13-10
Cisco IE 3000 Switch Software Configuration Guide
OL-13018-03
Chapter 13 Configuring Interface Characteristics
Configuring Ethernet Interfaces
Configuring Ethernet Interfaces
These sections contain this configuration information:
• Default Ethernet Interface Configuration, page 13-10
• Setting the Type of a Dual-Purpose Uplink Port, page 13-11
• Configuring Interface Speed and Duplex Mode, page 13-13
• Configuring IEEE 802.3x Flow Control, page 13-15
• Configuring Auto-MDIX on an Interface, page 13-16
• Adding a Description for an Interface, page 13-17
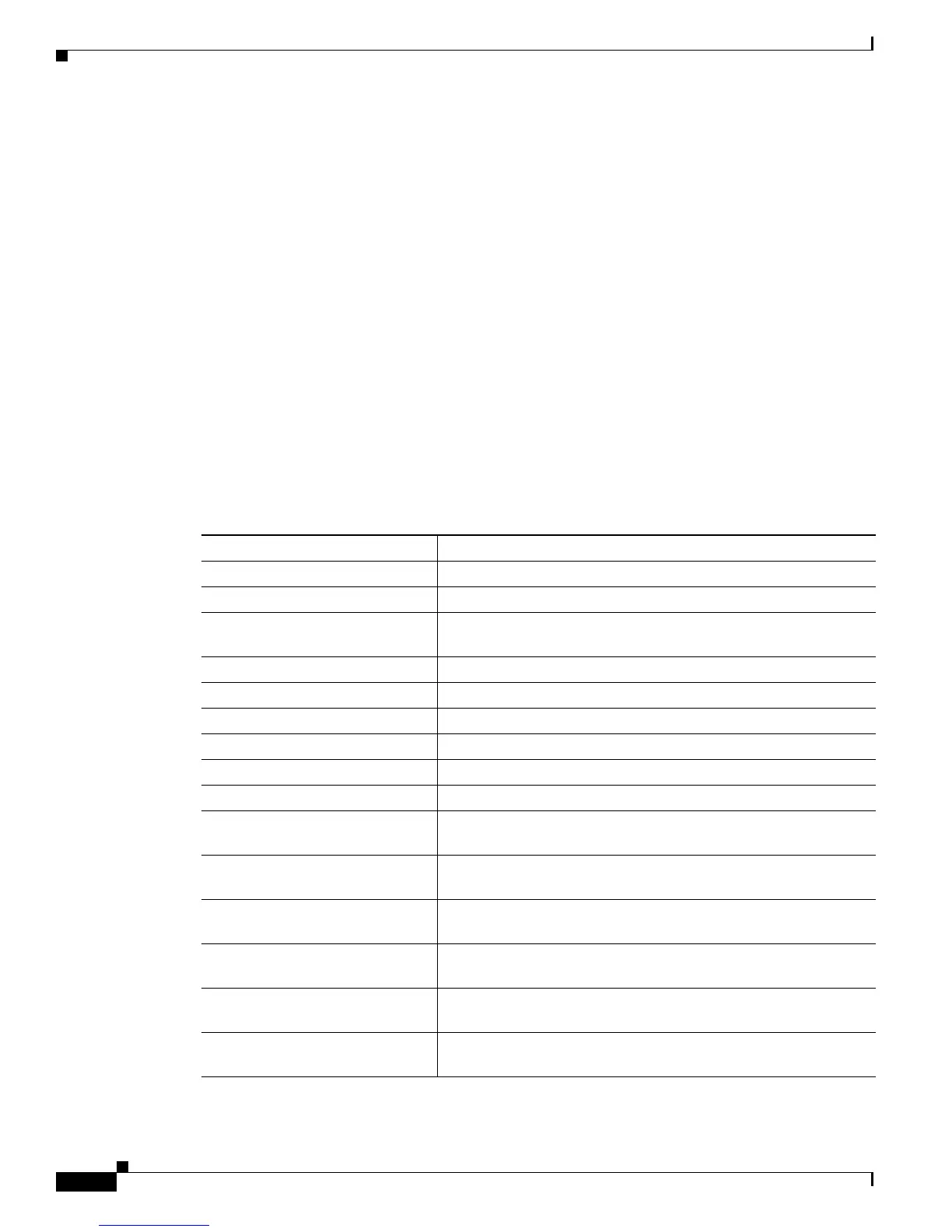
Default Ethernet Interface Configuration
Table 13-2 shows the Ethernet interface default configuration. For more details on the VLAN parameters
listed in the table, see Chapter 15, “Configuring VLANs.” For details on controlling traffic to the port,
see Chapter 26, “Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control.”
Ta b l e 13-2 Default Layer 2 Ethernet Interface Configuration
Feature Default Setting
Allowed VLAN range VLANs 1 to 4094.
Default VLAN (for access ports) VLAN 1.
Native VLAN (for IEEE 802.1Q
trunks)
VLAN 1.
VLAN trunking Switchport mode dynamic auto (supports DTP).
Port enable state All ports are enabled.
Port description None defined.
Speed Autonegotiate.
Duplex mode Autonegotiate.
Flow control Flow control is set to receive: off. It is always off for sent packets.
EtherChannel (PAgP) Disabled on all Ethernet ports. See Chapter 38, “Configuring
EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking.”
Port blocking (unknown multicast
and unknown unicast traffic)
Disabled (not blocked). See the “Configuring Port Blocking”
section on page 26-7.
Broadcast, multicast, and unicast
storm control
Disabled. See the “Default Storm Control Configuration” section
on page 26-3.
Protected port Disabled. See the “Configuring Protected Ports” section on
page 26-6.
Port security Disabled. See the “Default Port Security Configuration” section
on page 26-11.
Port Fast Disabled. See the “Default Optional Spanning-Tree
Configuration” section on page 20-9.
 Loading...
Loading...











