Basics of Sequential Sampling
The HP 83480A digital communications analyzer and HP 54750A digitizing
oscilloscopes use digital sampling oscilloscope technology to acquire and
display high bandwidth waveforms. A sampling oscilloscope does not
continuously monitor the input signal applied to the channel, but looks at it
only at discrete points in time. At each discrete point, the scope samples the
signal and stores a replica of the input voltage on an input sampling capacitor.
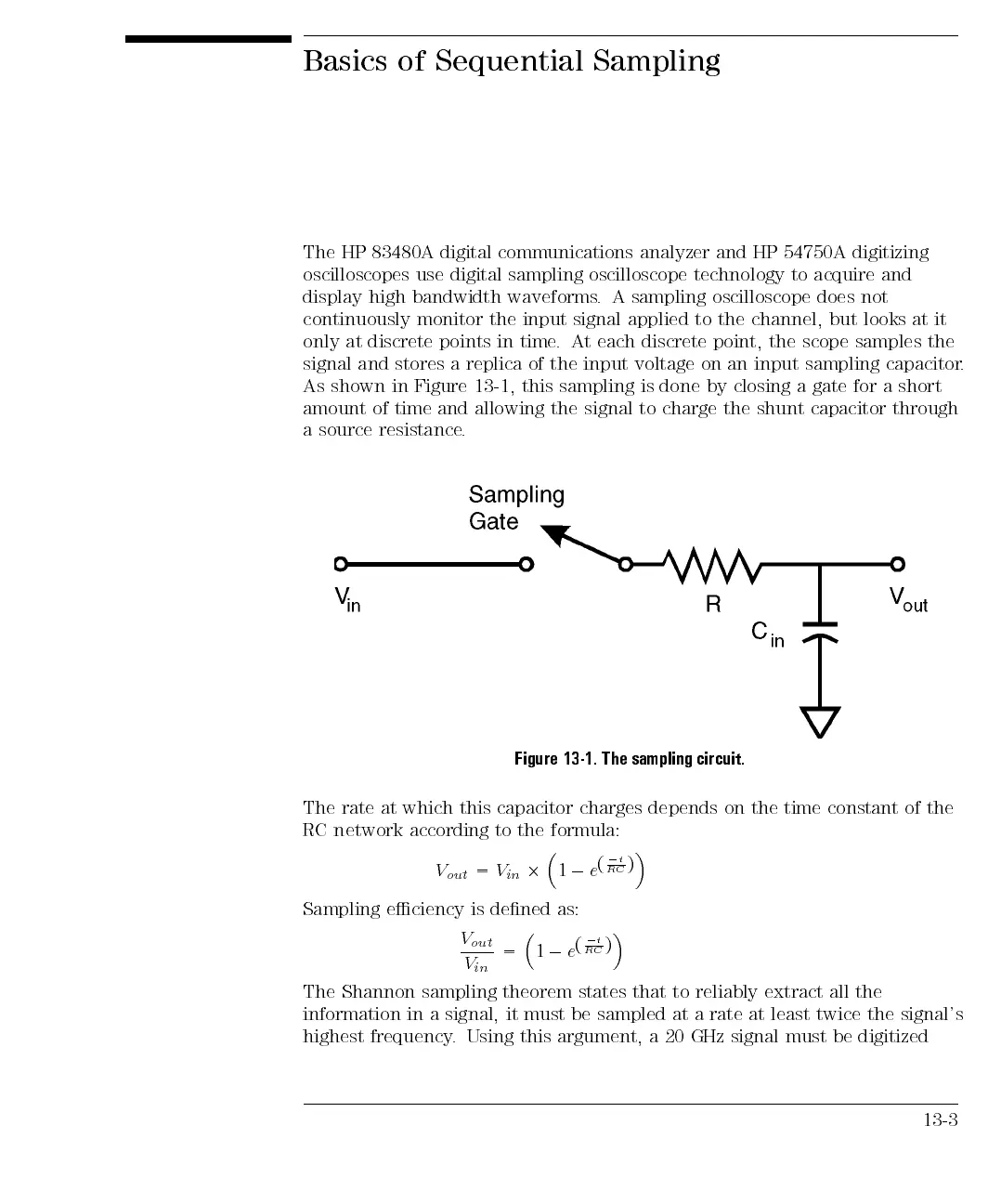
As shown in Figure 13-1, this sampling is done by closing a gate for a short
amount of time and allowing the signal to charge the shunt capacitor through
a source
resistance.
Figure
13-1.
The
sampling
circuit.
The rate at which this capacitor charges depends on the time constant of the
RC network according to the formula:
V
out
=
V
in
2
1
0
e
(
0
t
RC
)
Sampling
eciency
is
dened
as:
V
out
V
in
=
1
0
e
(
0
t
RC
)
The Shannon sampling theorem states that to
reliably extract all the
information in a signal, it must be sampled
at a rate at least twice the signal's
highest frequency
. Using this argument, a 20 GHz signal
must be digitized
13-3

 Loading...
Loading...