d
2
–– (
f
(
x
),
a
)
–––
f
(
a
)
dx
2
dx
2
''(a) =
180h
2
2 f(a + 3h) – 27 f(a + 2h) + 270 f(a + h) – 490 f(a) + 270 f(a – h) – 27 f(a –2h) + 2 f(a – 3h)
''(a) =
180h
2
2 f(a + 3h) – 27 f(a + 2h) + 270 f(a + h) – 490 f(a) + 270 f(a – h) – 27 f(a –2h) + 2 f(a – 3h)

 Loading...
Loading...