Terms, laws, and definitions
31
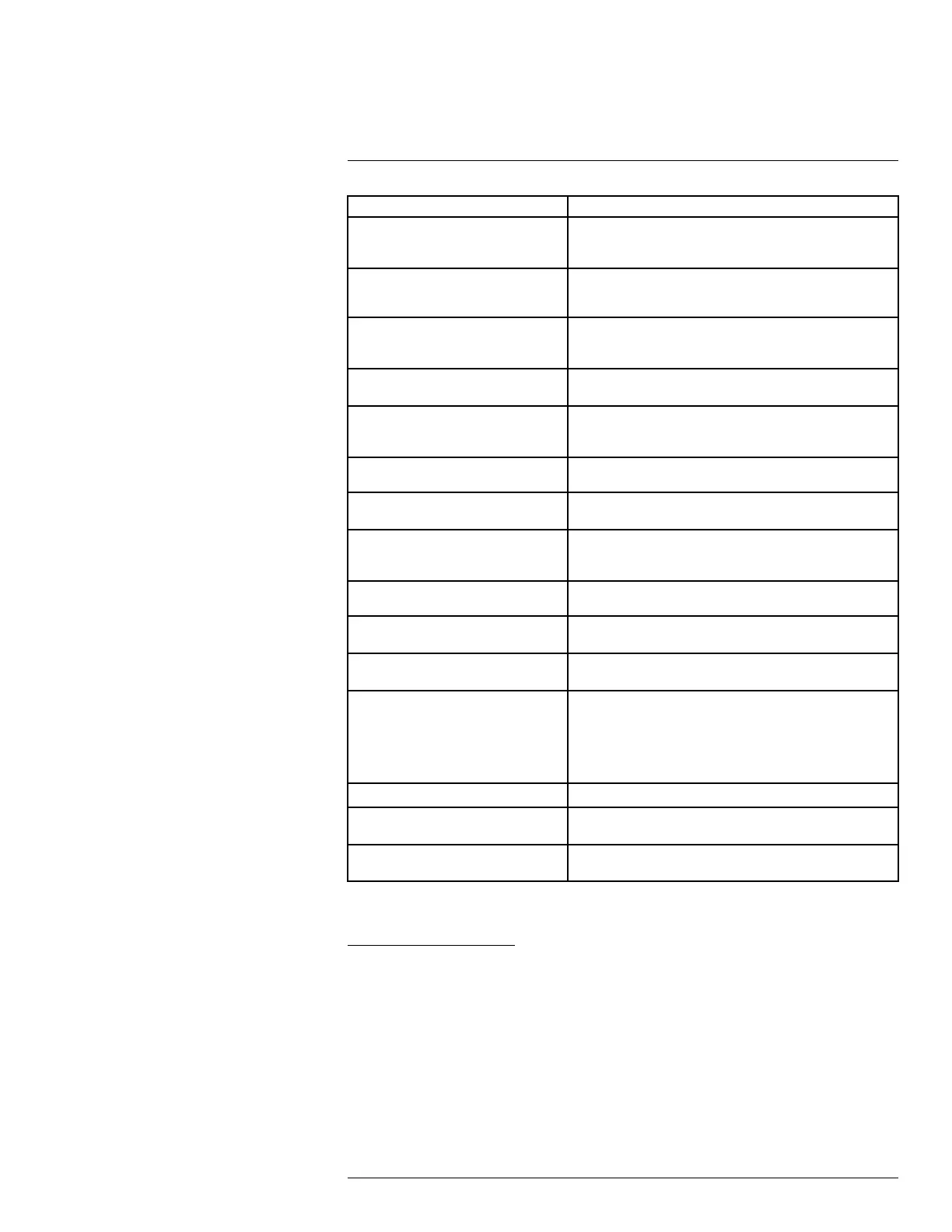
Term Definition
Absorption and emission
2
The capacity or ability of an object to absorb incident radiated
energy is always the same as the capacity to emit its own en-
ergy as radiation
Apparent temperature uncompensated reading from an infrared instrument, contain-
ing all radiation incident on the instrument, regardless of its
sources
3
Color palette assigns different colors to indicate specific levels of apparent
temperature. Palettes can provide high or low contrast, de-
pending on the colors used in them
Conduction direct transfer of thermal energy from molecule to molecule,
caused by collisions between the molecules
Convection heat transfer mode where a fluid is brought into motion, either
by gravity or another force, thereby transferring heat from one
place to another
Diagnostics examination of symptoms and syndromes to determine the
nature of faults or failures
4
Direction of heat transfer
5
Heat will spontaneously flow from hotter to colder, thereby
transferring thermal energy from one place to another
6
Emissivity ratio of the power radiated by real bodies to the power that is
radiated by a blackbody at the same temperature and at the
same wavelength
7
Energy conservation
8
The sum of the total energy contents in a closed system is
constant
Exitant radiation radiation that leaves the surface of an object, regardless of its
original sources
Heat thermal energy that is transferred between two objects (sys-
tems) due to their difference in temperature
Heat transfer rate
9
The heat transfer rate under steady state conditions is directly
proportional to the thermal conductivity of the object, the
cross-sectional area of the object through which the heat
flows, and the temperature difference between the two ends
of the object. It is inversely proportional to the length, or thick-
ness, of the object
10
Incident radiation radiation that strikes an object from its surroundings
IR thermography process of acquisition and analysis of thermal information
from non-contact thermal imaging devices
Isotherm replaces certain colors in the scale with a contrasting color. It
marks an interval of equal apparent temperature
11
#T810190; r. AI/41890/41890; en-US
226
2. Kirchhoff’s law of thermal radiation.
3. Based on ISO 18434-1:2008 (en).
4. Based on ISO 13372:2004 (en).
5. 2nd law of thermodynamics.
6. This is a consequence of the 2nd law of thermodynamics, the law itself is more complicated.
7. Based on ISO 16714-3:2016 (en).
8. 1st law of thermodynamics.
9. Fourier’s law.
10.This is the one-dimensional form of Fourier’s law, valid for steady-state conditions.
11.Based on ISO 18434-1:2008 (en)

 Loading...
Loading...